Study on resistance of Aquilaria sinensis against Heortia vitessoides
-
摘要:目的
黄野螟Heortia vitessoides是珍贵树种土沉香Aquilaria sinensis的重要食叶害虫,通过大面积林间调查土沉香受害情况,筛选可能存在的抗虫植株,为黄野螟的科学预防和土沉香抗虫品种的选育奠定基础。
方法在黄野螟危害盛期,对野外土沉香林定期进行大面积调查,在严重受害的土沉香林中,观察不同受害水平土沉香的外观形态和叶片物理结构,同时采集具有不同抗虫性植株的叶片饲养黄野螟幼虫,观察初孵幼虫对不同抗性植株叶片的选择和拒食情况,取食不同抗性土沉香叶片后,测定黄野螟幼虫存活率、生长发育、化蛹和羽化的差异。
结果在土沉香严重受害的林分中发现了2株未受害的土沉香植株,其表现出较好的抗虫性(抗1和抗2)。抗性植株(抗1和抗2)与感虫植株在叶片长度和厚度上差异显著(P<0.05),而叶片长宽比无显著差异。在叶片物理结构上,抗2土沉香叶片的上表皮角质层厚度显著高于感虫叶片。抗2土沉香植株对幼虫取食抑制率高于抗1土沉香植株,两者均达44.81%以上。强迫取食抗性土沉香试验的幼虫存活率、成虫羽化率、蛹质量、成虫寿命均显著低于取食感虫土沉香叶片幼虫的相应指标,而取食抗性土沉香的幼虫、蛹发育历期均显著长于取食感虫土沉香叶片的害虫。
结论叶片嫩绿的土沉香植株较易受黄野螟的为害,而叶片厚的或叶片颜色偏黄、墨绿的土沉香植株对黄野螟具有较强的抗性。抗性土沉香植株对黄野螟幼虫取食活性具有较强的抑制作用,对幼虫的发育有阻碍作用。
Abstract:ObjectiveHeortia vitessoides is an important defoliator attacking the precious tree species of Aquilaria sinensis. The goal was to screen potential insect-resistant plants by surveying A. sinensis victimization in a large area of forest, and provide a basis for the scientific prevention of H. vitessoides and the breeding of insect-resistant plants.
MethodIn the harmful period of H. vitessoides, regular surveys on large area of A. sinensis forests were conducted. In the seriously damaged A. sinensis forests, plant appearances and leaf physical structures at different levels of victimization were observed, and leaves from different insect-resistant plants were collected to feed the newly-hatched larvae of H. vitessoides. Whether the leaves from different insect-resistant plants were chosen or rejected by the larvae was observed. The differences in larva survival rate, growth and development, pupation and feathering by feeding on different resistant A. sinensis leaves were tested.
ResultThere were two undamaged A. sinensis plants in the severely damaged A.sinensis forests, showing good resistance to insect pests (anti-1 and anti-2). There were significant differences in leaf length and thickness between the insect-resistant plants (anti-1 and anti-2) and susceptible plants(P<0.05), while the ratio of leaf length to width had no significant difference. As for leaf physical structures, the leaf upper epidermis cuticle thickness of anti-2 was significantly higher than that of the susceptible plant. The antifeedant rate ofH. vitessoides larvae against anti-2 plant was significantly higher than that against anti-1 plant, and both were above 44.81%. Larvae fed on resistant leaves had significant lower survival rate, adult emergence rate, pupal weight and shorter adult longevity, but longer duration of pupa compared to larvae fed on normal A. sinensis leaves.
ConclusionA. sinensis plants with tender green leaves are more susceptible to H. vitessoides, while the plants with thick, yellow or dark green leaves have strong resistance to H. vitessoides. Resistant A. sinensis plants have a higher inhibitory effect on feeding activity of H. vitessoides larvae and hinder larval development.
-
Keywords:
- Aquilaria sinensis /
- Heortia vitessoides /
- forest survey /
- resistance identification
-
土沉香Aquilaria sinensis属于桃金娘目Myrtales瑞香科Thymelaeaceae沉香属Aquilaria,又名白木香[1]。《2000年世界自然保护联盟受威胁植物红色名录》把土沉香列为易危植物[2]。土沉香在国外主要分布于印度、马来西亚以及亚洲东南部,在国内分布于海南、广东、广西、福建和台湾等低纬度地区[3-4]。土沉香是我国唯一能够生产正品中药沉香的植物资源,是珍贵的药用植物,具有极高的经济价值[5-9]。
黄野螟Heortia vitessoides属于鳞翅目Lepidoptera草螟科Crambidae齿螟亚科Odontiinae,是一种严重危害土沉香的单食性食叶害虫。黄野螟在国外主要分布于印度、尼泊尔、斐济、斯里兰卡以及东南亚、东印度群岛、新赫布里底群岛等地[10],在国内主要分布于广东、广西、云南、海南、福建、台湾和香港等地。目前仅知该虫危害土沉香[11-12]。近年来,随着广东和海南等地大规模种植土沉香,病虫害问题日益突出。据广东化州、电白和广州等地区统计,黄野螟发生危害时,土沉香的被害株率可高达90% 以上,严重地块甚至100%受害。
近年来,关于黄野螟的生物学特性、生态学特性和化学防治技术等方面的研究报道较多[13-22],鲜见关于土沉香抗虫品种选育及其抗虫机制方面的研究报道。土沉香抗虫植株的筛选与抗虫性测定,可为下一步抗虫品种选育以及抗虫机制研究提供技术支持。土沉香抗虫性的研究和利用,有助于发掘一种新型无公害的黄野螟防控方法,保障土沉香大面积种植业的健康发展。
害虫与其寄主植物有着长远的相互协同进化关系,在长期共同进化过程中,寄主植物演化出一些不利于害虫生存或生长发育的防御机制,即非选择性、抗生性和耐害性[23]。林间调查发现,土沉香在黄野螟为害极其严重的情况下,其中某些植株确实能表现出避免受害、耐害或虽受害而有补偿能力的特性。为明确其中2株土沉香的抗虫性,进一步探索2种不同土沉香叶片的形态、解剖特征以及对黄野螟的拒食作用和忌避活性,特开展本试验研究,以期为黄野螟无公害化防治及开发环保型农药提供试验依据和科学参考。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 试验地概况
试验地设在广州市天麓湖土沉香种植基地(东经113°8′51″~113°11′7″,北纬23°12′35″~23°14′26″),海拔162 m;该地区属海洋性亚热带季风气候。年平均气温22 ℃,年平均相对湿度77%,年平均降雨量约为1 720 mm。地貌类型属低、中丘陵,土壤为花岗岩风化形成的微酸性沙壤土。基地现种植土沉香1万株,间距2 m×2 m,树龄5~8年,树高2~4 m。
1.2 试验材料
供试黄野螟及其寄主土沉香于2014年11月采自广州市土沉香种植基地。将野外剪取的土沉香枝叶带回实验室,用清水洗净,晾干后插入水中待用;将林间采集的黄野螟卵或幼虫置于室内养虫笼(60 cm×60 cm×80 cm)的土沉香植株上饲养,以获得虫龄一致的试虫及成虫,室内温度控制在25~27 ℃,相对湿度70%~80%,光︰暗=14 h︰10 h。
1.3 抗性调查
为寻找具有抗虫性的土沉香植株,2012年6月至2015年12月,在黄野螟危害盛期(每年4—6月和10—11月)先后多次对广州、茂名、中山的森林公园和乡镇种植的土沉香林中黄野螟的发生危害情况进行实地调查,重点调查黄野螟发生危害较重的林分,观察记录土沉香受害情况(以叶片发现卵块或幼虫和叶子被咬食为准)及危害率,标记未受害土沉香植株,以确定土沉香林中可能具有抗虫性的植株。在黄野螟多次严重发生危害的广州天麓湖土沉香林中发现了2株具有明显抗虫性的植株(分别记为抗1和抗2)。2013—2014年期间,每周调查这2株具有明显抗虫性的植株枝叶上黄野螟的发生情况,并记录其受害率。
1.4 抗性鉴定
1.4.1 土沉香叶片的外部形态特征测定
根据不同受害程度选择感虫和抗虫土沉香,从每棵树上随机采集3个枝条为一组插入干净水瓶并编号,每处理3组。把土沉香叶片擦拭干净,观察土沉香叶片的外部形态特征:叶片形状和颜色,用游标卡尺测量叶片长度、宽度和厚度等,每棵树观察50片叶。
1.4.2 土沉香叶片解剖结构观察
用徒手切片的方法对土沉香的叶片解剖结构进行研究。每个试验处理选取土沉香植株顶端第3片成熟叶,每株共30片,用直尺测量叶片长度,取其中间部位,沿着垂直于主脉的方向取长约5 cm左右的小块叶片(可取其主脉)。采用徒手切片方法,制成临时切片,然后在数码成像显微镜(OMT-1000,北京科技有限公司)下拍照观察,并测量土沉香叶片横切面角质层厚度、上下表皮厚度、栅栏组织厚度、海绵组织厚度、栅栏组织与海绵组织厚度比等指标。
1.4.3 初孵幼虫对土沉香叶片的选择性试验
选择有4~6片叶的土沉香小枝条,在基部包以含水的脱脂棉,将感虫枝叶、抗1枝叶和抗2枝叶分别置于内垫细沙的30 cm×30 cm×15 cm保鲜盒的3个角,同时设置感虫枝叶与抗1枝叶、感虫枝叶与抗2枝叶2种组合对比试验。然后在保鲜盒中央放入即将孵化的卵块。幼虫开始孵化后,每隔2 h观察初孵幼虫迁移状况,并记录幼虫在不同枝叶的分布情况,连续观察24 h,每个处理4次重复。按照下面公式计算分布率:
某种枝叶分布率=某种枝叶上幼虫数/总枝叶虫数×100%。
1.4.4 抗性土沉香叶片对黄野螟幼虫拒食性的测定
1)选择性拒食测定:在温度25~27 ℃,相对湿度70%~80%,光∶暗=14 h∶10 h的室内,选取直径9 cm的玻璃培养皿,中间铺垫1张定性滤纸,加少量蒸馏水保湿。挑选大小、厚度、新鲜度较一致的感虫(对照)和抗虫土沉香叶片,用圆形打孔器将叶片打成直径2 cm的叶碟,每皿内“十”字交叉的末端等距离放入感虫(对照1)与抗1或感虫(对照2)与抗2叶碟各2片,1枚正面朝上,1枚背面朝上。然后接入饥饿6 h的5龄初期幼虫1头,引入培养皿中央,每处理重复10次。24 h后将虫剔除,用座标纸分别量取各皿中感虫和抗虫植株叶片被食叶面积。在试验的同时设置无虫的空白对照,以确定试验期间叶片因水分蒸发而发生的叶面积变化。按下面公式计算食叶面积和选择性拒食率:
$$S = {S_1} - {S_2} - {S_1}\left( {{S_{01}} - {S_{02}}} \right)/{S_{01}},$$ 式中,S为校正食叶面积;S1为取食前叶面积;S2为取食后叶面积;S01为无虫对照初始叶面积;S02为24 h后无虫对照叶面积。
选择性拒食率=(校正感虫叶片被食面积–校正抗虫叶片被食面积)/(校正感虫叶片被食面积+校正抗虫叶片被食面积)×100%。
2)非选择性拒食测定:除感虫和抗虫植株叶片分放不同的培养皿外,其余方法与选择性拒食作用试验相同。按下面公式计算非选择性拒食率:
非选择性拒食率=(校正感虫叶片被食面积–校正抗虫叶片被食面积)/校正感虫叶片被食面积×100%。
1.4.5 饲喂抗虫土沉香对黄野螟生长发育的影响
挑取初孵幼虫30头置于培养皿,放入2 L的一次性饭盒内保湿,分别用抗性和感虫土沉香叶片饲养,及时更换新鲜叶片并清理虫粪,至预蛹时止,每天记录1次幼虫的生长发育和存活情况。化蛹后24 h之内,用1/10 000的电子天平称量蛹质量,记录幼虫和蛹历期及成虫寿命,计算成虫羽化率。试验过程中如有幼虫死亡,则清洗干净养虫盒,用同龄幼虫填补,继续饲养观察。
1.4.6 数据分析
用SPSS13.0统计软件对数据进行统计分析,多重比较使用Duncan’s新复极差检验。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 林间抗性调查
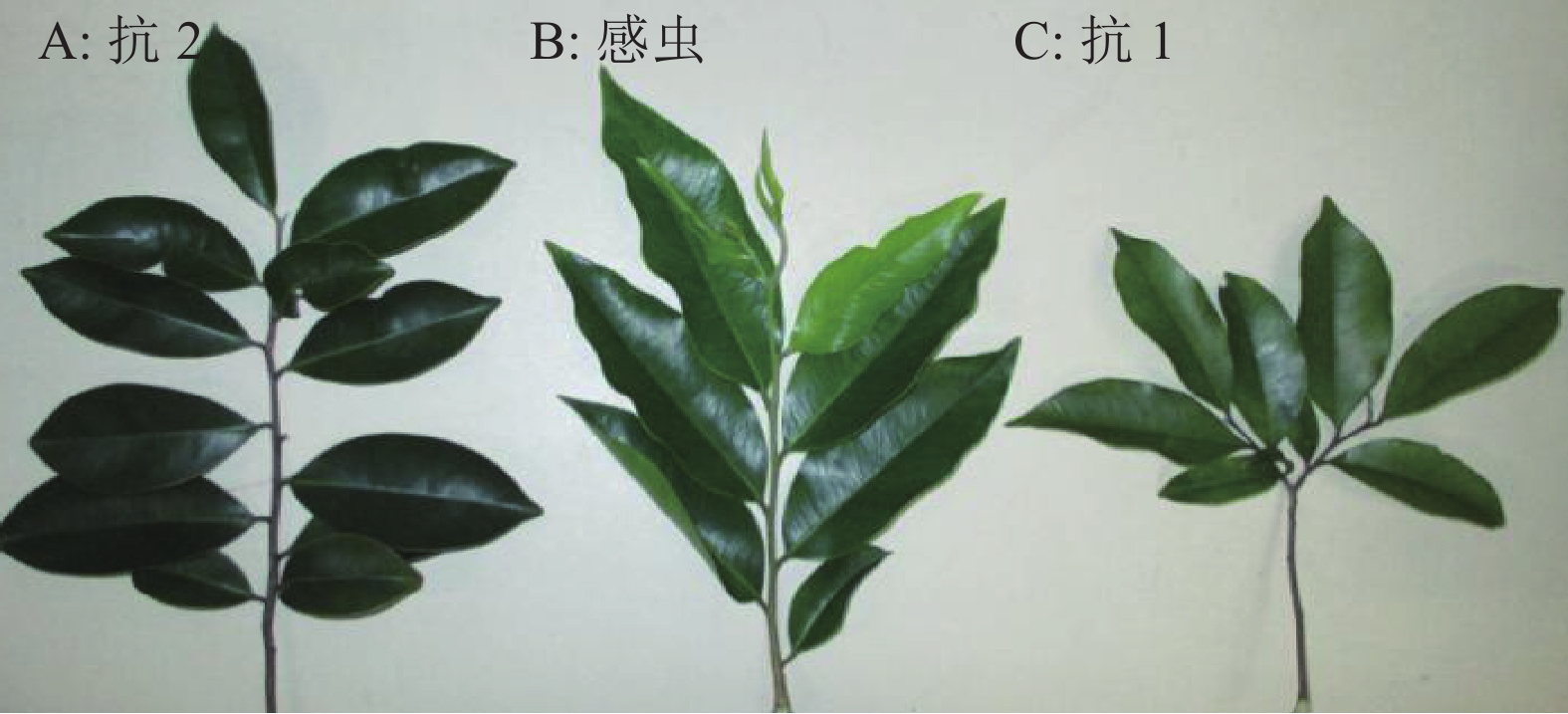
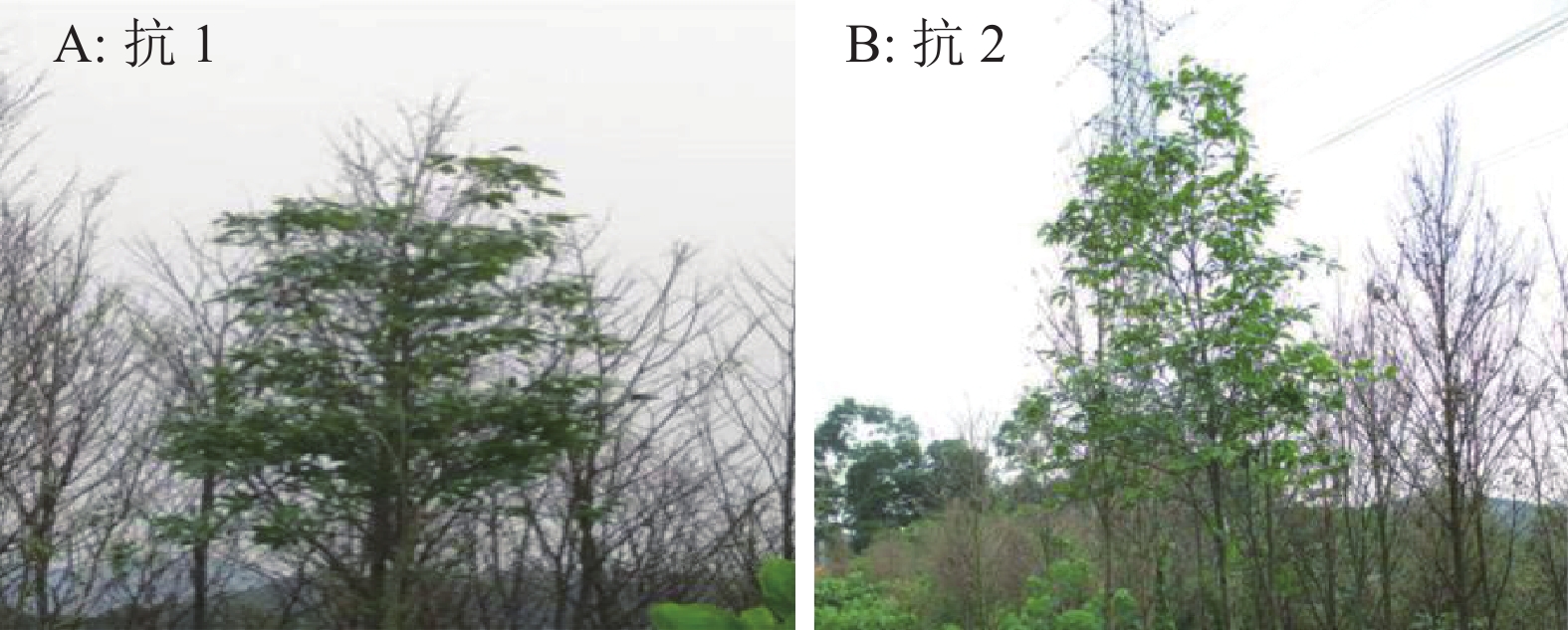
调查发现1株具有明显抗虫性的植株(抗1),周围30多m范围内上百株土沉香叶片全部被食光,只有这1株土沉香叶片完好,尽管在其叶片上发现10多块卵块,但叶片几乎没有被危害。另外1株抗虫土沉香(抗2)位于遭受严重危害的土沉香林缘,其周围土沉香叶片被害率均在80%以上,但该植株叶色墨绿,没有发现黄野螟卵块和幼虫危害症状,叶片完好率在95%以上(图1)。
2.2 抗性鉴定
2.2.1 抗性土沉香叶片的外部形态特征
林间调查发现,抗性土沉香叶片在形态特征上与感虫土沉香有明显不同。抗1植株的叶片较感虫土沉香植株的叶片细小,叶片发黄。抗2植株叶片较感虫土沉香植株叶片厚实,近椭圆形,叶片颜色近墨绿色。感虫土沉香叶片细长叶色嫩绿(图2)。
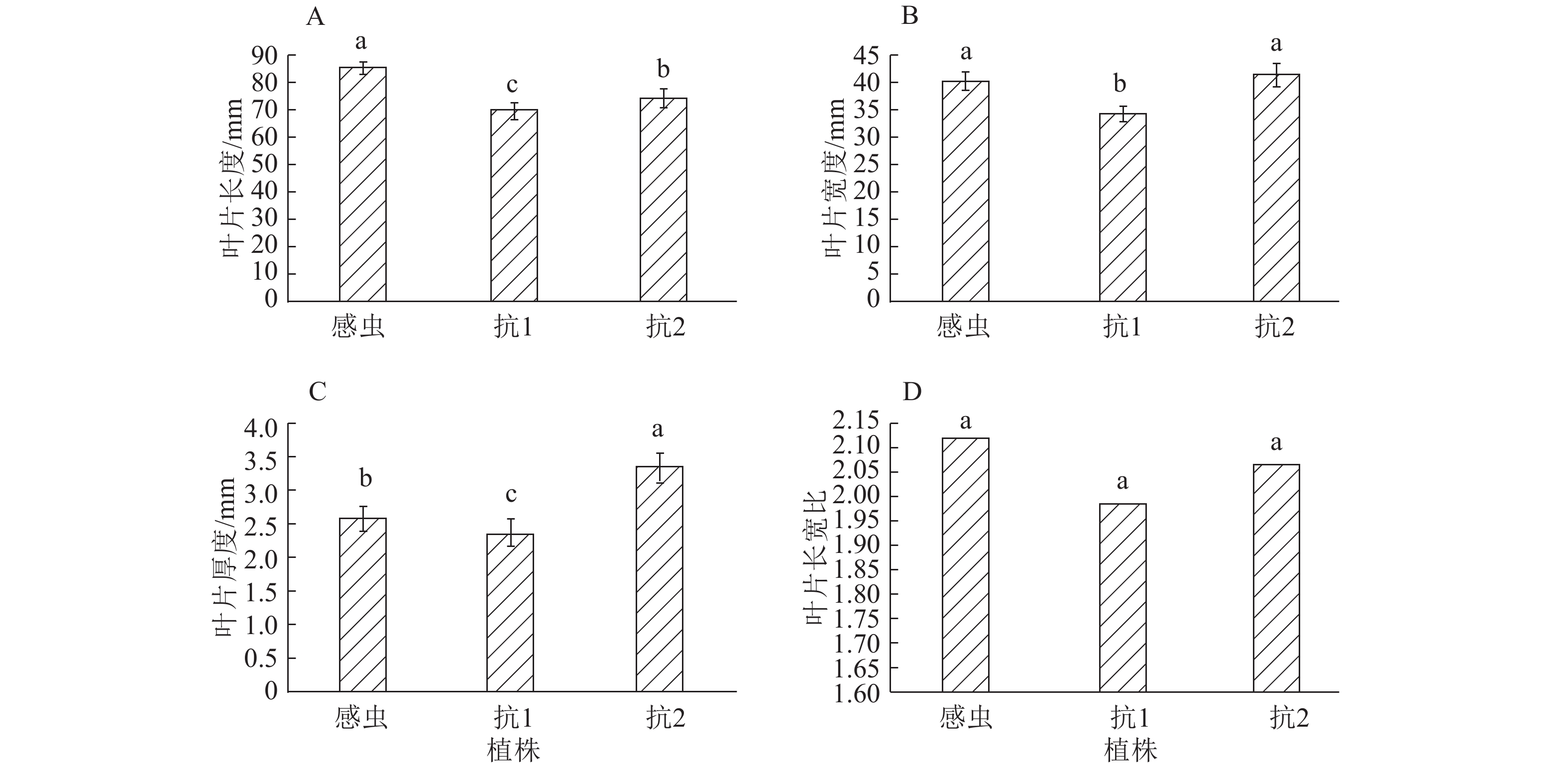
通过测量采集的土沉香叶片的长度、宽度和厚度等发现,不同土沉香叶片间叶长、叶宽、叶厚有差别(图3)。叶片长度为感虫>抗2>抗1,且相互间差异显著(P<0.05)。叶片宽度和厚度为抗2>感虫>抗1,其中叶片厚度相互间差异显著(P<0.05)。叶片长宽比为感虫>抗2>抗1,且相互间差异不显著。
2.2.2 抗性土沉香叶片解剖结构
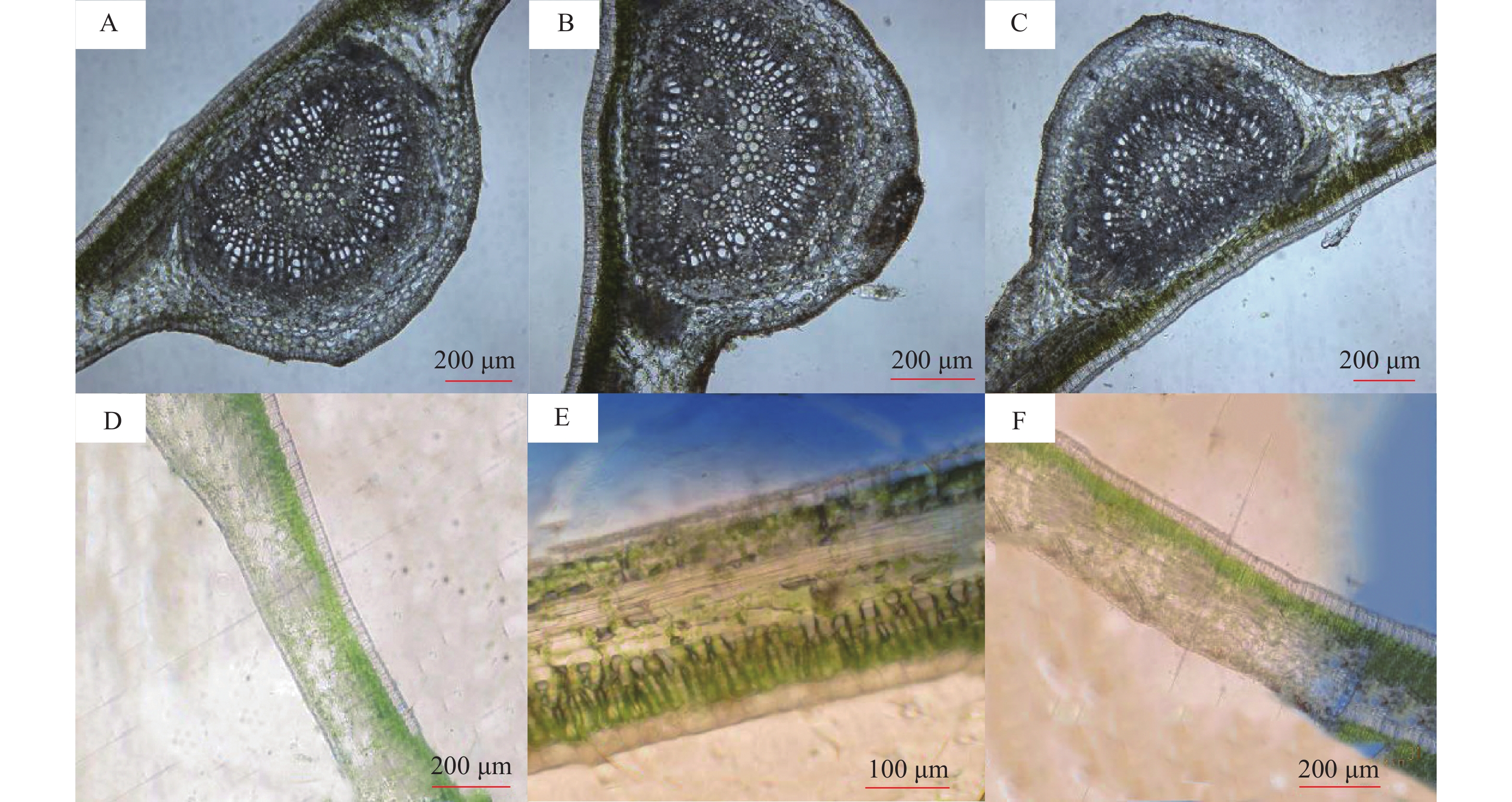
通过解剖土沉香叶片发现,在物理结构上不同土沉香叶片有差别(图4),土沉香叶片为典型的背腹型叶,感虫、抗2和抗1土沉香叶片厚度分别为2.58、3.35和2.36 mm。
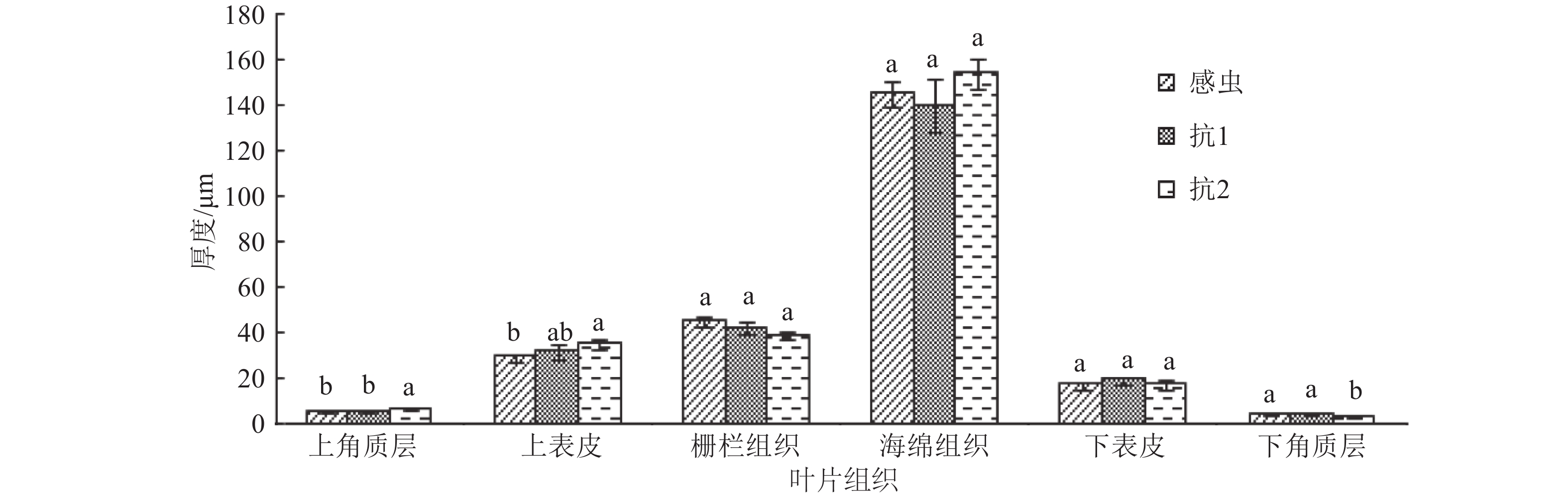
对解剖的土沉香叶片的表皮、叶肉等进行观察和测量发现,不同土沉香叶片间存在差别。表皮细胞排列紧密,下表皮细胞较小,多为近长方形或不规则形,1层。抗2土沉香叶片上、下表皮角质层厚度与感虫叶片和抗1叶片间差异显著(P<0.05)。抗2土沉香叶片上表皮厚度与感虫叶片差异显著(P<0.05)(图5)。
土沉香叶片叶肉组织发达,分化为栅栏组织和海绵组织。栅栏组织由1~2层排列整齐的柱状细胞构成,外层细胞排列紧密,染色较深,呈异细胞状,内层细胞染色较浅含丰富的叶绿体,土沉香叶片的栅栏组织厚度排序为感虫>抗1>抗2,差异不显著(图5)。
2.2.3 初孵幼虫对抗虫性土沉香叶片的选择性
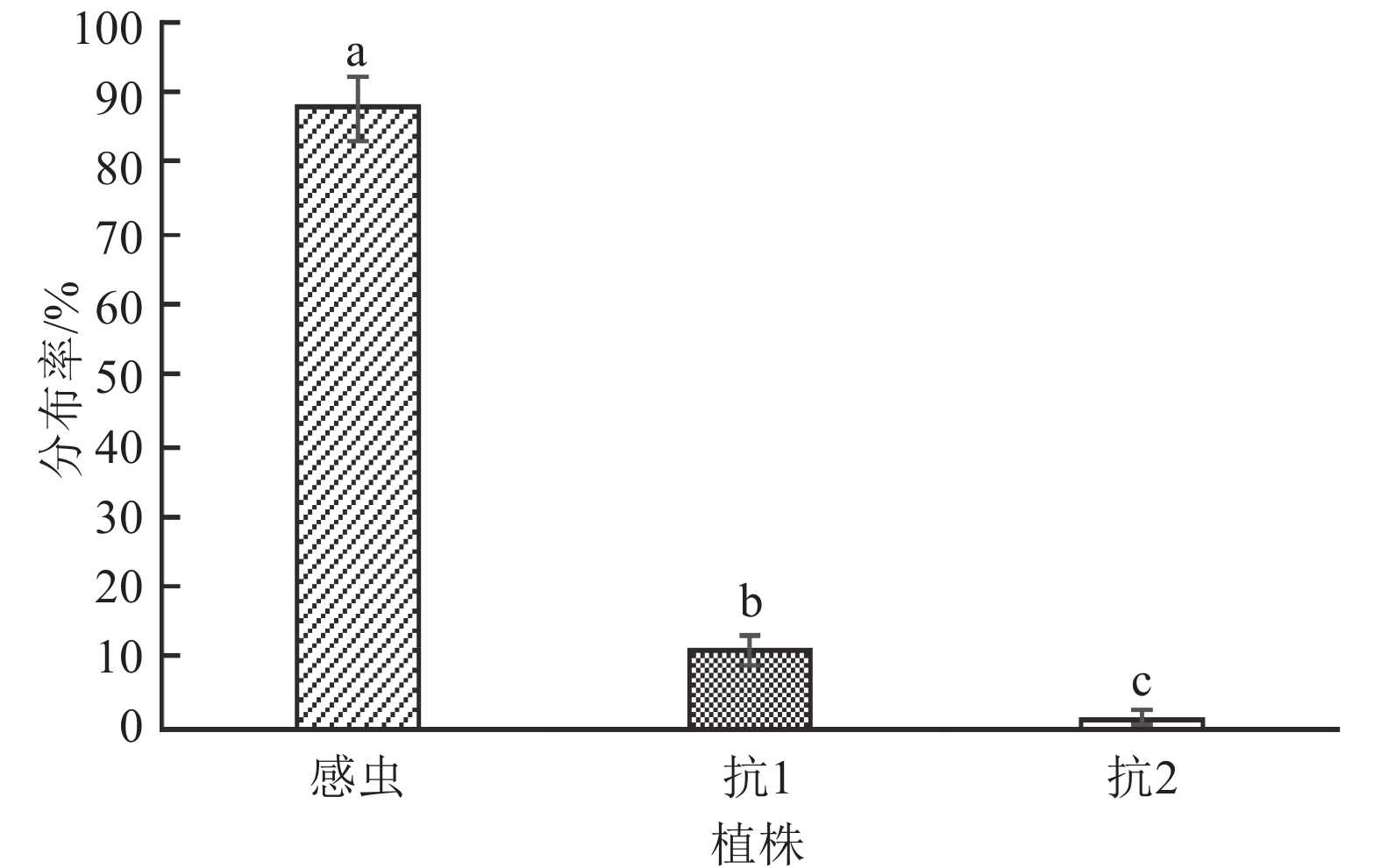
黄野螟初孵幼虫对不同土沉香叶片的选择趋向试验24 h后,检查不同土沉香植株嫩叶上的幼虫数,结果表明:幼虫对食物的选择在不同土沉香植株叶片间存在明显差异(图6)。黄野螟初孵幼虫在感虫植株叶片上的虫量最多,幼虫数占其总量的87.8%;抗1土沉香植株叶片上的虫量次之,占总虫量的10.8%;选择抗2土沉香植株叶片的虫量最少,仅占总虫量的1.4%,且不同抗性植株间差异显著。
在30 cm×30 cm×15 cm的保鲜盒内放入1种抗性叶片和感虫土沉香叶片进行黄野螟初孵幼虫对叶片的选择趋性测定,24 h后检查土沉香嫩叶上的幼虫数,结果表明:幼虫对抗性与感虫土沉香叶片间的选择存在明显差异。黄野螟初孵幼虫在感虫叶片上的虫量占其总量的86.0%,抗1土沉香上的虫量占总虫量的14.0%。黄野螟初孵幼虫在抗2土沉香上的虫量占总虫量的6.8%,感虫片上的虫量占其总量的93.2%
2.2.4 抗性土沉香叶片对黄野螟幼虫的拒食性
经幼虫选择性及非选择性拒食测定,24 h后各培养皿中抗性与感虫(对照)土沉香叶片被黄野螟幼虫取食掉的总叶面积及拒食率见表1和表2。从表1可知,选择性试验中,抗1和抗2土沉香被黄野螟幼虫取食的叶面积显著少于感虫土沉香(对照),拒食率分别为90.08%和92.91%;从表2可知,在非选择性试验中,抗1和抗2土沉香被黄野螟幼虫取食的叶面积也显著少于感虫土沉香(对照),拒食率分别为44.81%和56.21%。黄野螟幼虫对抗1和抗2土沉香植株具有很好的拒食活性,在选择性和非选择性试验中,黄野螟幼虫对抗2土沉香植株拒食率均高于抗1土沉香植株,两者均达44.81%以上(表1和表2)。
表 1 黄野螟幼虫对不同抗性土沉香叶片的选择性拒食测定Table 1. The selective feeding activity of Heortia vitessoides larvae to leaves of different resistant Aquilaria sinensis plants植株 被食叶面积1)/mm2 拒食率/% 抗1 56.00±4.35* 90.08 感虫(抗1对照) 1 033.43±159.95 抗2 51.50±3.68* 92.91 感虫(抗2对照) 180.48±178.56 1) *表示抗性植株与相应对照间在 0.05 水平上差异显著 (t 检验)。 表 2 黄野螟幼虫对不同抗性土沉香叶片的非选择性拒食测定Table 2. The non-selective feeding activity of Heortia vitessoides larvae to leaves of different resistant Aquilaria sinensis plants植株 被食叶面积1)/mm2 拒食率/% 抗1 647.68±125.48* 44.81 抗2 516.05±149.16* 56.21 感虫(对照) 1 173.92±113.94 1) *表示抗性植株与对照间在 0.05 水平上差异显著(t 检验)。 2.2.5 抗性土沉香对黄野螟生长发育的影响
由表3可知,取食感虫、抗1和抗2土沉香叶片的黄野螟幼虫存活率分别为90.56%、83.22%和78.31%,且感虫与抗2植株间差异显著。取食不同土沉香叶片1龄幼虫的历期无显著差异,而取食抗性植株3龄和4龄幼虫的历期与取食感虫对照组植株的差异显著。取食不同土沉香的幼虫历期、蛹历期均为抗2>抗1>感虫,且抗性植株与感虫植株间差异显著。取食感虫、抗1和抗2土沉香叶片的蛹羽化率分别为95.56%、91.67%和90.00%,且差异显著。此外,取食感虫、抗1和抗2土沉香叶片的蛹死亡率(包括成虫畸形)分别为4.44%、8.33%和10.00%。取食抗性土沉香的蛹体质量及成虫寿命与取食感虫土沉香叶片的蛹体质量及成虫寿命差异显著,蛹体质量及雌、雄成虫寿命均为:感虫>抗1>抗2。取食抗1植株的蛹体质量和雌、雄成虫寿命比取食感虫植株的分别少0.046 g、1.4 d和0.8 d;取食抗2植株的蛹体质量和雌、雄成虫寿命比取食感虫植株的分别少0.055 g、2.1 d和1.2 d, 取食抗1和抗2植株的蛹体质量分别为取食感虫叶片蛹体质量的75%和70%(表3)。
表 3 不同抗性土沉香叶片对黄野螟生长发育的影响1)Table 3. Effects of different resistant Aquilaria sinensis leaves on growth and development of Heortia vitessoides植株 幼虫发育历期/d 1龄 2龄 3龄 4龄 5龄 总计 感虫(对照) 2.8±0.2a 2.7±0.1b 2.3±0.1b 2.5±0.2b 3.7±0.2b 13.4±0.4b 抗1 3.0±0.1a 2.8±0.1b 2.6±0.3a 2.7±0.1a 3.9±0.3b 14.9±0.7a 抗2 2.9±0.1a 3.0±0.2a 2.7±0.1a 2.7±0.2a 4.1±0.2a 15.3±0.3a 植株 幼虫存活率/% 蛹历期/d 蛹体质量/g 成虫寿命/d 蛹羽化率/% 雌虫 雄虫 感虫(对照) 90.56±4.75a 9.8±0.5b 0.183±0.026a 6.4±0.9a 4.9±0.6a 95.56±2.72a 抗1 83.22±3.98ab 15.1±0.9a 0.137±0.031b 5.0±0.6b 4.1±0.4b 91.67±3.49b 抗2 78.31±2.41b 16.5±1.4a 0.128±0.019b 4.3±0.7c 3.7±0.5c 90.00±2.97c 1) 同列数据后凡具有一个相同小写字母者,表示植株间差异不显著(P>0.05,Duncan’s 法)。 3. 讨论与结论
抗虫性是寄主、昆虫、环境多因素作用的结果,寄主植物的形态学特征如叶片颜色、形状、叶片的厚度、茸毛有无及密度和长度等特性均能影响昆虫的入侵。对12个茶树品种新梢叶片的形态学与抗虫性研究发现叶背卷的品种或黄绿的新梢较易受茶假眼小绿叶蝉Empoasca vitis的为害,而叶片厚的品种对茶丽纹象甲Myllocerinus aurolineatus具有较强的抗性[24-25]。另有研究表明黄野螟趋向于在林缘嫩绿新梢上产卵[14]。本研究中的土沉香抗1植株叶薄、颜色偏黄,抗2植株叶厚、颜色墨绿,与上述抗虫性的研究结果较一致。
植株叶片角质层、表皮层厚度及叶厚等均影响抗虫性能,抗性品种叶片角质化程度高,下表皮较厚,这些形态结构的轻微变化都有可能改变植食性害虫的适口度,从而影响害虫的取食行为[26]。土沉香抗2植株叶片上表皮、角质层较厚,栅栏组织排列紧密,这些都可能与林间幼虫不喜取食该叶片有一定的相关性。本研究中,叶片下表皮、海绵组织等方面的差异与抗虫性间规律性不明显,其间的关系还需更详细的研究。
在初孵幼虫对叶片的选择试验中,发现有些黄野螟幼虫在抗性土沉香叶片上小范围内爬动或立即调头离开,趋近于感虫土沉香叶片所在位置。有研究表明,植食性昆虫对植物不选择的重要原因之一是这些植物能产生驱避和抑制昆虫取食、影响昆虫生长发育或使之中毒死亡的次生物质[27]。本研究中,无论土沉香抗1、抗2植株叶片同时还是单独存在,黄野螟幼虫对抗性植株和感虫植株的选择方式都有些差异,幼虫对抗1的选择率显著大于对抗2土沉香植株的选择率,但最终还是更倾向于选择感虫土沉香。害虫对抗性土沉香的非选择作用是明显的,可能是某些次生化合物起作用的结果,其活性及化学结构尚未明确,有待进一步研究。
抗性植株对害虫的作用是多方面的,以驱避和拒食作用为主[11]。本研究中,抗性土沉香植株对幼虫取食活性具有很好的抑制作用。选择性试验中,黄野螟幼虫对抗1和抗2土沉香叶片拒食率分别为90.08%和92.91%;在非选择性试验中,抗1和抗2土沉香被取食叶面积也显著少于感虫土沉香,拒食率分别为44.81%和56.21%。研究中采用选择性和非选择性试验,可以较为全面地反映试虫对抗性土沉香叶片的选择倾向和拒食程度。黄野螟幼虫一般有5个龄期,1~2龄幼虫群集在叶面啮食叶肉,3龄后才分散取食为害[28]。因此,本试验选择活动能力较强的5龄黄野螟幼虫作为取食选择行为研究的试验材料。开展抗虫性土沉香对害虫的拒食作用的研究,有利于抗性树种的鉴定、选育。
寄主植物对植食性昆虫的营养效应主要取决于取食部位所含成分的性质和份量[29]。昆虫都有自己特定的营养需求,对不同寄主植物喜食程度不同。抗性植物会使害虫发育不良、蛹体质量减轻、羽化率降低、体形变小、寿命缩短、生殖能力下降、死亡率增加[30]。本研究结果表明,黄野螟幼虫取食感、抗性土沉香植物叶片,幼虫发育历期、存活率、蛹体质量及成虫繁殖力等均存在显著差异,以取食抗2土沉香叶片的幼虫发育历期最长,存活率、蛹体质量和成虫羽化率降低。可见,抗性土沉香对黄野螟幼虫的发育有阻碍作用,选育抗性土沉香树种可对开发土沉香防治的新途径提供参考。
-
表 1 黄野螟幼虫对不同抗性土沉香叶片的选择性拒食测定
Table 1 The selective feeding activity of Heortia vitessoides larvae to leaves of different resistant Aquilaria sinensis plants
植株 被食叶面积1)/mm2 拒食率/% 抗1 56.00±4.35* 90.08 感虫(抗1对照) 1 033.43±159.95 抗2 51.50±3.68* 92.91 感虫(抗2对照) 180.48±178.56 1) *表示抗性植株与相应对照间在 0.05 水平上差异显著 (t 检验)。 表 2 黄野螟幼虫对不同抗性土沉香叶片的非选择性拒食测定
Table 2 The non-selective feeding activity of Heortia vitessoides larvae to leaves of different resistant Aquilaria sinensis plants
植株 被食叶面积1)/mm2 拒食率/% 抗1 647.68±125.48* 44.81 抗2 516.05±149.16* 56.21 感虫(对照) 1 173.92±113.94 1) *表示抗性植株与对照间在 0.05 水平上差异显著(t 检验)。 表 3 不同抗性土沉香叶片对黄野螟生长发育的影响1)
Table 3 Effects of different resistant Aquilaria sinensis leaves on growth and development of Heortia vitessoides
植株 幼虫发育历期/d 1龄 2龄 3龄 4龄 5龄 总计 感虫(对照) 2.8±0.2a 2.7±0.1b 2.3±0.1b 2.5±0.2b 3.7±0.2b 13.4±0.4b 抗1 3.0±0.1a 2.8±0.1b 2.6±0.3a 2.7±0.1a 3.9±0.3b 14.9±0.7a 抗2 2.9±0.1a 3.0±0.2a 2.7±0.1a 2.7±0.2a 4.1±0.2a 15.3±0.3a 植株 幼虫存活率/% 蛹历期/d 蛹体质量/g 成虫寿命/d 蛹羽化率/% 雌虫 雄虫 感虫(对照) 90.56±4.75a 9.8±0.5b 0.183±0.026a 6.4±0.9a 4.9±0.6a 95.56±2.72a 抗1 83.22±3.98ab 15.1±0.9a 0.137±0.031b 5.0±0.6b 4.1±0.4b 91.67±3.49b 抗2 78.31±2.41b 16.5±1.4a 0.128±0.019b 4.3±0.7c 3.7±0.5c 90.00±2.97c 1) 同列数据后凡具有一个相同小写字母者,表示植株间差异不显著(P>0.05,Duncan’s 法)。 -
[1] 黄蜀琼. 中国瑞香科新分类群[J]. 云南植物研究, 1985, 7(3): 277-278. [2] 田耀华, 原慧芳, 倪书邦, 等. 沉香属植物研究进展[J]. 热带亚热带植物学报, 2009, 17(1): 98-104. [3] 吴修仁. 广东药用植物简编[M]. 广州: 广东高等教育出版社, 1989: 307. [4] 冯志舟. 珍稀香料植物: 土沉香[J]. 云南林业, 2010, 31(5): 49-50. [5] 林伟强, 贺立静, 谢正生. 一种值得推广的优良园林树种: 白木香[J]. 广东园林, 2002, 34(4): 38-40. [6] 汪科元. 中药瑰宝: 沉香[M]. 广州: 南方日报出版社, 2005. [7] BARDEN A, ANAK N A, MULLIKEN T, et al. Heart of the matter: Agarwood use and trade and cites implementation for Aquilaria malaccensis[M]. Cambridge: Traffic International, 2000: 24-26.
[8] WU Y, LI E T, LI Y Y, et al. Iriflophenone glycosides from Aquilaria sinensis[J]. Chem Nat Compd, 2016, 52(5): 834-837.
[9] ZHOU M H, WANG H G, SUOLANGJIBA, et al. Antinociceptive and anti-inflammatory activities of Aquilaria sinensis (Lour.) Gilg. leaves extract[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2008, 117(2): 345-350.
[10] MUNROE E. Synopsis of Heortia Lederer, with descriptions of a new species and a new subspecies (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae: Odontiinae)[J]. Can Entomol, 1977, 109(3): 429-441.
[11] 苏跃平. 白木香黄野螟生物学特性[J]. 中药材, 1994, 17(2): 7-9. [12] 陈志云, 李东文, 王玲, 等. 土沉香黄野螟生物学特性研究[J]. 中国植保导刊, 2011, 31(11): 10-14. [13] MOITREYEE S, KARUNA S. Biological control of Heortia vitessoides Moore, the most serious insect defoliator of Aquilaria malaccensis Lamk., a commercially important tree species of Northeast India[J]. Ann Biol Res, 2015, 6(5): 26-32.
[14] 乔海莉, 陆鹏飞, 陈君, 等. 黄野螟生物学特性及发生规律研究[J]. 应用昆虫学报, 2013, 50(5): 1244-1252. [15] 周亚奎, 战晴晴, 卢丽兰, 等. 6种生物农药防治白木香黄野螟幼虫毒力和田间药效[J]. 中国森林病虫, 2016, 35(1): 31-33. [16] 乔海莉, 徐常青, 徐荣, 等. 杀虫灯与诱集植物联合防控白木香黄野螟效果研究[J]. 中国中药杂志, 2016, 41(11): 2025-2029. [17] KALITA J, BHATTACHARYYA P R, NATH S C. Heortia vitessoides Moore (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae): A serious pest of agarwood plant (Aquilaria malaccensis Lamk.)[J]. Geobios, 2001, 29(1): 13-16.
[18] QIAO H L, LU P F, CHEN J, et al. Antennal and behavioural responses of Heortia vitessoides females to host plant volatiles of Aquilaria sinensis[J]. Entomol Exp Appl, 2012, 143(3): 269-279.
[19] WEN Y Z, JIN X F, ZHU C Q, et al. Effect of substrate type and moisture on pupation and emergence of Heortia vitessoides (Lepidoptera: Crambidae): Choice and no-choice studies[J]. J Insect Behav, 2016, 29(4): 473-489.
[20] JIN X F, MA T, CHANG M S, et al. Aggregation and feeding preference of gregarious Heortia vitessoides (Lepidoptera: Crambidae) larvae to Aquilaria sinensis (Thymelaeaceae)[J]. J Entomol Sci, 2016, 51(3): 209-218.
[21] BARMAN H K, NATH R K. Pathogenicity of entomopathogenic fungi, Beauveria bassiana on Heortia vitessoides, a major insect pest of Aquilaria agallocha in Assam[J]. Insect Environ, 2002, 8(2): 79-80.
[22] RISHI R R, PANDEY S. Infectivity of Beauveria bassiana on Herotia vitessoides, a major pest of Aquilaria malaccensis Lamk[J]. Curr Biotica, 2014, 8(3): 300-302.
[23] 朱建国, 况荣平, 杨学均, 等. 猎物条件对七星瓢虫(Coccinella septempunctata L.)捕食作用的影响[J]. 昆虫天敌, 1993, 15(3): 116-123. [24] 张贻礼, 张觉晚, 杨阳, 等. 茶树抗虫品种资源调查及抗性机制研究: Ⅱ: 不同品种茶树特征特性对假眼小绿叶蝉抗性的相关分析[J]. 茶叶通讯, 1994, 21(2): 4-6. [25] 黄亚辉, 张觉晚, 张贻礼, 等. 茶树抗虫品种资源调查及抗性机制研究: Ⅳ: 茶树品种特性对丽纹象甲抗性的相关分析[J]. 茶叶通讯, 1994, 21(4): 5-6. [26] SMITH C M. Plant resistance to arthropods: Molecular and conventional approaches[M]. Netherlands: Springer, 2005: 1-19.
[27] 胡建军, 王克胜, 韩一凡. 林木抗虫育种研究进展[J]. 世界林业研究, 1998, 11(3): 15-21. [28] 朱麟, 古德祥, 吴海昌. 昆虫对植物次生性物质的生态适应机制[J]. 福建林业科技, 1998, 25(2): 59-62. [29] 秦厚国, 叶正襄, 黄水金, 等. 不同寄主植物与斜纹夜蛾喜食程度、生长发育及存活率的关系研究[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2004, 12(2): 40-42. [30] 吴坤君, 李明辉. 棉铃虫营养生态学的研究: 食物中糖含量的影响[J]. 昆虫学报, 1992, 35(1): 47-52.





 下载:
下载: