Effects of light intensity during internode elongation on rice lodging resistance and its mechanism
-
摘要:目的
探讨拔节期光强对水稻Oryza sativa L.抗倒伏能力的影响。
方法通过人工气候箱光强控制试验,在基部第1、第2、第3节间伸长期及第1~3节间伸长期进行不同光强处理,测定水稻茎秆倒伏指数和基部节间的形态和材料力学性状。
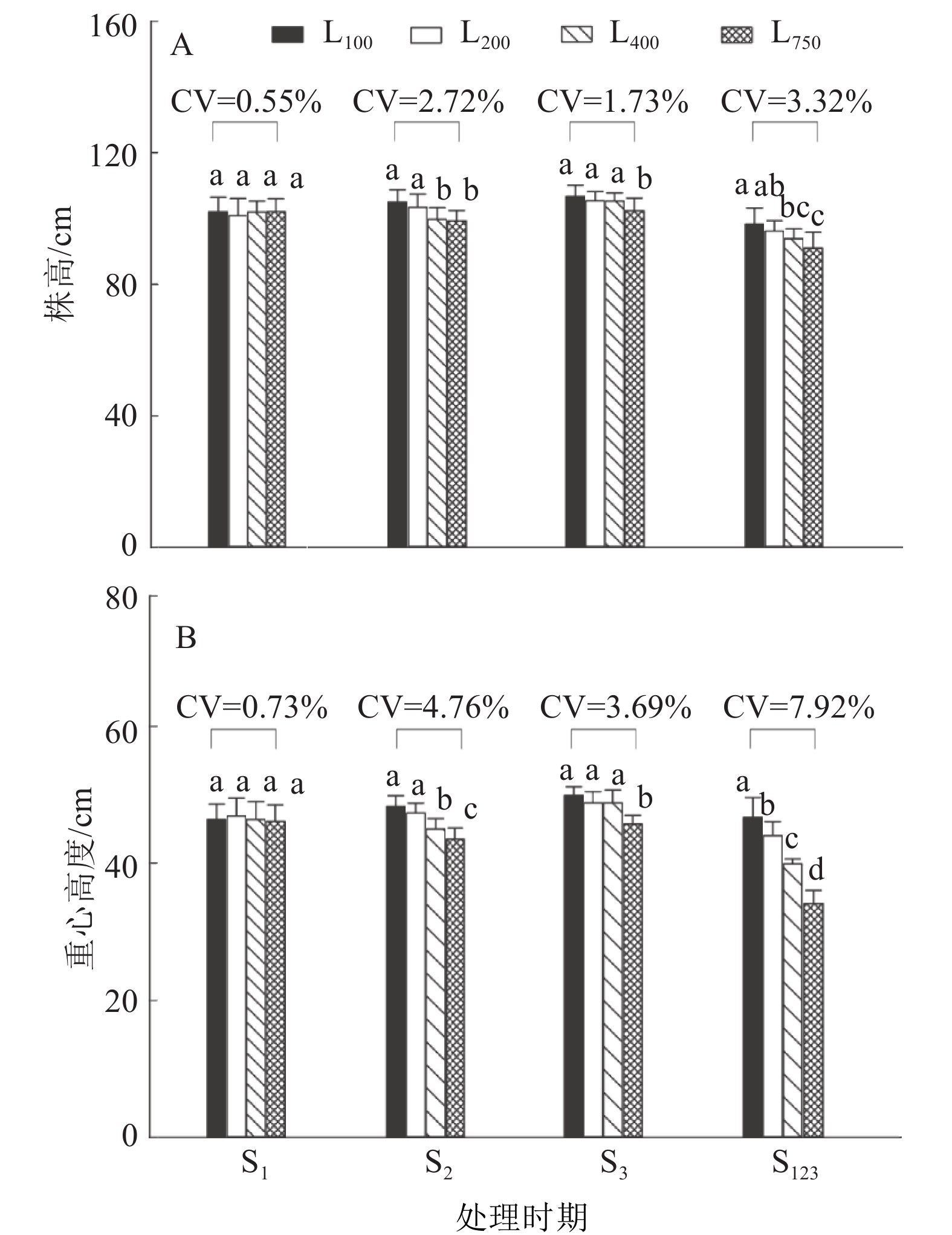
结果倒伏指数随着光强增加显著下降。在第1~3节间伸长期连续用中、高光强处理,茎秆倒伏指数比低光强处理降低34.8%~73.9%。倒伏指数与节间长度呈极显著正相关,与节间粗度、茎壁厚度和节间充实度呈显著负相关。第2节间伸长期是茎秆抗倒伏能力对光强反应最敏感的时期。光强对水稻抗倒伏能力的影响有累积效应。第1~3节间伸长期连续处理条件下,倒伏指数和多数形态、材料力学性状的变异系数高于单个节间伸长期处理。
结论节间长度、茎壁厚度和节间充实度是影响茎秆抗倒伏性的关键因子。光强改变了节间长度、单位体积节间干质量和茎壁厚度等形态特性,进而影响茎秆抗折力和弯曲力矩等材料力学性状,最终影响水稻抗倒伏能力。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo explore the effects of light intensity during internode elongation on rice (Oryza sativa L.) lodging resistance.
MethodRice plants were subjected to different light intensities in phytotrons at the 1st (S1), 2nd (S2), 3rd (S3) and 1st to 3rd (S123) internode elongation stages. The lodging resistance of rice stem and the morphological and material mechanical traits of basal internodes were measured.
ResultThe lodging index (LI) of rice stem significantly decreased with the increasing of light intensity. LI of medium or high light intensity treatments was 34.8%–73.9% lower than that of low light intensity treatment at the S123 internodes elongation stage. LI was significantly positively correlated with internode length, and negatively correlated with internode diameter, culm wall thickness and internode plumpness. The S2 stage was the most sensitive period of lodging resistance to light intensity variation. Light intensity had accumulative effects on lodging resistance. The variation coefficient of lodging index at the S123 stage was greater than those at the S1, S2 and S3 stages, and similar results were found in most morphological and material mechanical traits.
ConclusionThe key factors to determine the lodging resistance are internode length, culm wall thickness and internode plumpness. Light intensity can significantly change the three morphological traits of basal internodes, which further affect the material mechanical characteristics of rice stem and lodging resistance.
-
目前,我国食糖生产成本过高、蔗糖产业国际竞争力十分低下、糖价大大高于国际标准[1],巴西、美国等进口蔗糖的到岸价比我国蔗糖的完税价要低8到10个百分点[2]。造成这一情况的主要原因是我国大部分蔗区的生产收获基本靠人工作业,甘蔗收获机械化程度低。断尾除叶作为甘蔗收获的关键环节,是制约甘蔗收获机械发展的瓶颈[3]。甘蔗断尾是刚性体(机械)和柔性体(甘蔗尾茎)相互作用的过程[4],现阶段研究[5-9]通常是根据经验估算从而进行断尾机构的设计研究,对甘蔗尾茎力学特性的分析很少,难以从本质上揭示甘蔗断尾的机理。因此,研究甘蔗尾茎的力学特性对于甘蔗断尾机械的设计开发、建立虚拟蔗尾模型进行断尾动力学仿真及有限元分析是非常必要的。在甘蔗尾茎的力学特性研究中,泊松比参数是不可或缺的,它是建立甘蔗茎秆力学模型和虚拟仿真模型的必要参数之一[10]。鲜见明确的测定甘蔗尾茎泊松比的方法[11-12],构建甘蔗力学模型时所需的泊松比参数是根据横观各向异性材料力学公式及甘蔗尾茎各组分弹性模量推导得出[10],或者部分泊松比参数根据农业生物力学由其他物料泊松比比拟得出[13]。由于误差的累加以及各种农业物料的微观结构的差异,以上方法间接得到的甘蔗泊松比参数会产生较大误差[14],而用电测法直接试验得到泊松比参数,过程大为简化,可缩短科研周期[15]。
本研究借鉴竹子、苜蓿秆、苎麻、玉米等茎秆类作物的力学分析方法[16-21],结合甘蔗茎秆力学特性与复合材料力学理论,建立甘蔗尾茎力学模型;借鉴对农林作物泊松比的相关研究[22-25],将电测法试验与理论分析相结合,确立甘蔗尾茎的泊松比参数,以期为深入研究甘蔗断尾机理提供理论基础。
1. 甘蔗尾茎结构及力学模型
1.1 甘蔗尾茎结构特点
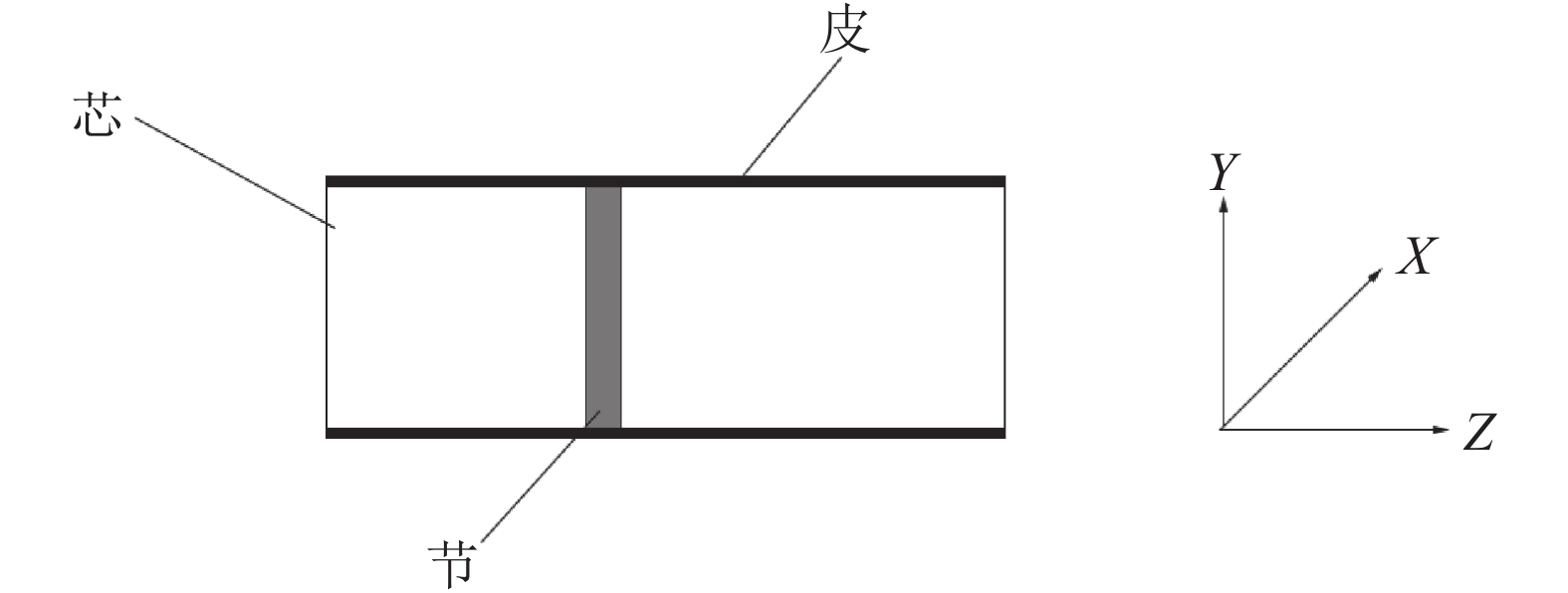
甘蔗属于实芯秸秆类植物,内部有明显的芯结构,且不同部位具有不同的结构特点。甘蔗尾茎的横截面近似圆形,横截面由内到外分为甘蔗芯和甘蔗皮2部分,蔗茎由若干节和节间组成。甘蔗皮特点是细胞小,排列紧密;甘蔗芯有许多纤维状结构,这些纤维沿轴向整齐排列;甘蔗节的纤维结构较甘蔗芯紧密。因此甘蔗茎秆在微观结构上不连续,并且在空间排列上具有明显的方向性。成熟期蔗茎尾梢被叶鞘包裹,以生长点以下约1~5节包裹最为紧密,这部分蔗尾含糖极少,脆弱易断,前期试验证明蔗尾茎生长点以下1~5节的抗弯强度明显低于6~9节的抗弯强度,差异极显著,蔗尾在第5节位置断裂,可以将甘蔗尾部5~6片包裹紧密的青叶连同茎秆尾梢部分一起断除,大大降低剥叶难度,有效提高原料蔗的质量[26-28]。所以建立甘蔗材料模型进行断尾动力学研究的时候,可将甘蔗整秆简化为蔗尾部分和蔗身部分,中间是蔗节连接,蔗尾部分和蔗身部分及蔗节部分力学性能差异很大,本研究将蔗尾生长点以下第5节的力学参数作为蔗尾部分力学参数,第6节的力学参数作为蔗身部分的力学参数。
1.2 甘蔗尾茎力学模型
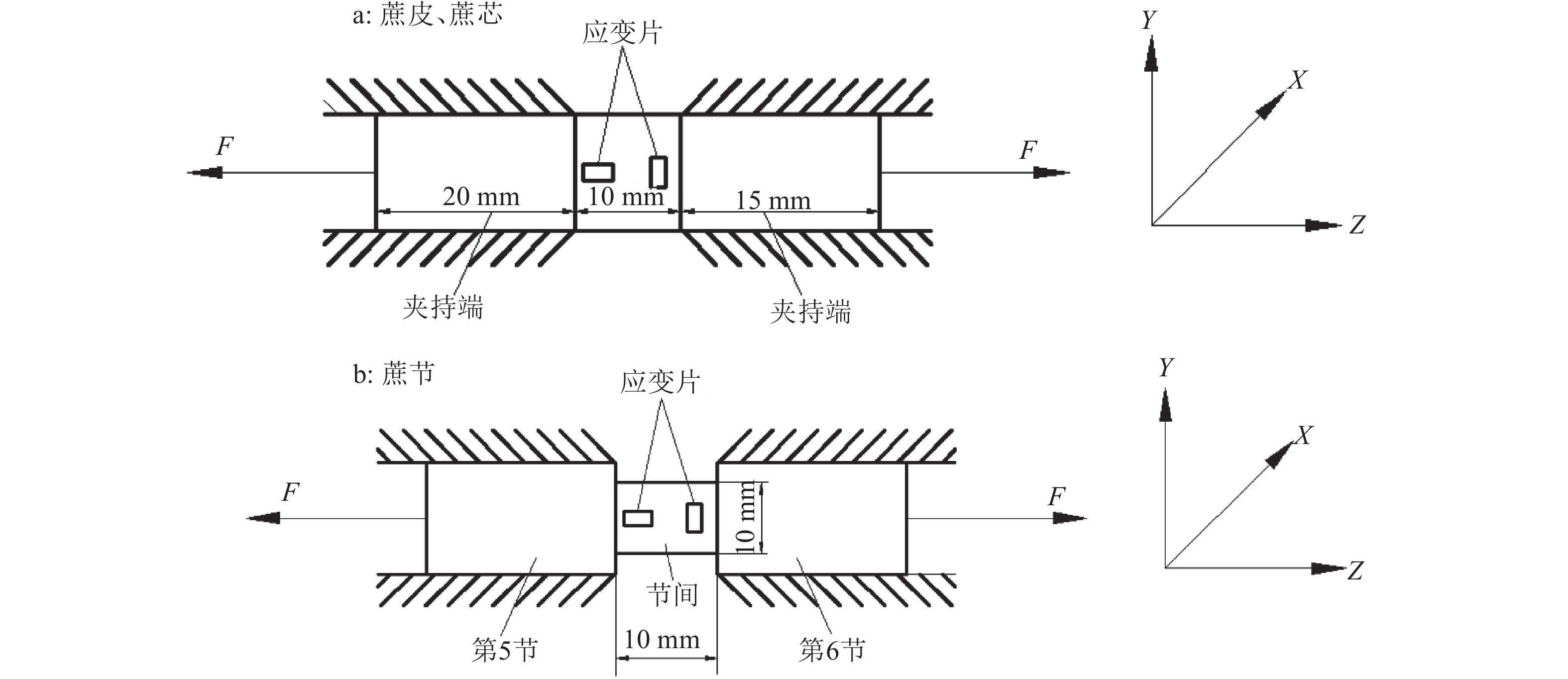
甘蔗尾茎皮、芯、节3部分可以抽象为具有正交各向异性,且横观各向同性的材料[29-30],该材料的结构沿轴向对称,忽略甘蔗节径向尺寸的细微差异,可将甘蔗尾茎试样视为类似圆柱体的几何形状;甘蔗尾茎分别由甘蔗皮、甘蔗芯和甘蔗节3种不同材质组成,各材质的纤维均沿轴向整齐排列,建立如图1所示坐标系,沿甘蔗尾茎轴向建立 Z轴,沿甘蔗尾茎径向分别建立X轴和Y轴。
1.3 甘蔗尾茎泊松比参数的确立
根据复合材料力学理论,甘蔗尾茎各组分泊松比可由9个工程弹性参数来表征,分别为甘蔗皮同性平面泊松比
$ \mu _{{}_{{\rm 1}XY}}$ ;甘蔗皮异性平面泊松比$\mu _{{}_{{\rm 1}XZ}} $ 、$ \mu _{{}_{{\rm 1}YZ}}$ ;甘蔗芯同性平面泊松比$\mu _{{}_{{\rm 2}XY}} $ ;甘蔗芯异性平面泊松比$ \mu _{{}_{{\rm 2}XZ}}$ 、$\mu _{{}_{{\rm 2}YZ}} $ ;甘蔗节轴向泊松比$ \mu _{{}_{{\rm 3}XY}}$ ;甘蔗节径向泊松比$ \mu _{{}_{{\rm 3}XZ}}$ 、$ \mu _{{}_{{\rm 3}YZ}}$ 。根据甘蔗几何形状的假定以及上述推论,甘蔗尾茎属于特殊的复合材料,正交各向异性,且甘蔗尾茎横截面具有横观各向同性的特点,其各组分泊松比参数满足式(1)[31]。
$$ \left\{ \begin{aligned} &{\mu _{{}_{iXZ}}} = {\mu _{{}_{iYZ}}}\\ &{\mu _{{}_{iXY}}} = \displaystyle\frac{{{E_{{}_{iX}}}}}{{2{G_{{}_{iXY}}}}} - 1 \end{aligned} \right. \text{,}$$ (1) 式中,E为弹性模量,MPa;G为剪切模量,MPa;X、Y和Z分别为3个坐标轴方向;i=1, 2, 3分别代表甘蔗皮、甘蔗芯和甘蔗节。
采用电测法,设计专门夹具来测量甘蔗尾茎各组分轴向拉伸泊松比,由试验得出甘蔗尾茎各组分横向应变(
$\varepsilon' $ )和纵向应变($\varepsilon $ ),根据式(2)计算出各组分轴向泊松比[32]。$$ \mu {\text{ = |}}\frac{\varepsilon' }{\varepsilon }{\text{|}}\text{。} $$ (2) 最后根据复合材料力学中关于正交各向异性材料的泊松比关系式(3),结合甘蔗各组分径向拉伸弹性模量、各组分轴向拉伸弹性模量和各组分异性平面泊松比所得数据,确定甘蔗各组分径向泊松比参数。
$$ {\mu _{{}_{iXY}}} < \frac{{E_{iX}^2}}{{2\mu _{iYZ}^2E_{iZ}^2}}\;\;\;\;\text{。} $$ (3) 2. 力学试验
2.1 试验材料
WD-E精密型微控电子式万能试验机;YJ-4501A/SZ静态数字电阻应变仪;辅助测试工具包括砝码、游标卡尺、直尺、兆欧表、电烙铁、砂轮机等。
本试验根据甘蔗尾茎的结构特点设计专用夹具(图2),该夹具主要由支座、压块、螺栓等组成。为使甘蔗各组分样本受力均匀,得到较为准确的试验数据,将甘蔗各组分样本制成规则矩形,并在压块和支座上加工有凹槽,上面有斜纹滚花,以增大摩擦。
试验材料为成熟期甘蔗粤糖159,采自广东省广前糖业发展有限公司前进农场,采样时间为2016年1月。将甘蔗尾梢相互重叠的青叶剥除干净,取蔗尾茎顶端生长点以下第5节和第6节制作试验样本。
2.2 方法
2.2.1 拉伸试验
将甘蔗第5节和第6节的甘蔗皮和甘蔗芯制成长60 mm、宽10 mm、厚2 mm的样本,两端夹持尺寸分别为20和15 mm,中间留10 mm标距粘贴应变片,应变片粘贴方法如图3a所示;将甘蔗第5节和第6节中间的蔗节部位制成如图3b所示试样,两端蔗身用于夹具夹持,蔗节部位开槽后长宽高均为10 mm,用于粘贴应变片,沿着试样的轴向进行拉伸试验。试验时为避免拉伸速率太慢,出现滑移现象并造成数据错误,经过测试对比,本试验拉伸速率设定为5 mm·min–1。
为避免甘蔗试样在夹紧的过程中发生滑移和破坏,试验样本在装夹部位用纱布、胶水和橡胶手套固紧。为保证拉伸试验的准确性,防止试样表面不平而引起的应力集中,在拉伸试验前用砂轮机将试验样本装夹表面磨平,并用石蜡抹平试样装夹表面的凹凸处。
2.2.2 泊松比的提取
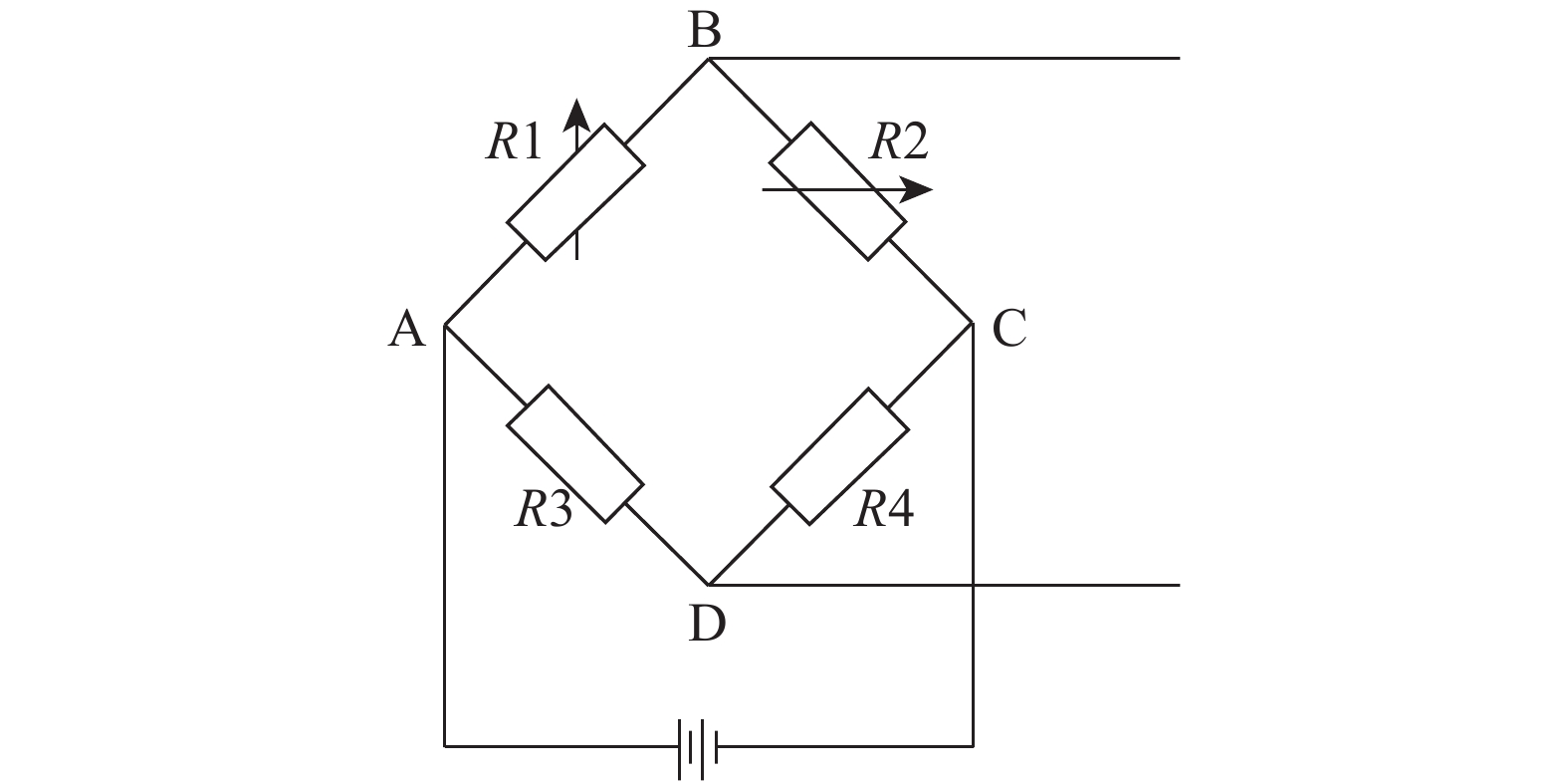
为了获得较为精确的泊松比数值,每个试样在进行拉伸试验前都要用兆欧表进行绝缘检查,防止应变片与样本短路。YJ-4501A/SZ静态数字电阻应变仪采用半桥测量电路[33],外接2个固定电阻,电阻应变片的贴片及接桥方式如图4所示。试验时用2台电阻应变仪分别测量试样的横向应变和轴向应变,运用公式算出试样泊松比,防止切换测量通道时引起的测量误差。同一部位的样本做20个试样,去除试验过程中不可抗力因素引起的失败样品,最后取15个成功试样进行统计分析,得出不同组分的泊松比参数值。统计公式如下:
$$ {\mu _{{}_0}} = \frac{1}{n}\sum\limits_{i = 1}^n {(\frac{{\varepsilon {'_i}}}{{{\varepsilon _i}}}} )\;\;\;\;\;\;, $$ (4) 式中,μ0为泊松比;n为取样数;εi'为横向应变;εi为轴向应变。
2.3 试验结果与分析
2.3.1 轴向拉伸泊松比
对甘蔗皮、芯、节的15组试样进行轴向拉伸试验,为保证结果的准确性,分别在10、20、30、40、50 g载荷下测量样本泊松比,最后取其平均值,第5、6节甘蔗皮的泊松比为0.233±0.073和0.238±0.051;第5、6节甘蔗芯的泊松比为0.271±0.045和0.289±0.049;第5、6节间甘蔗节的泊松比为0.344±0.086。
2.3.2 甘蔗尾茎各组分泊松比
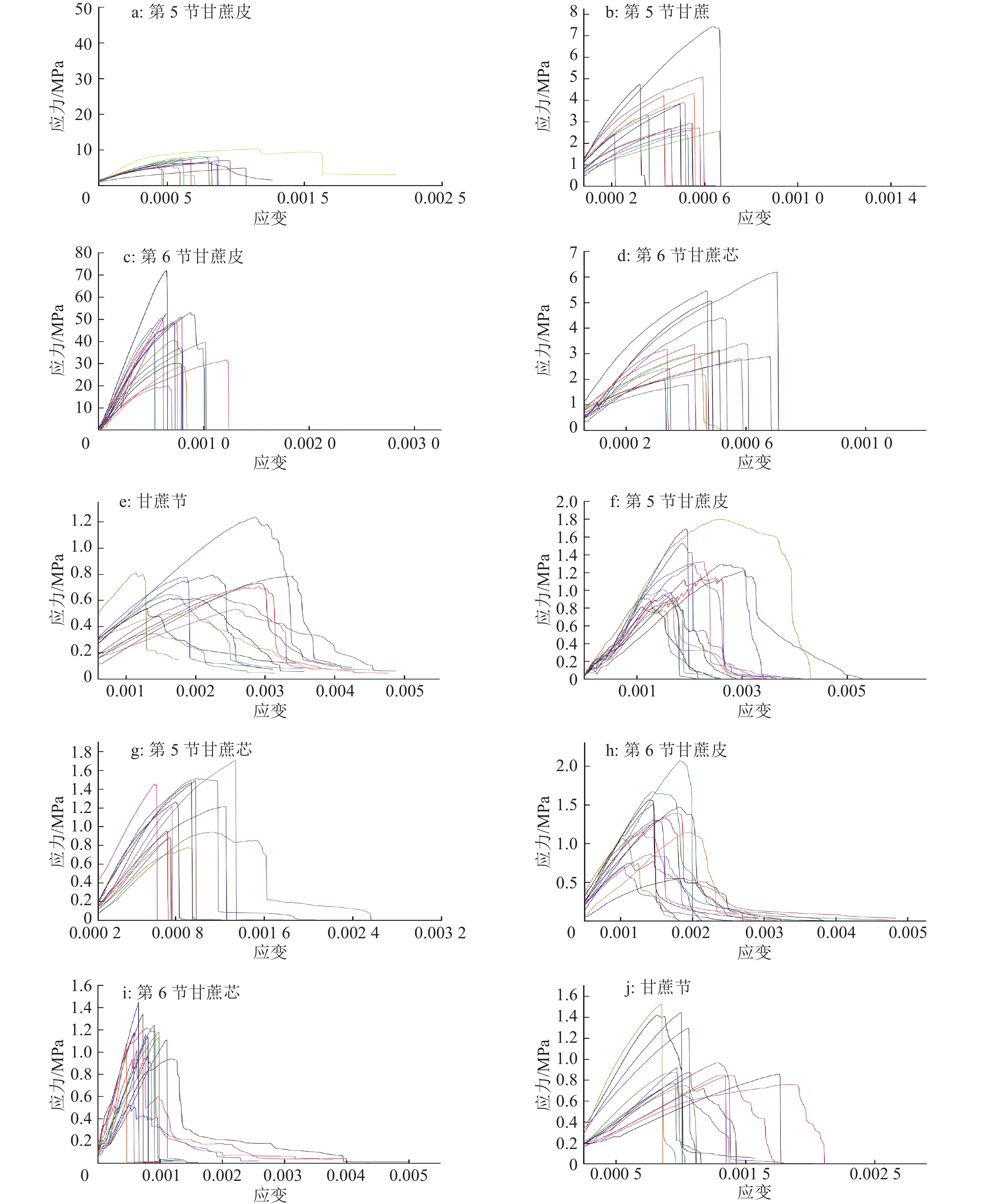
采用WD-E精密型微控电子式万能试验机分别对甘蔗第5、6节各组分的15个试样进行轴向和径向拉伸试验,并在万能试验机上得到试样的载荷–位移曲线。为消除尺寸的影响,将试验机上的载荷–位移曲线转化为应力–应变曲线,如图5所示。
载荷、位移、应力和应变相互转化关系见以下公式:
$$ \sigma = \frac{P}{A}, $$ (5) $$ E = \frac{{{\rm d}\sigma }}{{{\rm d}\varepsilon }}, $$ (6) $$ \varepsilon = \frac{{\Delta L}}{L}, $$ (7) $$ {\sigma _{\max }} = \frac{{{P_{\max }}}}{A}, $$ (8) 式(5)~(8)中,σ为应力,MPa;P为拉伸载荷,N;A为断面面积,mm2;ε为应变;∆L为伸长量,mm;L为标距原始长度,mm;σmax为抗拉强度,MPa;Pmax为最大拉伸载荷,N。
运用SPSS软件对上述应力–应变曲线进行最小二乘法拟合分析,求取甘蔗尾茎各组分弹性模量平均值得到如下结果:第5节甘蔗皮和甘蔗芯的径向弹性模量分别为6.90和14.30 MPa,相应的轴向弹性模量分别为124.97和89.55 MPa;第6节甘蔗皮和甘蔗芯的径向弹性模量分别为8.14和15.95 MPa,相应的轴向弹性模量分别为705.93和82.66 MPa;第5、6节间甘蔗节的径向弹性模量为63.87 MPa,轴向弹性模量为237.58 MPa。
从图5可以看出,部分应力-应变曲线差异较大,分析其原因主要是:甘蔗各样本结构尺寸差异大,要制作统一的样本很困难;各样本含水率对试验的结果影响很大,样品含水率的差异使应力-应变曲线差异较大;甘蔗自身组织结构的差异,导致试验结果存在较大差异,已有研究证明蔗尾茎秆的力学性能与其微观组织结构有关[34];试验加载速率也会对试验结果产生影响。
将甘蔗皮、甘蔗芯及蔗尾茎第5、6节各组分轴向弹性模量和径向弹性模量代入式(3)得各组分同性面的泊松比,第5节甘蔗同性面芯和皮泊松比分别小于0.174和0.028;第6节甘蔗同性面芯和皮泊松比分别小于0.223和0.001。甘蔗节同性面泊松比小于0.305。综合试验和计算所到的泊松比参数,结合式(1),可得甘蔗尾茎各组分泊松比,如表1所示。
表 1 甘蔗尾茎各组分泊松比参数Table 1. Poisson’s ratio parameters of each part of sugarcane tail stalk组分 同性面泊松比(μXY) 异性面泊松比(μYZ) 异性面泊松比(μXZ) 第5节 第6节 第5节 第6节 第5节 第6节 甘蔗皮 <0.028 <0.001 0.233 0.238 0.233 0.238 甘蔗芯 <0.174 <0.223 0.271 0.289 0.271 0.289 甘蔗节 <0.305 0.344 0.344 运用SPSS软件对第5、6节的甘蔗皮、芯试样的同性面泊松比和异性面泊松比分别进行独立样本t检验,分析蔗尾顶端生长点以下5、6节各组分泊松比的差异显著性。分析结果表明:第5、6节的甘蔗皮和芯试样同性面泊松比,P<0.01,由此可以认为第5、6节的甘蔗皮和甘蔗芯的同性面泊松比差异均显著;第5、6节甘蔗皮和芯试样异性面泊松比,P分别为0.096和0.012,由此可以认为第5、6节的甘蔗皮和甘蔗芯的异性面泊松比差异均不显著。
分别对甘蔗第5、6节不同节位各组分对应参数进行单因素方差分析(表2)。从表2可以看出,甘蔗皮同性面泊松比的P=0<0.05,甘蔗芯同性面泊松比的P=0.041<0.05,表明在95%的置信区间内,第5、6节不同节位各组分的同性面泊松比参数有显著差异;甘蔗皮异性面泊松比的P=0.791>0.05,甘蔗芯异性面泊松比的P=0.324>0.05,表明在95%的置信区间内,第5、6节不同节位各组分的异性面泊松比参数差异不显著。分析结果表明,甘蔗尾茎各组分的泊松比参数不一致,差异显著;甘蔗芯部同性面泊松比参数比甘蔗皮部大0.145,在一定范围内,甘蔗从表皮到内部泊松比逐渐变大,说明在建立甘蔗尾茎材料模型的时候,甘蔗皮、芯应视为完全不同的材料,可简化为由皮、芯2种单向复合材料组合而成的复杂复合材料,蔗皮与芯部存在结合力[35]。第5、6节不同节位的各组分泊松比力学参数存在明显差异,证明将蔗尾模型简化为蔗尾部分和蔗身部分,蔗尾生长点以下第5节的力学参数作为蔗尾部分力学参数,第6节的力学参数作为蔗身部分的力学参数这一假设的正确性。
表 2 甘蔗节位对泊松比参数影响方差分析Table 2. Variance analysis of Poisson’s ratio parameters affected by different sugarcane nodes性状 差异来源 平方和 自由度 均方 F P1) 甘蔗皮同性面泊松比 组间 0.009 1 0.009 34.188 0.000** 组内 0.008 28 0.000 总和 0.017 29 甘蔗皮异性面泊松比 组间 0.000 1 0.000 0.072 0.791 组内 0.110 28 0.004 总和 0.110 29 甘蔗芯同性面泊松比 组间 0.024 1 0.024 4.142 0.041* 组内 0.164 28 0.006 总和 0.188 29 甘蔗芯异性面泊松比 组间 0.002 1 0.002 1.008 0.324 组内 0.063 28 0.002 总和 0.065 29 1) *和**分别表示在 0.05、0.01 水平差异显著。 3. 结论
运用复合材料力学理论假定甘蔗力学模型,采用电测法代替传统的比拟法测量分析获得甘蔗各组分试样的横纵向变形量,得到较为准确的甘蔗第5、6节各组分泊松比参数值。
试验得到甘蔗尾茎生长点以下第5节甘蔗皮同性面泊松比小于0.028,异性面泊松比为0.233;第5节甘蔗芯同性面泊松比小于0.174,异性面泊松比为0.271;甘蔗生长点以下第6节甘蔗皮同性面泊松比小于0.001,异性面泊松比为0.238;第6节甘蔗芯同性面泊松比小于0.223,异性面泊松比为0.289;甘蔗节同性面泊松比小于0.305,异性面泊松比为0.344。甘蔗尾茎内部不同部位的同性面泊松比有显著差异,异性面泊松比差异不大;甘蔗芯部同性面泊松比参数比甘蔗皮部大0.145。试验结果表明,在一定范围内,甘蔗从表皮到内部泊松比逐渐变大。甘蔗尾茎第5、6节不同节位的皮、芯同性面泊松比参数有显著差异;第5、6节不同节位的皮、芯异性面泊松比参数差异不显著。甘蔗第5节皮部同性面泊松比参数比第6节大0.027,第5节芯部同性面泊松比参数比第6节小0.050。本研究可为甘蔗断尾机构的设计及数学模型的建立进行动力学仿真提供理论基础。
-
表 1 不同光强处理下水稻茎秆的倒伏指数1)
Table 1 The lodging index of rice stem under different light intensity treatments
光照度 不同处理时期的倒伏指数 S1 S2 S3 S123 L100 115.9 a 119.8 a 108.6 a 127.4 a L200 103.0 a 90.5 b 99.5 ab 83.1 b L400 84.2 a 72.3 c 90.1 bc 33.3 b L750 81.8 a — 78.9 c — CV/% 16.8 25.5 13.5 57.9 1) S1、S2 和 S3 分别表示从基部向上第 1 、第 2 和第 3 节间伸长期,S123 表示第 1 至第 3 节间伸长期;L100、L200、L400 和 L750 分别表示光照度水平为 100、200、400 和 750 μmol·m–2·s–1;“—” 表示因节间长度小于 4 cm 而未能测量;同列数据后凡是有一个相同小写字母者,表示差异不显著 (P>0.05,LSD 法)。 表 2 不同光强处理下水稻植株基部节间长度、茎壁厚度和节间粗度1)
Table 2 The basal internode length, culm wall thickness and basal internode diameter of rice plant under different light intensity treatments
处理时期 光处理 基部节间长度/cm 茎壁厚度/mm 节间粗度/mm I1 I2 I3 I1 I2 I3 I1 I2 I3 S1 L100 3.50 a 3.83 a 9.57 c 1.01 c 0.84 b 0.78 a 6.36 b 6.19 b 6.00 a L200 2.83 b 4.13 a 10.80 b 1.07 b 0.92 a 0.73 b 6.63 a 6.58 a 5.81 a L400 2.73 b 3.85 a 11.60 b 1.11 ab 0.95 a 0.74 b 6.75 a 6.60 a 5.79 a L750 2.58 b 4.27 a 12.70 a 1.13 a 0.97 a 0.72 b 6.78 a 6.62 a 5.74 a S2 L100 3.38 a 6.27 a 7.67 c 1.09 a 0.81 c 0.72 c 6.52 a 5.95 b 5.50 c L200 3.49 a 4.76 b 9.04 ab 1.08 a 0.87 b 0.74 bc 6.65 a 6.14 ab 5.78 b L400 3.26 a 4.28 c 8.88 b 1.12 a 0.91 b 0.76 b 6.67 a 6.33 a 5.92 b L750 2.97 a 3.58 d 9.68 a 1.14 a 0.97 a 0.79 a 6.67 a 6.36 a 6.22 a S3 L100 3.33 a 5.80 a 10.90 a 1.09 a 0.86 a 0.69 b 6.62 a 6.07 a 5.36 a L200 3.33 a 5.24 a 9.98 b 1.10 a 0.90 a 0.75 a 6.55 a 6.07 a 5.59 a L400 3.41 a 5.31 a 9.21 c 1.09 a 0.86 a 0.73 a 6.71 a 6.11 a 5.53 a L750 3.01 a 5.16 a 8.38 d 1.13 a 0.88 a 0.74 a 6.49 a 6.02 a 5.41 a S123 L100 3.57 a 6.13 a 6.78 a 1.01 c 0.74 d 0.66 d 6.22 c 5.92 c 5.31 c L200 2.71 b 3.48 b 7.47 a 1.07 b 0.91 c 0.76 c 6.48 b 6.31 b 5.66 b L400 3.12 ab 3.61 b 8.48 a 1.13 ab 0.98 b 0.83 b 6.89 a 6.53 ab 5.85 b L750 2.72 b 2.83c 7.62 a 1.17 a 1.09 a 0.91 a 7.07 a 6.76 a 6.40 a S1 CV/% 14.00 5.37 11.70 4.90 6.21 3.54 2.89 3.17 1.95 S2 CV/% 6.84 24.10 9.52 2.49 7.57 3.97 1.09 3.07 5.12 S3 CV/% 5.42 5.36 11.30 1.72 2.19 3.62 1.44 0.61 1.94 S123 CV/% 13.50 36.20 11.30 6.39 15.80 13.40 5.79 5.60 7.84 1) S1、S2 和 S3 分别表示从基部向上第 1 、第 2 和第 3 节间伸长期,S123 表示第 1 至第 3 节间伸长期;L100、L200、L400 和 L750 分别表示光照度水平为 100、200、400 和 750 μmol·m–2·s–1;CV 为不同光强处理下的变异系数;I1、I2、I3 表示第 1、第 2 和第 3 节间;相同处理时期、同列数据后凡是有一个相同小写字母者,表示差异不显著 (P>0.05,LSD 法)。 表 3 不同光强处理的基部节间干质量、单位长度节间干质量和单位体积节间干质量1)
Table 3 The dry weight, dry weight per unit length and dry weight per unit volume of basal internode under different light intensity treatment
处理时期 光处理 节间干质量/g 单位长度节间干质量/(mg·cm–1) 单位体积节间干质量/(mg·cm–3) I1 I2 I3 I1 I2 I3 I1 I2 I3 S1 L100 0.181 a 0.168 b 0.259 a 52.1 a 45.5 a 28.0 a 307.3 a 318.5 a 217.5 a L200 0.175 a 0.217 a 0.295 a 63.7 a 54.7 a 27.5 a 339.7 a 330.0 a 233.4 a L400 0.166 a 0.182 b 0.263 a 61.0 a 47.8 a 22.8 ab 309.6 a 281.9 ab 193.5 ab L750 0.142 a 0.165 b 0.228 a 55.2 a 40.4 a 18.1 b 275.5 a 235.7 b 158.6 b S2 L100 0.148 b 0.185 b 0.158 c 45.6 b 29.9 c 20.6 b 243.1 b 223.8 c 189.6 a L200 0.199a 0.204 ab 0.210 b 58.1 a 43.9 b 23.6 ab 306.5 a 300.4 b 200.0 a L400 0.214 a 0.233 a 0.244 a 68.7 a 56.1 a 28.2 a 351.9 a 360.6 a 227.0 a L750 0.199 a 0.199 b 0.243 a 68.8 a 56.3 a 25.3 a 346.9 a 341.6 ab 187.1 a S3 L100 0.169 b 0.193 b 0.219 ab 52.2 b 34.4 b 20.1 b 283.0 b 245.9 b 203.6 bc L200 0.161 b 0.174 b 0.198 b 49.7 b 34.4 b 19.9 b 266.3 b 232.1 b 175.3 c L400 0.234 a 0.246 a 0.253 a 70.8 a 48.3 a 27.8 a 365.8 a 333.0 a 251.6 a L750 0.167 b 0.198 b 0.196 b 57.5 b 39.1 b 23.6 b 302.6 b 271.1 b 217.3 b S123 L100 0.188 b 0.204 b 0.184 b 53.4 b 33.5 c 27.1 b 320.7 b 275.0 b 273.0 a L200 0.201 b 0.217 b 0.318 a 76.3 a 65.1 b 43.3 a 420.2 a 415.7 a 363.3 a L400 0.263 a 0.270 a 0.334 a 84.4 a 75.6 ab 41.4 a 413.5 a 442.5 a 312.7 a L750 0.227 ab 0.230 ab 0.340 a 83.1 a 81.5 a 47.0 a 382.8 a 418.2 a 299.0 a S1 CV/% 10.5 14.4 10.9 9.1 12.6 19.2 8.5 14.6 16.2 S2 CV/% 17.2 8.5 17.8 18.3 26.8 13.0 16.1 19.8 9.1 S3 CV/% 17.5 16.8 10.9 16.4 16.8 16.0 14.3 16.5 15.0 S123 CV/% 14.4 12.8 25.8 19.4 33.5 22.0 11.8 19.7 12.2 1) S1、S2 和 S3 分别表示从基部向上第 1 、第 2 和第 3 节间伸长期,S123 表示第 1 至第 3 节间伸长期;L100、L200、L400 和 L750 分别表示光照度水平为 100、200、400 和 750 μmol·m–2·s–1;CV 为不同光强处理下的变异系数;I1、I2、I3 表示第 1、第 2 和第 3 节间;相同处理时期、同列数据后凡是有一个相同小写字母者,表示差异不显著 (P>0.05,LSD 法)。 表 4 不同光强处理的基部节间抗折力、弹性模量、弯曲力矩和抗弯刚度1)
Table 4 The breaking resistance, elastic modulus, bending moment and bending stiffness of basal internode under different light intensity treatment
处理时期 光处理 抗折力/N 弹性模量/GPa 弯曲力矩/(cm·g) 抗弯刚度/(10–3 N·m2) I2 I3 I2 I3 I2 I3 I2 I3 S1 L100 18.0 a 13.8 a 3.56 a 1.59 a 1 965.7 a 1 830.3 a 188.1 a 69.9 a L200 19.9 a 14.7 a 4.75 a 1.90 a 1 876.0 a 1 729.7 a 306.1 a 76.0 a L400 22.7 a 14.0 a 6.72 a 1.40 a 1 919.4 a 1 778.1 a 445.5 a 53.5 a L750 22.4 a 12.6 a 6.63 a 1.36 a 1 847.4 a 1 695.2 a 429.7 a 48.6 a S2 L100 17.2 b 14.2 a 8.55 a 4.88 a 2 030.0 a 1 819.8 a 414.0 a 162.7 a L200 21.9 a 13.4 a 4.91 a 2.17 b 1 947.7 ab 1 780.7 a 253.4 a 82.5 b L400 23.2 a 15.3 a 6.21 a 2.40 b 1 791.0 b 1 642.2 a 361.0 a 102.0 b L750 — 14.7 a — 1.61 b 1 814.1 b 1 684.9 a — 81.8 b S3 L100 17.0 b 11.2 c 9.31 a 2.54 a 1 833.9 a 1 647.6 a 459.4 a 71.6 b L200 20.3 bc 14.5 b 6.43 a 2.97 a 1 921.6 a 1 743.7 a 308.1 a 99.2 ab L400 21.7 ab 16.0 ab 7.34 a 4.02 a 1 934.5 a 1 750.6 a 355.2 a 129.6 a L750 23.9 a 18.1 a 6.78 a 3.16 a 1 863.3 a 1 695.7 a 334.5 a 99.2 ab S123 L100 14.6 b 10.8 c 5.46 a 3.50 a 1 805.9 a 1 616.8 a 240.5 a 100.3 a L200 22.4 ab 17.9 b 3.63 a 1.05 b 1 774.5 a 1 653.7 a 184.4 a 36.2 b L400 30.5 a 20.3 ab 4.04 a 1.33 b 790.1 c 696.0 c 250.2 a 55.9 ab L750 — 23.6 a — 1.10 b 1 463.3 b 1 361.7 b — 69.1 ab S1 CV/% 10.7 6.3 28.3 15.8 2.7 3.3 35.1 21.0 S2 CV/% 15.2 5.6 28.1 52.4 6.0 4.8 23.9 35.6 S3 CV/% 14.0 19.4 17.2 19.6 2.5 2.8 18.2 23.7 S123 CV/% 35.3 29.9 21.9 67.4 32.3 33.3 15.8 41.2 1) S1、S2 和 S3 分别表示从基部向上第 1 、第 2 和第 3 节间伸长期,S123 表示第 1 至第 3 节间伸长期;L100、L200、L400 和 L750 分别表示光照度水平为100、200、400 和 750 μmol·m–2·s–1;CV 为不同光强处理下的变异系数;I2 和 I3 表示第 2 和第 3 节间;“—” 表示因节间长度小于 4 cm 而未能测量;相同处理时期、同列数据后凡是有一个相同小写字母者,表示差异不显著 (P>0.05,LSD 法)。 -
[1] ISLAM M S, PENG S B, VISPERAS R M, et al. Lodging-related morphological traits of hybrid rice in a tropical irrigated ecosystem[J]. Field Crops Res, 2007, 101: 240-248.
[2] SETTER T L, LAURELES E V, MAZAREDO A M. Lodging reduces yield of rice by self-shading and reductions in canopy photosynthesis[J]. Field Crops Res, 1997, 49: 95-106.
[3] 申广勒, 石英尧, 黄艳玲, 等. 水稻抗倒伏特性及其与茎秆性状的相关性研究[J]. 中国农学通报, 2007, 23: 58-62. [4] ZHANG W J, WU L M, WU X R, et al. Lodging resistance of japonica rice (Oryza Sativa L.): Morphological and anatomical traits due to top-dressing nitrogen application rates[J]. Rice, 2016, 9: 1-11.
[5] ZHANG J, LI G, SONG Y, et al. Lodging resistance characteristics of high-yielding rice populations[J]. Field Crops Res, 2014, 161: 64-74.
[6] 陈友订, 万邦惠, 张旭. 华南双季超高产水稻抽穗期理想株型结构研究[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2005, 19(1): 52-58. [7] 张秋英, 欧阳由男, 戴伟民, 等. 水稻基部伸长节间性状与倒伏相关性分析及QTL定位[J]. 作物学报, 2005, 31(6): 712-717. [8] 郑亭, 陈溢, 樊高琼, 等. 株行配置对带状条播小麦群体光环境及抗倒伏性能的影响[J]. 中国农业科学, 2013, 46(8): 1571-1582. [9] 杨世民, 谢力, 郑顺林, 等. 氮肥水平和栽插密度对杂交稻茎秆理化特性与抗倒伏性的影响[J]. 作物学报, 2009, 35(1): 93-103. [10] ZHANG W J, LI G H, YANG Y M, et al. Effects of nitrogen application rate and ratio on lodging resistance of super rice with different genotypes[J]. J Integr Agr, 2014, 13(1): 63-72.
[11] MILLER F L. Studies on the relationships of lodging stem physical character and fertilization in wheat[J]. Crop Sci, 1963(6): 468-471.
[12] HWANG S J, HAMAYUN M, KIM H Y, et al. Effect of nitrogen and silicon nutrition on bioactive gibberellin and growth of rice under field conditions[J]. J Crop Sci Biotech, 2007, 10(4): 281-286.
[13] 李国辉, 钟旭华, 田卡, 等. 施氮对水稻茎秆抗倒伏能力的影响及其形态和力学机理[J]. 中国农业科学, 2013, 46(7): 1323-1334. [14] 张明聪, 刘元英, 罗盛国, 等. 养分综合管理对寒地水稻抗倒伏性能的影响[J]. 中国农业科学, 2010, 43(21): 4536-4542. [15] 王振昌, 郭相平, 杨静晗, 等. 旱涝交替胁迫对水稻干物质生产分配及倒伏性状的影响[J]. 农业工程学报, 2016, 32(24): 114-123. [16] 王抄抄, 孔雷蕾, 李妹娟, 等. 分蘖期控水处理对超级稻产量和生理特性的影响[J]. 华北农学报, 2015, 30(5): 146-152. [17] KAHLEN K, STÜTZEL H. Simplification of a light-based model for estimating final internode length in greenhouse cucumber canopies[J]. Ann Bot, 2011, 108(6): 1055-1063.
[18] 戴云云, 丁艳锋, 刘正辉, 等. 花后水稻穗部夜间远红外增温处理对稻米品质的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2009, 23(4): 414-420. [19] NIKLAS K J. A statistical approach to biological factors of safety: Bending and shearing in Psilotum axes[J]. Ann Bot, 1998, 82: 177-187.
[20] 濑古秀生. 水稻の倒伏に关する研究[J]. 九州农试学报, 1962, 7: 419-495. [21] 艾治勇. 超级杂交稻形态及生理特性与抗倒性关系的研究[D]. 长沙: 湖南农业大学, 2006. [22] 陈喜凤, 孙宁, 谷岩, 等. 不同群体结构下大豆植株抗倒性能的比较[J]. 华南农业大学学报, 2015, 36(1): 33-41. [23] XUE J, GOU L, ZHAO Y S, et al. Effects of light intensity within the canopy on maize lodging[J]. Field Crops Res, 2016, 188: 133-141.
[24] SPARKES D L, KING M. Disentangling the effects of PAR and R: FR on lodging associated characters of wheat (Triticum aestivum)[J]. Ann Appl Biol, 2008, 152: 1-9.
[25] OOKAWA T, ISHIHARA K. Varietal difference of the cell wall components affecting the bending stress of the culm relating to the lodging resistance in paddy rice[J]. Jpn J Crop Sci, 1993, 62: 378-384.
[26] 吴耀民, 卓亚男. 水稻倒伏及栽培技术对策[J]. 垦殖与稻作, 1999(3): 12-14. [27] 闫川, 丁艳峰, 王强盛, 等. 行株距配置对水稻茎秆形态生理与群体生态的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2007, 21(5): 530-536. [28] 李杰, 张洪程, 龚金龙, 等. 不同种植方式对超级稻植株抗倒伏能力的影响[J]. 中国农业科学, 2011, 44(11): 2234-2243. [29] 王小菁, 潘瑞炽. 红光、远红光、钙及IAA对绿豆下胚轴切段伸长的影响[J]. 植物生理学通讯, 1990, 26(5): 13-16. [30] 张忠旭, 陈温福, 杨振玉, 等. 水稻抗倒伏能力与茎秆物理性状的关系及其对产量的影响[J]. 沈阳农业大学学报, 1999, 30(2): 81-85. [31] LIU W, DENG Y, HUSSAIN S, et al. Relationship between cellulose accumulation and lodging resistance in the stem of relay intercropped soybean [Glycine max (L.) Merr. ][J]. Field Crops Res, 2016, 196: 261-267.
[32] CAMPBELL C A, READ D W L. Influence of air temperature, light intensity and soil moisture on the growth, yield and some growth analysis characteristics of Chinook wheat grown in the growth chamber[J]. Can J Plant Sci, 1968, 48(3): 299-311.
[33] 徐正进, 张树林, 周淑清, 等. 水稻穗型与抗倒伏性关系的初步分析[J]. 植物生理学通讯, 2004, 40(5): 561-563. [34] 田保明, 杨光圣, 曹刚强, 等. 农作物倒伏及其影响因素分析[J]. 中国农学通报, 2006, 22(4): 163-167. [35] 郭玉明, 袁红梅, 阴妍, 等. 茎秆作物抗倒伏生物力学评价研究及关联分析[J]. 农业工程学报, 2007, 23(7): 14-18. [36] 杨艳华, 朱镇, 张亚东, 等. 不同水稻品种(系)抗倒伏能力与茎秆形态性状的关系[J]. 江苏农业学报, 2011, 27(2): 231-235. [37] 华泽田, 郝宪彬, 沈枫, 等. 东北地区超级杂交粳稻倒伏性状的研究[J]. 沈阳农业大学学报, 2003, 34(3): 161-164. [38] 陈书强, 杜晓东, 杨丽敏, 等. 水稻倒伏粒重损失及不同品种抗倒能力差异比较[J]. 黑龙江农业科学, 2015(10): 34-37. [39] 杨静晗, 郭相平, 杨骕, 等. 旱涝交替胁迫对水稻抗折力的影响及其机理分析[J]. 山东农业大学学报(自然科学版), 2014, 45(3): 328-333. [40] 莫永生, 杨亲琼, 刘丕庆, 等. 高大韧稻的抗折力与茎秆结构的关系[J]. 作物杂志, 2007(2): 40-42. [41] 谷海东, 赵宏伟, 刘洋, 等. 插秧密度对寒地粳稻抗倒伏能力的影响[J]. 作物杂志, 2014(2): 101-106. -
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 许凯,马英,陈三雄,骆金初,黄伟城,郭微,王龙远. 广东德庆县香山森林公园黄牛木种群特征研究. 安徽农业科学. 2022(13): 125-129 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)



 下载:
下载: