Genetic variation analysis of growth and form traits of Castanopsis hystrix in the second generation seed orchard
-
摘要:目的
有效评价和利用红锥Castanopsis hystrix 2代种子园资源、挖掘其优良性状。
方法对广东省龙眼洞林场2代种子园内56个红锥无性系生长和形质性状进行调查,分析各性状的变异系数、不同性状间的相关关系,并进行主成分分析和聚类分析。
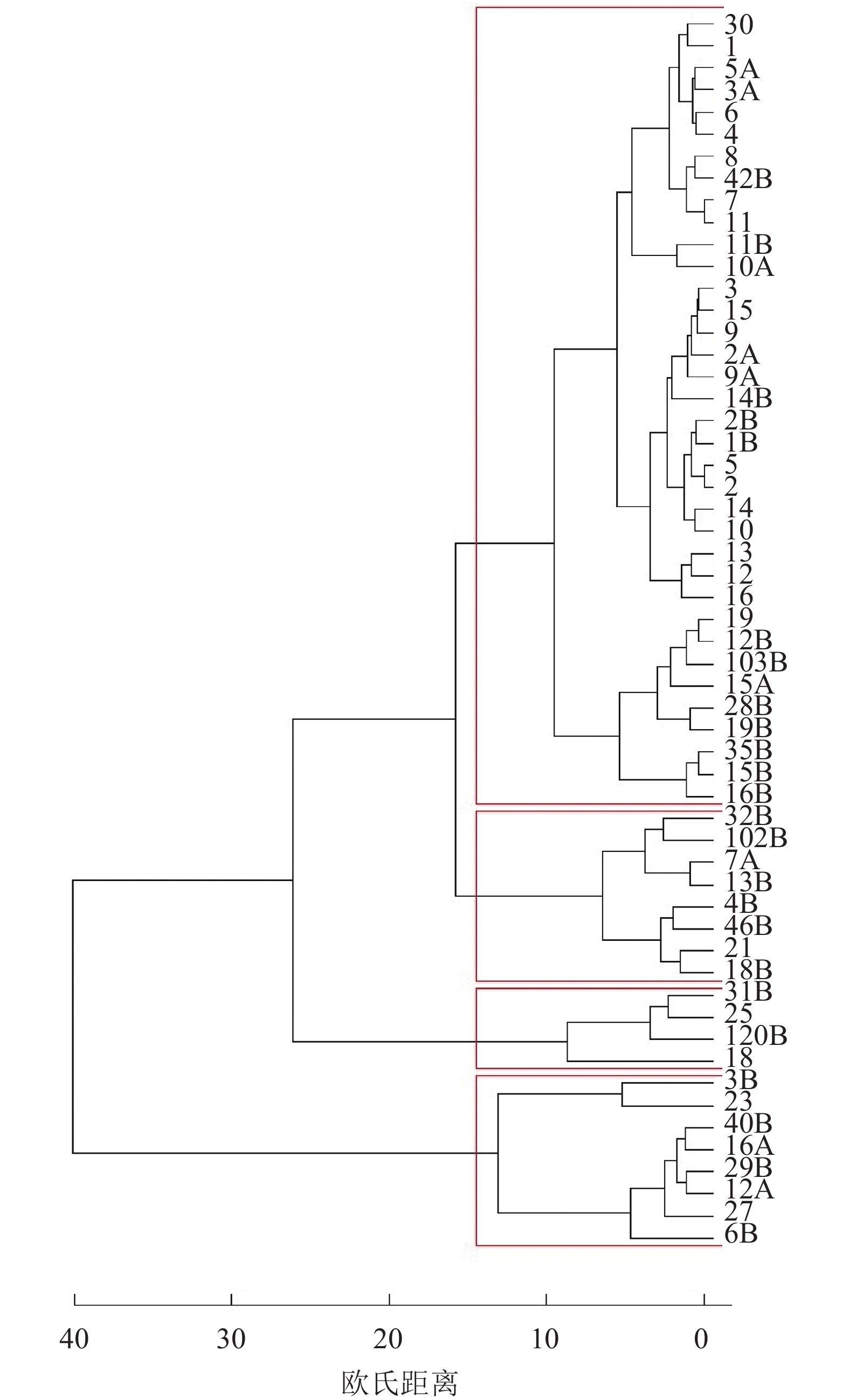
结果56个红锥无性系的10个生长和形质性状的变异系数介于11%~47%,平均变异系数为28.2%。树高与胸径、冠幅与树高、胸径间呈极显著正相关,胸径与分枝数、分枝大小与叶片疏密间也存在极显著正相关,冠幅与分枝角度、尖削度与分枝大小存在显著的负相关。10个性状可以综合为3个主成分,前3个主成分累计贡献率达85%。根据系统聚类将56个红锥无性系划分为4个组。
结论不同红锥无性系的生长性状和形质性状间变异系数较大,遗传多样性较丰富,且性状间存在不同程度的相关性,为开展红锥种内杂交育种的亲本选择奠定基础。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo evaluate and utilize the resources in the second generation seed orchard of Castanopsis hystrix, and develop elite genotypes with genetic merit.
MethodWe investigated the growth and form traits of 56C. hystrix clones in the second generation seed orchard at Longyandong forest farm, Guangdong Province. The variation coefficients and correlations of different traits were analyzed. Principal component analysis and cluster analysis were performed.
ResultThe variation coefficients of ten growth and form traits of 56 C. hystrix clones ranged from 11% to 47%, and the average was 28.2%. Height and diameter at breast height, crown width and height, crown width and diameter at breast height, diameter at breast height and branch number, branch size and leaf density all had significant positive correlations(P<0.01). Crown width and branch angle, taper degree and branch size had significant negative correlations(P<0.05). Principal component analysis indicated that ten traits could be explained by the first three principal components, accounting for 85% of cumulative proportion of variations. Based on hierarchical cluster analysis, 56 clones were divided into four groups.
ConclusionGrowth and form traits among C. hystrix clones had extensive variation with rich genetic diversity. Different degrees of correlations are found among traits. This study provides a basis for parent selection in breeding intraspecific hybrid of C. hystrix.
-
-
表 1 2代种子园红锥生长和形质性状变异分析
Table 1 Variation analysis for growth and form traits of Castanopsis hystrix in the second generation seed orchard
项目 树高/m 胸径/cm 尖削度 冠幅/m 通直度 分枝角度/(°) 分枝数/个 分枝大小/级 叶片疏密 树形 最小值 5.0 5.0 0.37 1.50 1.0 30 2.0 1.00 1.0 1.00 最大值 16.0 17.0 0.97 6.60 5.0 100 19.0 3.00 2.0 3.00 平均值 7.8 9.1 0.80 3.90 3.9 56 5.8 2.20 1.4 1.60 标准差 1.4 2.2 0.09 0.86 1.0 15 2.7 0.73 0.5 0.62 变异系数(CV)/% 18 24 11 22 27 26 47 34 35 38 表 2 2代种子园红锥生长和形质性状方差分析
Table 2 Variance analysis for growth and form traits of Castanopsis hystrix in the second generation seed orchard
性状 变异来源 自由度 平方和 均方 F P 重复力 树高 无性系 55 173.10 3.16 1.71 <0.001 0.42 区组 6 164.20 16.55 8.96 <0.001 误差 330 1 624.30 1.85 胸径 无性系 55 365.00 6.56 1.50 0.010 0.33 区组 6 193.00 19.10 4.38 <0.001 误差 330 3 848.00 4.37 尖削度 无性系 55 0.68 0.01 1.50 0.010 0.33 区组 6 0.10 0.01 1.28 0.240 误差 330 6.90 0.01 冠幅 无性系 55 75.00 1.34 1.98 <0.001 0.50 区组 6 31.40 3.14 4.64 <0.001 误差 330 595.00 0.68 通直度 无性系 55 114.80 2.05 2.14 <0.001 0.53 区组 6 58.70 5.88 6.13 <0.001 误差 330 845.10 0.96 分枝角度 无性系 55 14 469.00 258.40 1.27 0.090 0.21 区组 6 16 304.00 1 630.40 8.03 <0.001 误差 330 178 829.00 203.00 分枝数 无性系 55 711.00 12.70 1.92 <0.001 0.48 区组 6 294.00 29.37 4.45 <0.001 误差 330 5 628.00 6.61 分枝大小 无性系 55 48.60 0.87 1.74 <0.001 0.42 区组 6 12.30 1.23 2.46 0.010 误差 330 436.50 0.50 叶片疏密 无性系 55 23.51 0.42 1.86 <0.001 0.46 区组 6 11.01 1.10 4.88 <0.001 误差 330 198.68 0.23 树形 无性系 55 32.60 0.57 1.35 0.070 0.32 区组 6 13.30 1.03 1.26 0.060 误差 30 236.50 0.60 表 3 2代种子园红锥生长和形质性状间的相关性分析1)
Table 3 Correlation analysis of different growth and form traits of Castanopsis hystrix in the second generation seed orchard
性状 树高 胸径 尖削度 冠幅 通直度 分枝角度 分枝数 分枝大小 叶片疏密 胸径 0.51*** 尖削度 0.20 0.04 冠幅 0.60*** 0.63*** 0.19 通直度 0.06 0.01 0.39** 0.07 分枝角度 0.06 0.04 –0.14 –0.13*** –0.22 分枝数 0.50*** 0.51*** –0.06 0.44* 0.22 0.08 分枝大小 0.11 0.60*** –0.28* 0.32 –0.07 –0.16 0.31* 叶片疏密 0.22 0.55*** 0.20 0.22 –0.09 0.29* 0.40** 0.35** 树形 0.22 0.17 0.18 0.11 0.17 0.00 0.21 –0.16 –0.02 1)*、**和***分别表示 0.05、0.01 和 0.001 水平显著相关(简单相关系数法)。 表 4 2代种子园红锥生长和形质性状间的主成分分析
Table 4 Principal component analysis of growth and form traits of Castanopsis hystrix in the second generation seed orchard
特征向量 PC1 PC2 PC3 树高 0.71 0.23 0.15 胸径 0.88 –0.16 –0.06 尖削度 0.15 0.73 0.16 冠幅 0.77 0.14 –0.19 通直度 0.12 0.68 –0.22 分枝角度 0.04 –0.34 0.84 分枝数 0.74 0.02 0.07 分枝大小 0.55 –0.50 –0.50 叶片疏密 0.61 –0.26 0.35 树形 0.23 0.49 0.28 特征值 3.18 1.77 1.29 解释的方差贡献率/% 44 28 13 累积贡献率/% 44 72 85 -
[1] 中国树木志编委会. 中国要树种造林技术[M]. 北京: 中国林业出版社, 1981: 520-524. [2] 郑万均. 中国树木志: 第1卷[M]. 北京: 中国林业出版社, 1983. [3] 《广东森林》编辑委员会. 广东森林[M]. 广州: 广东科技出版社, 1990. [4] 王明怀, 陈建新. 红锥等8个阔叶树种抗旱生理指标比较及光合作用特征[J]. 广东林业科技, 2005, 21(2): 1-5. [5] 黄永权, 梁东成, 张方秋. 广东省红锥遗传改良进展及改良策略初探[J]. 广东林业科技, 2004, 20(4): 58-60. [6] 王明庥. 林木育种学概论[M]. 北京: 中国林业出版社, 1989. [7] 周邦社, 杨新兵. 植被和坡向对土壤温度与土壤热通量变化的影响[J]. 河北农业大学学报, 2011, 34(2): 80-85. [8] 潘勇军, 王兵, 陈步峰, 等. 短轮伐期桉树人工林土壤温度特征分析[J]. 林业科学研究, 2011, 24(3): 404-409. [9] 廖焕琴, 张卫华, 张方秋, 等. 红锥1.5代改良种子园无性系生长和形质性状变异分析[J]. 林业与环境科学, 2016, 32(4): 23-27. [10] 黄少伟, 谢维辉. 实用SAS编程与林业试验数据分析[M]. 广州: 华南理工大学出版社, 2001. [11] 崔宝禄, 杨俊明, 郑辉, 等. 我国针叶树种子园结实量的研究进展[J]. 河北林果研究, 2005, 20(2): 120-123. [12] 曹汉洋. 杉木第2代种子园半同胞子代测定及早期选择[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2011, 35(1): 19-23. [13] 陈苏英, 马祥庆, 吴鹏飞, 等. 1.5代杉木种子园不同无性系生长和结实性状的评价[J]. 热带亚热带植物学报, 2014, 22(3): 281-291. [14] 孙文生. 红松种子园优质高产经营技术研究[D]. 北京: 北京林业大学, 2006: 1-100. [15] 刘玉皎, 宗绪晓. 青海蚕豆种质资源形态多样性分析[J]. 植物遗传资源学报, 2008, 9(1): 79-83. [16] 王明明, 王建华, 宋振巧, 等. 木瓜属品种资源的数量分类研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2009, 36(5): 701-710.



 下载:
下载:
