Effects of external N and P on decomposition of mixed leaf litters of Michelia macclurei and Pinus massoniana woodlands
-
摘要:目的
研究外源性N和P对火力楠Michelia macclurei和马尾松Pinus massoniana凋落叶分解速率的影响,以及分解过程中的N、P、K含量变化,了解混合凋落叶分解对外源性N和P的响应机制,为森林资源管理提供参考。
方法将火力楠和马尾松混合凋落叶置于火力楠林地及马尾松林地,分别设立4块5 m×5 m的小样方,喷施N、P和N+P,比较其分解速率及分解过程中的N、P、K含量变化。
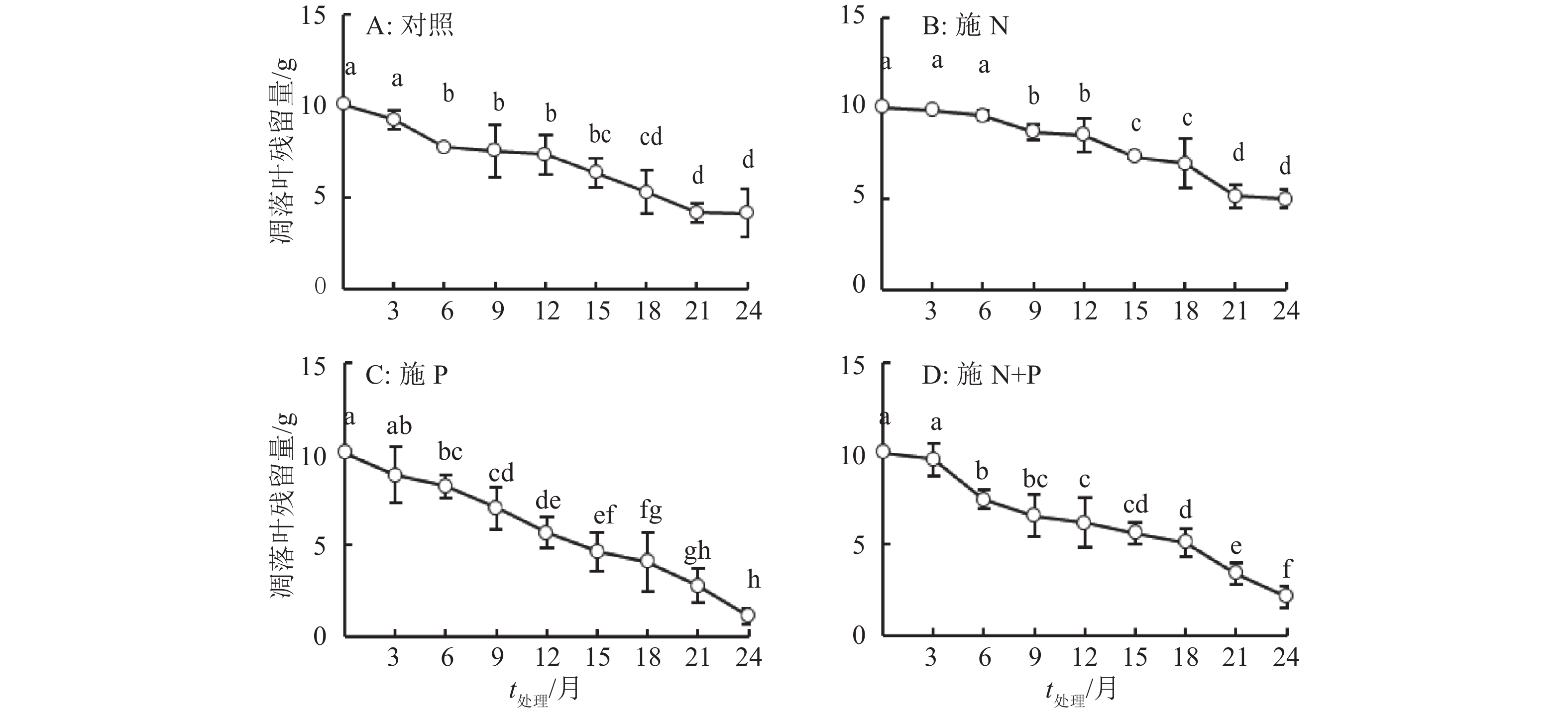
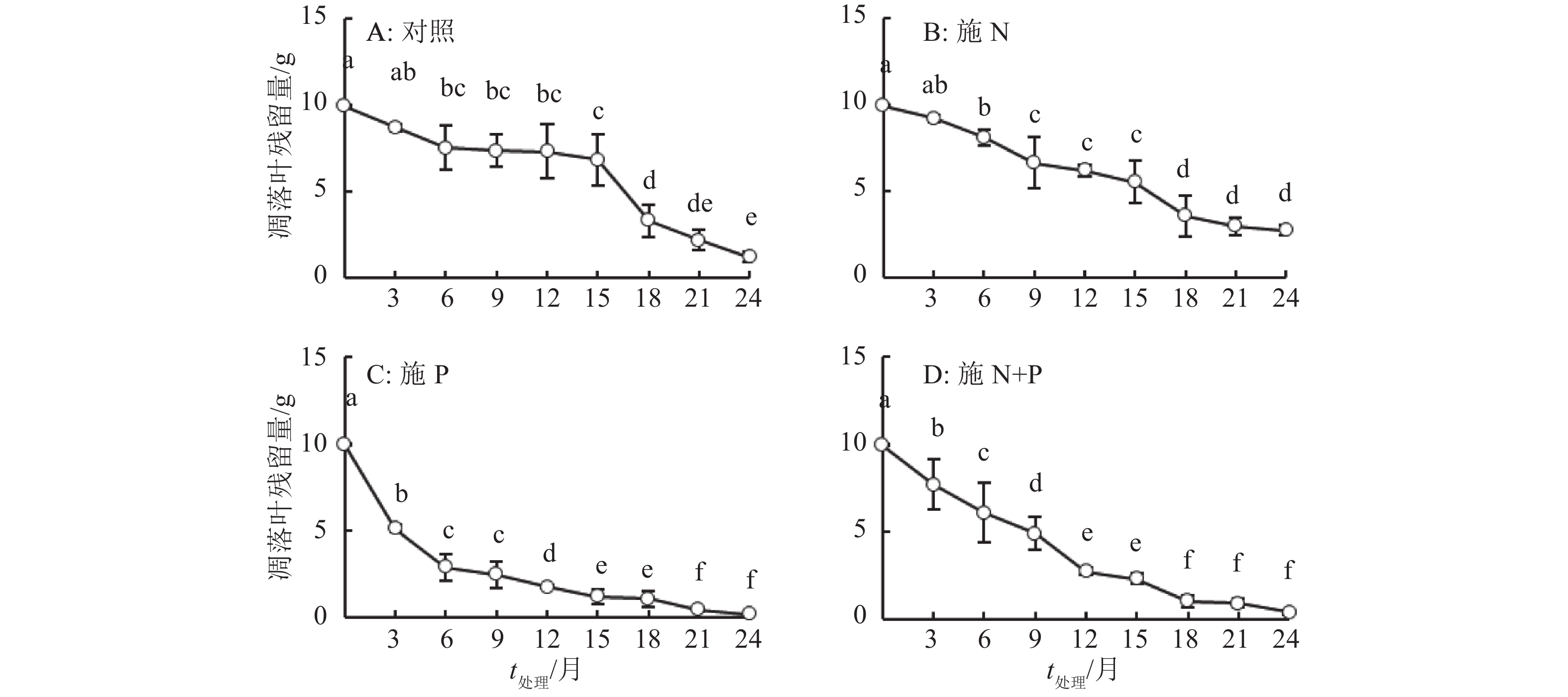
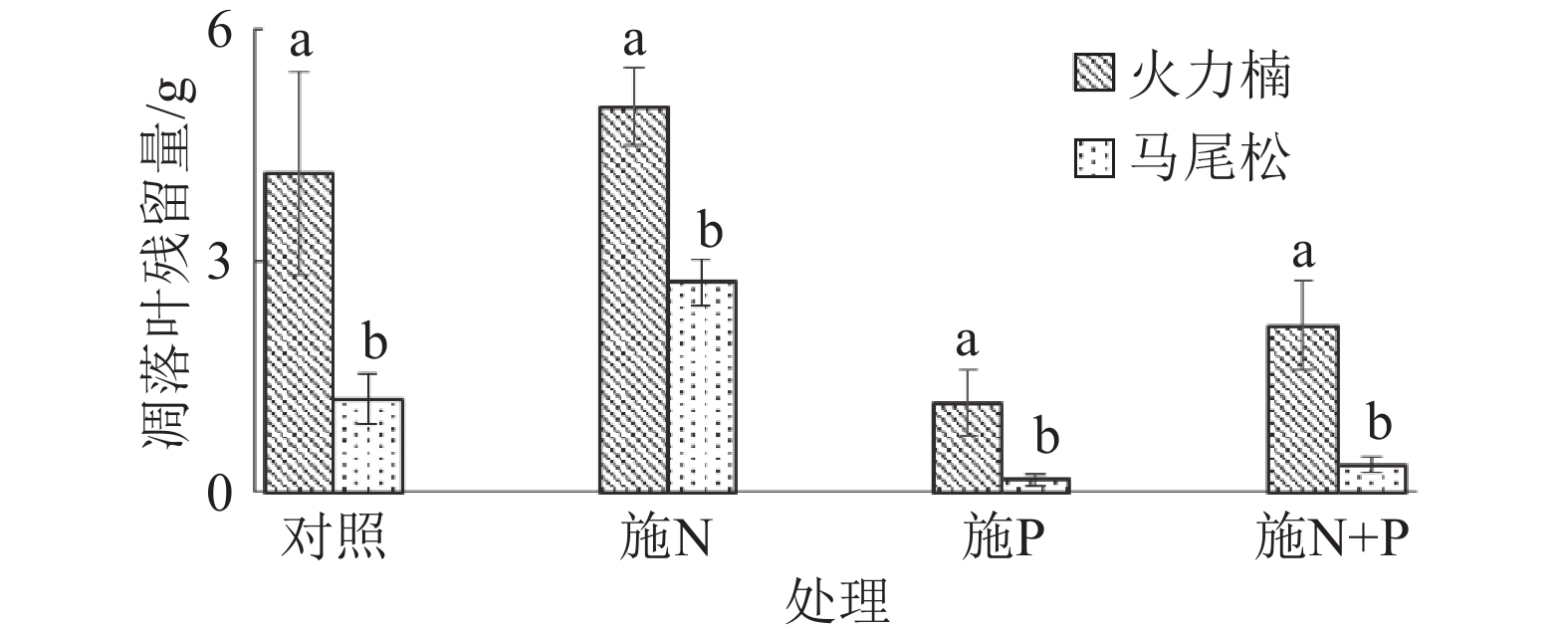
结果在2种林地的不同处理下,24个月后,火力楠林地混合凋落叶残留量为施N(4.99 g)>对照(4.14 g)>施N+P(2.17 g)>施P(1.16 g),马尾松林地混合凋落叶残留量为施N(2.72 g)>对照(1.21 g)>施N+P(0.36 g)>施P(0.16 g),施N对火力楠和马尾松林下的混合凋落叶的分解有抑制作用;施P后两者的混合凋落叶的分解速率均不同程度地有所加快;施N+P后两者的混合凋落叶的分解速率也均加快,但慢于施P处理。马尾松林下混合凋落叶残留量均小于火力楠林下混合凋落叶残留量。分解24个月后,火力楠林地施N、P和N+P的混合凋落叶N质量分数分别为13.72、12.34和13.70 g·kg–1,而马尾松林地分别为12.63、13.46和14.54 g·kg–1, 均显著大于其凋落叶的初始N质量分数(9.90 g·kg–1);施P和N+P处理的火力楠林地混合凋落叶P质量分数由初始的0.38 g·kg–1分别增至0.86和0.74 g·kg–1,而马尾松林地混合凋落叶P质量分数由初始的0.38 g·kg–1分别增至1.37和1.05 g·kg–1。凋落叶K含量的变化无规律。
结论火力楠和马尾松混交可促进火力楠凋落叶分解,提高混合凋落叶的分解速率。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo investigate the effects of external nitrogen(N) and phosphorus(P) on decomposition rate of mixed leaf litters of Michelia macclurei and Pinus massoniana woodlands, and analyze changes in N,P and potassium(K) contents during deposition process, in order to understand the response mechanism of leaf litter decomposition to external N and P, and provide reference for forest resource management.
MethodMixed leaf litters of M. macclurei and P. massoniana were placed in woodlands of M. macclurei and P. massoniana. Four 5 m×5 m plots were set in each wood land and were sprayed with N, P or N+P. The decomposition rates and changes in N, P, K contents of leaf litters were compared.
ResultTwenty-four months after treatments, the amounts of leaf litter residue were N addition (4.99 g) > control (4.14 g) > N+P addition (2.17 g) > P addition (1.16 g) in M. macclurei woodland, and N addition (2.72 g) > control (1.21 g) > N+P addition (0.36 g) > P addition (0.16 g) in P. massoniana woodland. N addition inhibited decomposition of mixed leaf litters under M. macclurei and P. massoniana woodlands, whereas P and N+P additions both accelerated decomposition of mixed leaf litters with a faster decomposition rate compared to N+P addition. The amounts of leaf litter residue in P. massoniana woodland were less than those in M. macclurei woodland. Twenty-four months after treatments, N contents of mixed leaf litters treated with N, P and N+P additions were 13.72, 12.34 and 13.70 g·kg–1 respectively in M. macclurei woodland, and 12.63, 13.46, and 14.54 g·kg–1 respectively in P. massoniana woodland, Which were greater than the initial N content of mixed leaf litters (9.90 g·kg–1). The P content of mixed leaf litters treated with P and N+P additions increased from the initial value of 0.38 to 0.86 and 0.74 g·kg–1 respectively in M. macclurei woodland, and increased from 0.38 to 1.37 and 1.05 g·kg–1 respectively in P. massoniana woodland. K contents of mixed leaf litters changed irregularly.
ConclusionDecomposition of M. macclurei leaf litter can be accelerated and decomposition rate of mixed leaf litters can be enhanced by mixed-planting M. macclurei and P. massoniana.
-
Keywords:
- Michelia macclurei /
- Pinus massoniana /
- mixed leaf litter /
- decomposition rate /
- external N and P
-
植物内生真菌(Endophytic fungus)是指那些生活史的部分阶段或全部生活于健康植物组织或器官内部,且在长期的协同进化过程中与宿主植物形成互惠共生关系的一类真菌[1-2]。内生真菌与宿主植物形成的这种互惠共生关系为研究者从植物内生真菌次生代谢产物中寻找新型的天然活性先导物提供了新的方向[3]。近年来,内生真菌次生代谢产物的研究越来越受到人们的重视,尤其是从短叶红豆杉Taxus brevifolia韧皮部分离到产紫杉醇的内生真菌Taxomyces andreanae后,掀起了人们对内生真菌次生代谢产物研究的热潮[4-5]。内生真菌作为一种新型的天然活性物质资源宝库,能够产生多种结构新颖的次生代谢产物,其具有抗菌、杀虫、抗氧化、抗肿瘤以及促进植物生长和提高植物抗病性等多种生物活性,从植物内生真菌中寻找具有开发潜能的生物活性物质引起了人们极大的兴趣[6-9]。
目前对于桉树内生真菌及其次生代谢产物的研究多集中在内生真菌的生理学和生态学作用方面。谢安强等[10-12]研究发现桉树内生真菌能够显著提高桉树的抗逆能力,如促进植株对磷的吸收能力,提高桉树的抗寒能力,促进植株的光合作用效能等。Kharwar等[13]从柠檬桉Eucalyptus citriodora中分离得到的曲霉属Aspergillussp.和毛壳菌属Chaetomiumsp.内生真菌表现出较强的抗真菌和抗细菌活性。格希格图等[14]从不同桉树根部分离到的内生真菌对桉树青枯病菌Ralstonia solanacearum有不同程度的拮抗作用,其中以大叶桉Eucalyptus robusta内生真菌的抗菌活性最为明显。Mohali等[15]从桉树和金合欢Acacia farnesiana中分离到2株新的内生真菌Fusicoccum sp.,但并未对其次生代谢产物的生物活性进行研究。华南农业大学林学与风景园林学院森林保护教研室的前期研究表明,窿缘桉Eucalyptus exserta果实内生真菌Eef-10表现出较好的抗桉树青枯病菌活性[16],本文在前期研究的基础上,以内生真菌Eef-10为研究对象,通过形态学和分子生物学相结合的方法确定其分类地位,同时分离和鉴定内生真菌Eef-10中的活性成分,并测定其抗细菌和抗肿瘤细胞活性,以期为内生真菌资源的开发和利用提供理论依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 供试菌株和肿瘤细胞
内生真菌Eef-10分离自健康的窿缘桉果实,目前保藏于华南农业大学林学与风景园林学院植物和微生物健康实验室。
供试细菌包括大肠埃希菌Escherichia coli(G-)、根癌土壤杆菌Agrobacterium tumefaciens(G-)、黄瓜角斑病菌Pseudomonas lachrymans(G-)、桉树青枯病菌Ralstonia solanacearum(G-)和番茄疮痂病菌Xanthomonas vesicatoria(G-),以上菌株均保藏于华南农业大学林学与风景园林学院植物和微生物健康实验室。
供试细胞株系为肝癌细胞(Hep-G2)和宫颈癌细胞(HeLa),供试肿瘤细胞由中国医学科学院北京协和医学院医药生物技术研究所提供。
1.2 仪器与试剂
核磁共振波谱仪(Bruker Avance-600,美国Bruker公司),半制备型液相色谱仪(泵:UC-3281,紫外检测器:UC-3292S,上海Welch公司),分析型液相色谱仪(LC-10F,天津博纳艾杰尔科技有限公司),三用紫外仪(ZQ-1,上海安亭科学仪器厂),超净工作台(SW-CJ-2G,苏州净化设备有限公司),生化培养箱(LRH-250,上海一恒科技有限公司)。
Sephadex LH-20葡聚糖凝胶(瑞士GE Heaithcare公司),GF254薄层层析硅胶和正相柱层析硅胶(青岛化工有限公司),硫酸链霉素(w=98%,上海麦克林生化科技有限公司),噻唑蓝(MTT)生物显色剂(w=98%,美国Amresco公司),喜树碱(w≥99%,上海麦克林生化科技有限公司),真菌基因组DNA抽提试剂盒 [生工生物工程(上海)股份有限公司],甲醇、二甲基亚砜、丙酮、乙酸乙酯、三氯甲烷、二氯甲烷和石油醚(分析纯,天津富宇精细化工厂),甲醇(色谱纯,上海星可高纯溶剂有限公司),氘代氯仿、氘代丙酮(巴斯夫化学有限公司)。
1.3 内生真菌Eef-10的鉴定
采用形态学和分子生物学相结合的方法对内生真菌Eef-10进行鉴定。
1.3.1 形态学鉴定
用灭菌牙签挑取PDA培养基上菌落边缘生长旺盛的菌丝,接种于新的PDA培养基中,置于生化培养箱中培养7~10 d,然后用生物显微镜观察菌丝、有性孢子和产孢结构等特征,参照Sekhar等[17]对内生真菌Eef-10进行形态学鉴定。
1.3.2 分子生物学鉴定
参照单体江等[18]的方法对内生真菌Eef-10进行分子生物学鉴定。将纯化后的内生真菌Eef-10(在PDA培养基上生长5 d)接种到PDB培养基中,28 ℃、150 r/min条件下振荡培养5 d,分液漏斗过滤后收集菌丝,用液氮进行充分研磨至粉末状,采用真菌基因组DNA抽提试剂盒提取其总DNA,使用真菌的通用引物ITS4(5′-TCCTCCGCTTATTGATATGC-3′)和ITS5(5′-GGAAGTAAAAGTCGTAACAAGG-3′)扩增其ITS序列。PCR反应体系(50 μL):去离子水21 μL,2×Taq PCR MasterMix(含染料)25 μL,ITS4(10 μmol/L)1 μL,ITS5(10 μmol/L)1 μL,模板DNA(10 ng/ μL)2 μL;PCR扩增程序:94 ℃预变性3 min;94 ℃变性40 s,56 ℃退火40 s,72 ℃延伸1 min 20 s,共30个循环;72 ℃延伸10 min。PCR产物送至生工生物工程(上海)股份有限公司进行测序。将测序成功的ITS序列提交至GenBank数据库,获得登录号。通过在NCBI网站上进行BLAST,下载与其相似性较高的序列及其近似属的序列,使用MAFTT version 7处理后,用MEGA6软件采用最大似然法构建系统发育树。
1.4 内生真菌Eef-10次生代谢产物的制备
采用大米固体培养基对内生真菌Eef-10进行大规模发酵。首先从4 ℃冻存管中挑取少许Eef-10菌丝接种到PDA平板上活化培养5~7 d,再将其菌丝接种在500 mL装有200 mL PDB培养基的三角瓶中,置于28 ℃、150 r/min条件下振荡培养3~5 d。将获得的液体种子接入已灭菌的大米培养基中,共发酵6 kg,28 ℃条件下暗培养60 d,以确保菌丝将大米培养基营养消耗完毕。而后将发酵好的固体发酵物用甲醇冷浸提取3次,每次7 d,减压浓缩后水混悬,依次用等体积的石油醚和乙酸乙酯萃取,分别得到石油醚层和乙酸乙酯层粗提物。
1.5 次生代谢产物的分离、纯化和鉴定
乙酸乙酯层提取物(51.40 g)经减压硅胶柱层析,先用石油醚洗脱,再用二氯甲烷和甲醇梯度洗脱,通过薄层层析合并成A~D 4个部分。其中B部分(25.19 g)再经减压硅胶柱层析,采用二氯甲烷和甲醇梯度洗脱,通过薄层层析合并成11个馏分,分别编号为B1~B11。B4馏分(2.9 g)经Sephadex LH-20柱层析(三氯甲烷︰甲醇体积比为1︰1),通过薄层层析检测后合并为7个组分,分别编号为B4-1~B4-7。B4-7(30 mg)经semi-HPLC(甲醇︰水体积比为 65︰35,流速5 mL/min,λ = 210 nm,进样体积为0.1 mL)制备,得到化合物Ⅰ(4.5 mg)和化合物Ⅱ(5.5 mg)。B6馏分(9.5 g),经Sephadex LH-20(三氯甲烷︰甲醇体积比为1︰1)柱层析,通过薄层层析检测后合并成6个组分,编号为B6-1~B6-6。其中B6-3(95 mg)经semi-HPLC(甲醇︰水体积比为50︰50,流速5 mL/min,λ = 210 nm,进样体积为0.1 mL)制备,得到化合物Ⅲ(30 mg)。
单体化合物的结构主要通过1H NMR、13C NMR等波谱学数据进行鉴定,并与文献比对后确定。
1.6 抗细菌活性的测定
抗细菌活性的测定参照刘志强等[19]的方法,精密称取单体化合物Ⅰ~Ⅲ各2.0 mg分别溶于0.3 mL丙酮中,再加入0.7 mL蒸馏水,配成质量浓度为2 000 μg/mL的母液,然后用φ为30%的丙酮溶液依次稀释成质量浓度为2 000.000、1 000.000、500.000、250.000、125.000、62.500、31.250、15.625 μg/mL的样品溶液。阳性对照为硫酸链霉素,采用相同的方法配成质量浓度为500.000 00、250.000 00、125.000 00、62.500 00、31.250 00、15.625 00、7.812 50、3.906 25 μg/mL的溶液,备用。在无菌的96微孔板中加入106 CFU/mL的供试菌液90 μL,然后加入不同浓度的测试样品溶液10 μL。同时设空白对照(H2O)和溶剂对照(φ为30%的丙酮溶液),每处理6个重复。用封口膜将96微孔板四周封口,于28 ℃、黑暗条件下振荡(15 r/min)培养24 h,每孔加入10 μL MTT溶液(5 mg/mL),继续培养4 h后,以3 000 r/min 离心20 min,去上清,每孔加入二甲基亚砜(DMSO)150 μL,振荡(15 r/min)30 min,为了测定半抑制浓度(IC50),多孔板离心后,每孔取100 μL,于510 nm 下测定吸光度(D510 nm)。按下面公式计算待测样品对供试细菌的抑制率:
$${\text{抑制率}} = \frac{{{\text{溶剂对照孔}}{D_{510\;{\rm{nm}}}} - {\text{药液孔}}{D_{510\;{\rm{nm}}}}}}{{{\text{溶剂对照孔}}{D_{510\;{\rm{nm}}}}}} \times 100\% {\text{。}}$$ 所得数据采用 Microsoft excel 软件进行分析,供试样品浓度取对数(X),抑制率换算成概率值(Y),求得抑制活性回归方程(Y = aX+b)和半抑制浓度(IC50)。
1.7 抗肿瘤细胞活性测定
抗肿瘤细胞活性的测定参照Ouyang等[20]的方法,阳性对照为喜树碱。将对数生长期细胞接种于96孔细胞培养板(Nest)中,待6~8 h后细胞贴壁。用含有5%(w)FBS(Gibco)的DMEM(Hyclone)细胞培养基将化合物以2倍梯度稀释,共制备8个梯度(质量浓度分别为80.000、40.000、20.000、10.000、5.000、2.500、1.250和0.625 μg/mL)备用。小心吸弃各孔内原生长培养基后,将制备好的各浓度化合物分别加入对应孔中,每孔200 μL,每个化合物每个浓度设置4组重复孔。对照孔加入相应浓度的DMSO。在37 ℃,φ(CO2)为5%条件下,化合物与细胞继续共培养48 h。每孔加入CCK8试剂15 μL,在37 ℃、φ(CO2)为5%条件下继续培养4 h后,采用多功能微孔板检测仪在450 nm下检测各孔的吸光度(D450 nm),记录并保存数据。采用GraphPad Prism 5拟合各化合物在各细胞株的生长抑制曲线并计算其IC50值。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 内生真菌Eef-10的鉴定
内生真菌Eef-10的菌落和显微形态如图1所示。在PDA培养基上,菌落呈规则圆形(图1a),气生菌丝发达,绒毛状,初始时菌落白色,后期菌落颜色逐渐变灰,且随时间延长而逐渐加深,培养7 d后可布满整个培养皿(d = 7.5 cm)。在显微镜下观察发现,菌丝有隔(图1b),内含多个油滴,菌丝后期颜色较深且粗细不均,隔间距缩短;子囊果近球形(图1d),有孔口;附属丝较长,呈菌丝状,有隔,周生于子囊果且大部分集中生长于子囊果顶部;子囊孢子灰褐色(图1c),单孢,卵圆形,光滑,长×宽平均为7.0 μm×5.5 μm,有顶生萌发孔;与毛壳菌属Chaetomium的特征相一致[17, 21]。
进一步通过真菌通用引物ITS4和ITS5进行PCR扩增,获得大小为592 bp的目的序列,将该目的序列提交至GenBank,获得登录号MK120863。在GenBank数据库中进行同源性比对,采用最大似然法通过MEGA 6构建系统发育树(图2)。从图2可以看出,内生真菌Eef-10与Chaetomium sp.(登录号:KU504294.1)聚在同一支上,其最大相似度为99.82%,结合形态学特征最终将内生真菌Eef-10确定为子囊菌门Ascomycota核菌纲Pyrenomycetes粪壳目Sordariales毛壳菌科Chaetomiaceae毛壳菌属Chaetomium sp.真菌。
2.2 化合物的结构鉴定
通过1H NMR、13C NMR等波谱学数据以及与文献比对,确定了3种化合物的结构(图3)。
化合物Ⅰ,淡黄色固体,1H NMR谱在δH6.20 (1H, s)处有1个苯基质子信号,在δH2.09 (3H, s)和2.46 (3H, s)处有2个苯甲基质子信号,在δH3.91 (3H, s)处有1个甲氧基质子信号,δH 12.06 (1H, s)和 5.14 (1H, s)表明其结构中含有2个羟基信号,而且13C NMR谱中的2个芳香族碳信号δC163.37和158.20进一步支持了苯环在C-2和C-4处的氧化;通过1H NMR谱的相关信息及13C NMR谱δC163.37,158.20,140.39,110.75,108.70,105.46可以推导其结构中含有1个五取代苯环;13C NMR谱在δ 172.83处表明其结构中含有1个羰基。化合物Ⅰ的1H NMR (600 MHz,CDCl3)δH:12.06 (1H,s,2-OH),6.20 (1H,s,H-5),5.14 (1H,s,5-OH),3.91 (3H,s,H-1'),2.45 (3H,s,H-6),2.10 (3H,s,H-3);13C NMR (151 MHz,CDCl3) δC:172.83 (C-7),163.37 (C-2),158.20 (C-4),140.39 (C-6),110.75 (C-5),108.70 (C-3),105.46 (C-1),52.08 (C-1'),24.36 (C-6),7.89 (C-3)。上述数据与文献[22]数据一致,故将化合物Ⅰ鉴定为2, 4−二羟基−3, 6−二甲基苯甲酸甲酯(Methyl 2, 4-dihydroxy-3, 6-dimethylbenzoate,即Atraric acid)(图3a)。
化合物Ⅱ,白色固体,化合物Ⅱ的1H NMR谱和13C NMR谱与化合物Ⅰ数据非常接近,基本骨架一致,1H NMR谱中δH1.40 (t,J = 7.1 Hz,3H),4.38 (q,J = 7.1 Hz,2H)信号,表明其结构中含有1个R—CH2—CH3信号。化合物Ⅱ的1H NMR (600 MHz,CDCl3)δH:12.14 (1H,s,2-OH),6.19 (1H,s,H-5),5.18 (1H,s,5-OH),4.38 (2H,q,J= 7.1 Hz,H-1′),2.46 (3H,s,H-6),2.09 (3H,s,H-3),1.40 (3H,t,J= 7.1 Hz,H-2′);13C NMR (151 MHz,CDCl3) δC:172.17 (C-7),163.18(C-2),158.01 (C-4),140.18 (C-6),110.53 (C-5),108.55 (C-3),105.28(C-1),61.22(C-1′),24.23(C-6),14.26(C-2′),7.67(C-3)。上述数据与文献[23]数据一致,最终化合物Ⅱ鉴定为2, 4−二羟基−3, 6−二甲基苯甲酸乙酯(Ethyl 2, 4-dihydroxy-3, 6-dimethylbenzoate)(图3b)。
化合物Ⅲ,无色油状液体,化合物Ⅲ的1H NMR (600 MHz,Acetone-d6) δH:5.71(1H, s,H-3),4.32 (2H,t,J = 6.2 Hz,H-6),2.42 (2H,t,J = 6.2 Hz,H-5),2.01(3H,s,H-7);13C NMR (151 MHz,Acetone-d6)δC:164.55 (C-2),159.51 (C-4),116.95 (C-3),66.64 (C-6),29.75 (C-5),22.87(C-7)。上述数据与参考文献[24]数据基本一致,所以化合物Ⅲ鉴定为4−甲苯−5, 6−二氢−2H−吡喃−2−酮(4-methyl-5, 6-dihydro-2H-pyran-2-one)(图3c)。
2.3 抗细菌活性
内生真菌Eef-10次生代谢产物对5种供试细菌的抑制活性如表1所示。其中化合物Ⅲ在供试浓度下对5种供试细菌的IC50均大于200 μg/mL;化合物Ⅱ对所有供试细菌的抑制活性均强于化合物Ⅰ,其中对桉树青枯病菌的抑制活性最强,其IC50为35.87 μg/mL,与阳性对照硫酸链霉素非常接近,其次是对黄瓜角斑病菌和番茄疮痂病菌的抑制活性,其IC50分别为38.91和 40.80 μg/mL,对大肠埃希菌和根癌土壤杆菌的抑制活性较弱;化合物Ⅰ对黄瓜角斑病菌的抑制活性最强,其IC50为67.25 μg/mL,其次是对番茄疮痂病菌的抑制活性,其IC50为93.59 μg/mL,而对其他供试细菌的IC50均大于100 μg/mL。
表 1 内生真菌Eef-10次生代谢产物的抗细菌活性Table 1. Antibacterial activities of the secondary metabolites isolated from endophytic fungus Eef-10供试样品
Tested sampleIC50/(μg·mL−1) 大肠埃希菌
Escherichia
coli根癌土壤杆菌
Agrobacterium
tumefaciens黄瓜角斑病菌
Pseudomonas
lachrymans桉树青枯病菌
Ralstonia
solanacearum番茄疮痂病菌
Xanthomonas
vesicatoria化合物Ⅰ Compound Ⅰ 130.55 ± 3.57 105.39 ± 4.52 67.25 ± 1.23 113.11 ± 3.58 93.59 ± 0.43 化合物Ⅱ Compound Ⅱ 48.52 ± 0.33 55.50 ± 1.61 38.91 ± 0.54 35.87 ± 0.18 40.80 ± 0.70 化合物Ⅲ Compound Ⅲ > 200 > 200 > 200 > 200 > 200 硫酸链霉素 Streptomycin sulfate 18.51 ± 0.46 5.10 ± 0.03 30.54 ± 0.89 33.07 ± 2.46 13.81 ± 1.62 2.4 抗肿瘤细胞活性
抗肿瘤细胞活性的测定结果如表2所示,通过GraphPad Prism 5拟合各化合物在各细胞株的生长抑制曲线计算其IC50,除化合物Ⅱ之外,其他化合物对2种肿瘤细胞的IC50均大于50 μg/mL;化合物Ⅱ对HeLa细胞的IC50大于50 μg/mL,但对Hep-G2的IC50仅为1.50 μg/mL,明显强于阳性对照喜树碱的3.6 μg/mL,表明化合物Ⅱ对Hep-G2肿瘤细胞具有较好的生长抑制作用。
表 2 内生真菌Eef-10次生代谢产物的抗肿瘤细胞活性Table 2. Antitumor activities of the secondary metabolites isolated from endophytic fungus Eef-10供试细胞Tested cell IC50/(μg·mL−1) 化合物Ⅰ
Compound Ⅰ化合物Ⅱ
Compound Ⅱ化合物Ⅲ
Compound Ⅲ喜树碱
CamptothecinHep-G2 > 50 1.50 > 50 3.6 HeLa > 50 > 50 > 50 6.3 3. 讨论与结论
本研究以分离和鉴定抗细菌和抗肿瘤的活性化合物为导向,从窿缘桉内生真菌Chaetomium sp. Eef-10中共分离出3个化合物,包括2个苯酚类和1个戊烯酸内酯类化合物。前人的研究表明,化合物Ⅰ(Atraric acid)是一种天然的雄激素受体拮抗剂,主要应用于前列腺癌的治疗[25-26],该化合物曾在地衣植物Parmotrema cooperi[27]、Lecidella carpathica[28]和Pseudevernia furfuracea[22]以及地钱植物Frullania brasiliensis[29]、非洲臀果木Pygeum africanum[23]和紫葳科植物Newbouldia laevis[30]中被发现和报道,而有关化合物Ⅱ的研究却很少,一般是作为Atraric acid衍生物的形式被报道,但化合物Ⅱ对雄激素受体的拮抗作用甚至略高于Atraric acid,亦可作为抗前列腺癌优先级的候选药物[31]。本研究中活性测定的结果显示,化合物Ⅱ表现出较好的抗细菌活性,其中对桉树青枯病菌的抑制活性最强,IC50为35.87 μg/mL,与阳性对照结果相当,且化合物Ⅱ对Hep-G2肿瘤细胞也具有较好的抑制作用,研究结果为寻找抗桉树青枯病菌天然微生物源活性药物提供了新的思路。
致谢:感谢华南农业大学农学院谢辉和徐春玲老师在内生真菌形态学鉴定方面提供的帮助!
-
表 1 试验林概况
Table 1 General characteristics of experimental stands
林分 坡向/
(°)坡度/
(°)平均
胸径/cm郁闭度 平均
树高/m冠幅/m 主要林下植被1) 火力楠 SW20 35 13.1 0.85 10.8 6 山芝麻、黑面神、山苍子、粗叶榕、三叉苦、冬青、海金沙、五指毛桃、玉叶金花、梅叶冬青、漫山秀竹、乌毛蕨、羊角拗、铁线蕨 马尾松 SW25 23 12.4 0.80 8.4 4 半边旗、梅叶冬青、悬钩子、淡竹叶、乌毛蕨、鸭脚木、漫山秀竹、金毛狗、白花酸果藤、五指毛桃、铁线蕨、红椎、鬼灯笼 1) 山芝麻Helicteres angustifolia、黑面神Breynia fruticosa、山苍子Litsea cubeba、粗叶榕Ficus hirta、三叉苦 Evodia lepta、冬青 Ilex chinensis、海金沙Lygodium japonicum、五指毛桃Ficus simplicissima、玉叶金花Mussaenda pubescens、梅叶冬青Ilex asprella、漫山秀竹Microstegiumvagans、乌毛蕨Blechnum orientale、羊角拗Strophanthus divaricatus、铁线蕨Adiantum capillus、半边旗Pteris semipinnata、悬钩子Rubus palmatus、淡竹叶Lophatherum gracile、鸭脚木Schefflera octophylla、金毛狗Cibotium barometz、白花酸果藤Embelia ribes、红椎 Castanopsis hystrix、鬼灯笼 Clerodrndrum fortumatum。 表 2 火力楠与马尾松林地凋落叶中的N、P、K含量变化1)
Table 2 Changes in N,P and K contents of mixed leaf litters in Michelia macclurei and Pinus massoniana woodlands
w/(g·kg–1) 凋落叶
养分林地 处理 0个月 3个月 6个月 9个月 12个月 15个月 18个月 21个月 24个月 N 火力楠 对照 9.90±0.00e 12.72±0.14a 11.21±0.14d 12.54±0.19a 11.82±0.09c 11.23±0.13d 12.76±0.19a 2.76±0.06a 12.08±0.05b 施N 9.90±0.00f 12.36±0.09cd 12.16±0.14d 12.56±0.28c 13.14±0.19b 12.43±0.12c 11.69±0.02e 13.21±0.02b 13.72±0.13a 施P 9.90±0.00g 11.23±0.08d 12.51±0.06c 13.88±0.06a 10.21±0.34f 10.62±0.28e 12.41±0.20c 13.25±0.07b 12.34±0.08c 施N+P 9.90±0.00d 12.03±0.09d 11.07±0.16e 13.04±0.07b 13.26±0.07b 12.47±0.25c 12.67±0.25c 12.55±0.18c 13.70±0.18a 马尾松 对照 9.90±0.00g 10.60±0.16f 11.97±0.10b 9.80±0.05g 11.34± 0.04d 10.56±0.15f 12.78±0.03a 11.14±0.06e 11.68±0.07c 施N 9.90±0.00h 12.45±0.25cd 10.75±0.20g 12.35±0.13d 12.08±0.16e 14.33±0.16a 11.75±0.03f 12.72±0.08b 12.63±0.06bc 施P 9.90±0.00e 8.80±0.04f 7.73±0.03g 11.70± 0.07c 10.78±0.21d 10.98±0.14d 13.47±0.19b 14.28±0.13a 13.46±0.07b 施N+P 9.90±0.00g 10.66±0.25e 9.02±0.02h 10.27± 0.14f 11.38±0.04d 9.11±0.08h 13.30± 0.05c 13.56±0.16b 14.54±0.16a P 火力楠 对照 0.38±0.00c 0.38±0.01c 0.39±0.01c 0.38±0.00c 0.32±0.01d 0.38±0.00c 0.40±0.00b 0.42±0.01a 0.39±0.01c 施N 0.38±0.00b 0.36±0.01c 0.38±0.00b 0.38±0.01b 0.36±0.01c 0.33±0.01d 0.37±0.00b 0.38±0.00b 0.40±0.00a 施P 0.38±0.00h 0.56±0.02e 0.49±0.01g 0.66±0.00c 0.54±0.01f 0.60±0.01d 0.66±0.01c 0.74±0.01b 0.86±0.01a 施N+P 0.38±0.00g 0.54±0.00e 0.46±0.00f 0.64±0.01b 0.75±0.00a 0.62±0.01c 0.47±0.00f 0.58±0.01d 0.74±0.01a 马尾松 对照 0.38±0.00d 0.36±0.01e 0.46±0.01b 0.42±0.01c 0.42±0.00c 0.38±0.00d 0.47±0.01b 0.41±0.01c 0.58±0.00a 施N 0.38±0.00e 0.40±0.01d 0.40±0.00d 0.44±0.00b 0.42±0.00c 0.45±0.01a 0.43±0.01bc 0.42±0.00c 0.43±0.01bc 施P 0.38±0.00i 0.42±0.01h 0.64±0.01f 0.90±0.00c 0.70±0.01e 0.61±0.01g 0.77±0.00d 1.08±0.03b 1.37±0.02a 施N+P 0.38±0.00g 0.51±0.01f 0.68±0.00e 0.69±0.01e 0.76±0.00d 0.86±0.00c 0.99±0.00b 0.86±0.02c 1.05±0.02a K 火力楠 对照 1.02±0.00g 0.76±0.02h 1.66±0.03b 1.50±0.01c 3.42±0.05a 1.31±0.01d 1.71±0.07b 1.16±0.04f 1.23±0.02e 施N 1.02±0.00de 0.67±0.03g 1.41±0.01c 2.57±0.12a 1.33±0.05c 1.05±0.06d 1.64±0.03b 0.86±0.02f 0.94±0.02ef 施P 1.02±0.00g 1.26±0.02f 1.88±0.01d 1.35±0.01e 4.50±0.02a 2.43±0.08b 2.04±0.03c 1.26±0.02f 1.92±0.02d 施N+P 1.02±0.00g 1.44±0.04f 3.55±0.09a 1.53±0.02e 1.71±0.02d 1.91±0.02b 1.81±0.06c 1.90± 0.03b 1.88±0.04b 马尾松 对照 1.02±0.00g 1.06±0.02g 2.04±0.01e 3.01±0.09b 1.90±0.03f 4.18±0.05a 2.80±0.08c 2.00±0.02e 2.46±0.03d 施N 1.02±0.00g 1.16±0.03f 2.49±0.04b 2.07±0.08d 4.76±0.10a 2.06±0.03d 2.57±0.02b 1.68±0.02e 2.22±0.04c 施P 1.02±0.00g 1.95±0.02d 3.42±0.02b 2.42±0.08c 5.65±0.09a 1.68±0.02e 2.39±0.05c 1.60±0.02f 1.74±0.01e 施N+P 1.02±0.00h 1.34±0.02g 3.18±0.02c 6.27±0.09a 2.29±0.02e 4.35±0.14b 1.57±0.01f 2.68±0.02d 1.50±0.02f 1)表中数据为平均值±标准差;同行数据后凡具有一个相同小写字母者,表示处理时间之间差异不显著(P>0.05,Duncan’s 法)。 -
[1] 王相娥, 薛立, 谢腾芳. 凋落物分解研究综述[J]. 土壤通报, 2009, 40(6): 1473-1478. [2] JIANG Y F, YIN X Q, WANG F B. The influence of litter mixing on decomposition and soil fauna assemblages in a Pinus koraiensis mixed broadleaved forest of the Changbai Mountains, China[J]. Eur J Soil Biol, 2013, 55(1): 28-39.
[3] XU X N, HIRATA E, ENOKI T, et al. Leaf litter decomposition and nutrient dynamics in a subtropical forest after typhoon disturbance[J]. Plant Ecol, 2004, 173(2): 161-170.
[4] WANG Q K, WANG S L, HUANG Y. Comparisons of litterfall, litter decomposition and nutrient return in a monoculture Cunninghamia lanceolata and a mixed stand in Southern China[J]. Forest Ecol Manag, 2008, 255(3/4): 1210-1218.
[5] SCHLESINGER W H, BERNHARDT E S. Biogeochemistry: An analysis of global change: Vol.54 [M]. New York: Academic Press, 1991: 353-423.
[6] 李宜浓, 周晓梅, 张乃莉, 等. 陆地生态系统混合凋落物分解研究进展[J]. 生态学报, 2016, 36(16): 4977-4987. [7] LIMPENS J, BERENDSE F. How litter quality affects mass loss and N loss from decomposing sphagnum[J]. Oikos, 2003, 103(3): 537-547.
[8] 徐国良, 莫江明, SANDRA B, 等. 土壤动物对模拟N沉降的响应[J]. 生态学报, 2004, 24(10): 2245-2251. [9] 卢广超, 邵怡若, 薛立. 氮沉降对凋落物分解的影响研究进展[J]. 世界林业研究, 2014, 24(1): 35-42. [10] 王家骏, 程煜, 杨玉盛, 等. 米槠叶凋落物分解及养分释放对模拟N沉降的响应[J]. 福建林学院学报, 2014, 34(2): 113-119. [11] 张驰, 张林, 李鹏, 等. 亚热带常绿阔叶林凋落物生产及季节动态对模拟氮沉降增加的响应[J]. 生态学杂志, 2014, 33(5): 1205-1210. [12] 滕秋梅, 何斌, 梁添富, 等. 桂东南火力楠人工林生态系统碳储量及其分布格局[J]. 农业研究与应用, 2016(4): 7-11. [13] XUE L, HAGIHARA A. Growth analysis on the competition-density effect in Chinese fir (Cunninghamia lanceolata) and Masson pine (Pinus massoniana) stands[J]. Forest Ecol Manag, 2001, 150(3): 331-337.
[14] XUE L, LI Q J, CHEN H Y. Effects of a wildfire on selected physical, chemical and biochemical soil properties in a Pinus massoniana forest in South China[J]. Forests, 2014, 5(12): 2947-2966.
[15] XUE L, LIE G W, LU G C, et al. Allometric scaling among tree components in Pinus massoniana stands with different sites[J]. Ecol Res, 2013, 28(2): 327-333.
[16] 鲁如坤. 土壤农业化学分析方法[M]. 北京: 中国农业科技出版社, 2000. [17] AXELSSON G, BERG B. Fixation of ammonia (15N) to Pinus silvestris needle litter in different stages of decomposition[J]. Scand J Forest Res, 1988, 3(1/2/3/4): 273-279.
[18] LIU L, GUNDERSEN P, ZHANG T, et al. Effects of phosphorus addition on soil microbial biomass and community composition in three forest types in tropical China[J]. Soil Biol Biochem, 2012, 44(1): 31-38.
[19] LI J, LI Z A, WANG F M, et al. Effects of nitrogen and phosphorus addition on soil microbial community in a secondary tropical forest of China[J]. Biol Fert Soils, 2015, 51(2): 207-215.
[20] ALLISON S D, HANSON C A, TRESEDER K K. Nitrogen fertilization reduces diversity and alters community structure of active fungi in boreal ecosystems[J]. Soil Biol Biochem, 2007, 39(8): 1878-1887.
[21] 曾锋. 外源性氮和磷对6种人工林凋落叶分解及土壤特性的影响[D]. 广州: 华南农业大学, 2011. [22] 董喜光, 张越, 薛立, 等. 火力楠林的土壤特性对外源性N和P的响应[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 2016, 36(9): 104-108. [23] GILLOOLY J F, ALLEN A P, WEST G B, et al. The rate of DNA evolution: Effects of body size and temperature on the molecular clock[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2005, 102(1): 140-145.
[24] RIER S T, SHIRVINSKI J M, KINEK K C. In situ light and phosphorus manipulations reveal potential role of biofilm algae in enhancing enzyme-mediated decomposition of organic matter in streams[J]. Freshwater Biol, 2014, 59(5): 1039-1051.
[25] QUALLS R G, RICHARDSON C J. Phosphorus enrichment affects litter decomposition, immobilization and soil microbial phosphorus in wetland mesocosms[J]. Soil Sci Soc Am J, 2000, 64(2): 799-808.
[26] 郑棉海, 黄娟, 陈浩, 等. 氮、磷添加对不同林型土壤磷酸酶活性的影响[J]. 生态学报, 2015, 35(20): 6703-6710. [27] ZHAO Y J, LIU B, ZHANG W G, et al. Effects of plant and influent C∶N∶P ratio on microbial diversity in pilot-scale constructed wetlands[J]. Ecol Eng, 2010, 36(4): 441-449.
[28] JACOBSON T K, BUSTAMANTE M M , KOZOVITS A R. Diversity of shrub tree layer, leaf litter decomposition and N release in a Brazilian Cerrado under N, P and N plus P additions[J]. Environ Pollut, 2011, 159(10): 2236-2242.
[29] MULDER C, ELSER J J. Soil acidity, ecological stoichiometry and allometric scaling in grassland food webs[J]. Global Change Biol, 2009, 15(11): 2730-2738.
[30] LIU Z F, FU B J, ZHENG X X, et al. Plant biomass, soil water content and soil N∶P ratio regulating soil microbial functional diversity in a temperate steppe: A regional scale study[J]. Soil Biol Biochem, 2010, 42(3): 445-450.
[31] 包淑云, 周守标, 喻永红. 含笑属叶片的比较解剖学研究[J]. 广西植物, 2002, 22(2): 140-144. [32] GALLARDO A, MERINO J. Leaf decomposition in two Mediterranean ecosystems of Southwest Spain: Influence of substrate quality[J]. Ecology, 1993, 74(1): 152-161.
[33] PRESCOTT C E, KABZEMS R, ZABEK L M. Effects of fertilization on decomposition rate of Populus tremuloides foliar litter in a boreal forest[J]. Can J Forest Res, 1999, 29(3): 393-397.
[34] 庞丽, 张一, 周志春, 等, . 模拟氮沉降对低磷胁迫下马尾松生长和磷效率的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 2014, 25(5): 1275-1282. -
期刊类型引用(0)
其他类型引用(1)





 下载:
下载: