Virulence detection and molecular typing of Staphylococcus aureus isolated from rabbit in Sichuan area
-
摘要:目的
研究四川部分区域兔源金黄色葡萄球菌Staphylococcus aureus的基因型总体结构特征、遗传变异以及毒力因子的分布情况。
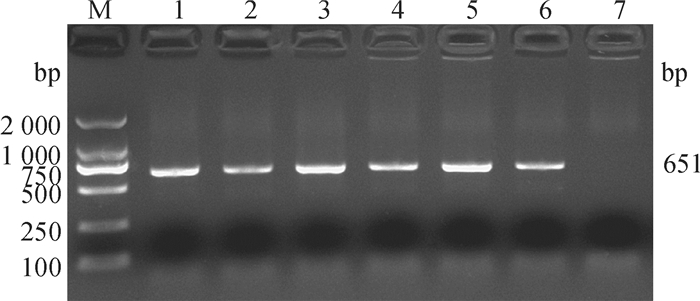
方法从四川地区分离41株兔源金黄色葡萄球菌,鉴定femB基因特异性,进行耐甲氧西林金黄色葡萄球菌(Methicillin-resistant S.aureus, MRSA)筛选,并通过PCR法检测13种常见的毒力基因,采用多位点序列分型(Multilocus sequence typing,MLST)和脉冲场凝胶电泳(Pulsed field gel electrophoresis,PFGE)确定基因型特征。
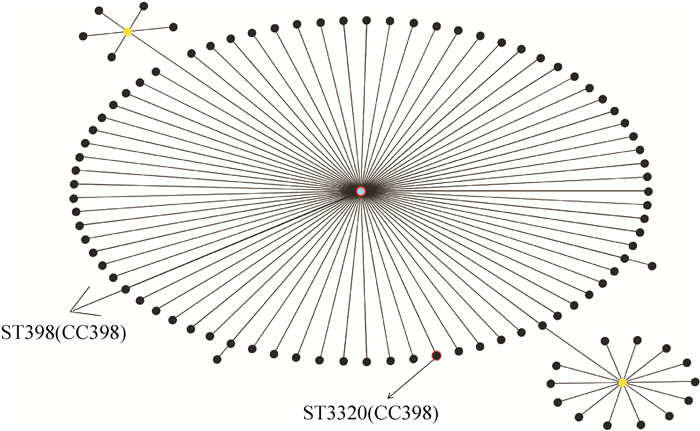
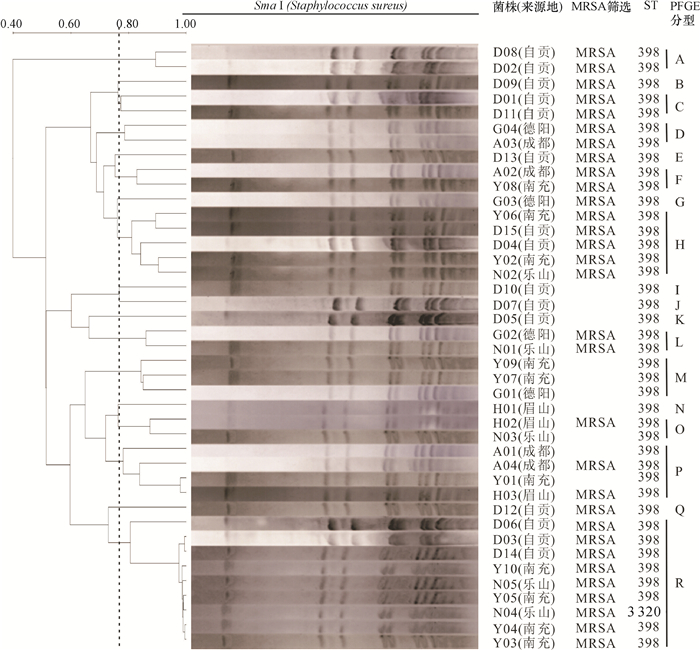
结果41株金黄色葡萄球菌中共检测出MRSA 31株,检出率为75.61%;共检出9种毒力基因,其中nuc、hla、eta和clfA在所有菌株中均存在,而sea、sec、see、hlb和PVL的阳性检出率分别为9.7%、85.4%、80.5%、90.2%和7.3%。MLST分型结果显示,41株金黄色葡萄球菌只存在2种序列型(ST398、ST3320) 和1个克隆群CC398,其中ST398为优势序列型,所占比例为97.6%。PFGE将41株金黄色葡萄球菌分为18个基因型,但不同区域间的基因型条带差异较小。
结论四川调查区域兔源金黄色葡萄球菌毒力因子携带率较高,其对家兔的养殖业存在较大的安全威胁;分型分析说明四川部分区域金黄色葡萄球菌的主要流行菌株遗传变异程度小,菌株间亲缘关系较近。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo understand genotyping characteristics, genetic variation and the distribution of virulence factors of Staphylococcus aureus isolated from rabbits in Sichuan area.
MethodForty-one S. aureus strains were isolated from rabbits in Sichuan area. The strains were identified for femB gene specifity. Methicillin-resistant S. aureus(MRSA) were screened out. Thirteen common virulence genes were detected using PCR. Genotyping characteristics were studied by using multilocus sequence typing (MLST) and pulsed field gel electrophoresis (PFGE).
ResultThere were 31 MRSA strains out of 41 S. aureus strains, and the detection rate was 75.61%. Totally nine virulence genes were detected, nuc, hla, eta and clfA genes existed in all strains, and the positive detection rates of sea, sec, see, hlb and PVL genes were 9.7%, 85.4%, 80.5%, 90.2% and 7.3%, respectively. MLST results showed that 41 S. aureus strains belonged to two sequence types (ST398, ST3320) and one clonal complex CC398. ST398 was the preponderant sequence type, and the proportion was 97.6%. PFGE analysis divided 41 S. aureus strains into 18 banding types, whereas strains from different regions had low variation in banding patterns.
ConclusionS. aureus strains isolated from rabbits in Sichuan area have high carrying rates of virulence factors, and therefore are potential security risk to rabbit farming industry. The genotyping analysis indicates that the prevalent strains of S. aureus isolated from parts of Sichuan Province have low genetic variation, and there are close genetic relationships among different strains.
-
我国是香蕉主要生产和消费国,香蕉是热带亚热带地区经济繁荣的重要支柱产业[1]。香蕉食用价值极高[2],副产品也具有衍生作用[3],但其易成熟、衰老和腐烂[4]。香蕉的表面积和体积等物理参数是重要的形态和表征特征,与其生长和成熟密切相关[5]。因此,定量评估香蕉的表面积、体积和黑斑面积等参数对其保鲜管理具有重要意义。
目前国内外测量植物形态和表征参数主要通过高通量成像、图像处理和三维重建技术来实现[6]。其中,高通量图像处理技术已实现对果实品质的快速检测,包括玉米的根系检测[7]、拟南芥和烟草表征分析[8]、大豆和小麦的种子尺寸及形态分析[9]、苹果火枯病表征分析[10]、柑橘资源分析[11]、草莓性状研究[12]等。
随着重组技术的发展和硬件成本的降低,三维成像技术被用于研究植物表征。三维扫描能够无损追踪植物的构造和生长变化[13]。淮永建等[14]利用三维点云模拟花瓣的生长形变和参数,并预测其形变。Kider等[15]利用三维点云研究水果表面真菌菌落的变化,模拟部分水果外观形态的变化。苏宝峰等[16]提出利用点云分割表面积重建叶片面积。Zhang等[17]基于三维点云的多特征融合和支持向量机实现了石榴植株的器官分类。Jiang等[18] 使用三维点云数据来定量表征灌木作物的大小和形状,从而预测与机械收获装置相关的性状和灌木形状。Wang等[19]通过点云重建分割提取植物生长参数和轮廓信息,从而研究其生长状态。
随着三维点云技术的发展,三维扫描技术也愈加成熟,广泛应用于农业生产、医疗技术和工业生产等领域。高智勇[20]利用三维激光扫描仪重建虚拟园林环境,可检查和分析环境数据。徐伟恒等[21]利用三维激光点云进行投影,计算出高精度的表面积和体积,为实际生产生活提供了便利。Chen等[22]设计自适应三维视觉算法,提高了现场应用多视觉系统的综合性能,实现了香蕉的高精度、稳定、高效的三维传感。Tsoulias等[23]使用LiDAR激光扫描仪实现了基于几何和辐射特征的苹果形状检测。Méndez等[24]通过三维激光扫描实现了对橙子数量和大小的现场估计。Huang等[25]使用手持式三维激光扫描仪实现了豆科植物种子高通量的表征分析。
上述研究主要是利用三维点云技术对树木及树叶表征特性建模,在果蔬类作物衰老、腐败方面的研究较少。此外,人工测量香蕉的体积和表面积等物理参数存在主观性强和效率低下等问题。因此,本文提出基于三维点云的采后香蕉表征褐变定量评估方法,对三维点云模型进行跟踪与分析。首先在15~20 ℃条件下,利用三维扫描仪采集10根表皮变黄且完全成熟的香蕉10 d的表征变化数据,并将三维数据转化为三维点云模型,重构香蕉的几何模型;然后利用欧式聚类对香蕉几何模型进行点云滤波降噪处理,再利用阈值分割和散点轮廓算法(Alpha Shapes)求出香蕉的体积、表面积和黑斑面积;最后利用傅里叶函数对香蕉表面黑斑变化过程进行模拟,确定香蕉表征褐变过程的评估模型。同时,通过设计本文算法与溢水法测量实际香蕉体积、手绘测量面积的对比试验,验证本算法的准确性和可行性。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 数据采集
国际标准中,香蕉成熟度按照果实颜色分为6个等级[26]。1级成熟度的香蕉表皮整体呈绿色; 2级成熟度的香蕉表皮绿色中略带有淡黄色; 3级成熟度的香蕉表皮呈黄绿色; 4级成熟度的香蕉表皮黄色中略带有淡绿色; 5级成熟度的香蕉表皮整体呈黄色; 6级成熟度的香蕉表皮黄色中带有褐色斑点。本文使用的香蕉样本于2022年1月18日购自广州市区某农贸市场,品种为云南高山香蕉,成熟度为5级。
试验选用威布三维Reeyee pro 2X手持式多功能三维扫描仪,带有纹理相机,可快速扫描出复杂结构的果蔬植物等,精度最高可达0.1 mm,体积最高精度达0.3 mm3。另外,该设备为白光扫描仪,支持标定点拼接,手持精细扫描速度为10帧/s,3 000 000点/s;手持快速扫描速度为30帧/s,15 000 000点/s。
首先准备标定点试验台,用于香蕉三维点云的扫描标定。选取一串品相良好、5级成熟度的香蕉, 并挑选10根大小均匀且无任何机械损伤和虫害等缺陷的样品。为避免温度对香蕉表面造成影响,操作过程中全程佩戴隔热手套。使用小刀将整串香蕉拆分,确保在拆分过程中不损伤香蕉表面,并对每根香蕉进行编号,依次标号为1~10。接着将香蕉整齐地放置于试验台,避免直接光照,控制室温为15~18 ℃,配置工业级温度计测量环境的湿度和温度。按照编号顺序采集数据,每根香蕉的采集时间大约是20 min,每隔24 h收集1次所有香蕉的数据。在试验期间,共进行持续10 d的香蕉数据采集,共收集100组试验数据,将试验数据分类后保存。由于香蕉是三维立体模型,在扫描记录过程中不能移动香蕉。因此,为获取香蕉完整的三维模型,需要对香蕉进行2次扫描,得到2个三维立体模型,然后通过纹理拼接的方法将2个香蕉模型拼接在一起,形成1个完整的立体模型。
1.2 采后香蕉表征褐变定量评估方法
三维点云数据处理使用Meshlab软件提取和匹配点云数据,并在Matlab平台进行软件编程。三维点云数据处理包括数据预处理、点云分割、香蕉表征参数测量和定量评估4个步骤,整体流程如图1所示。选取5根表面完好的香蕉进行预试验,接着再选取同一批且同一串表面几乎没有损伤的香蕉作为试验对象,保存在通风且室内温度恒定的环境中,通过三维扫描仪连续记录10 d香蕉表皮表面积和体积的变化情况,利用Meshlab软件将扫描好的香蕉模型全部转换为点云模型保存。使用Matlab设计香蕉表面积、体积和黑斑面积算法,具体包括:使用Alpha Shapes绘制香蕉的外包模型并求解其表面积和体积;设定颜色阈值,实现黑斑部分的分割和面积的计算;使用欧式聚类算法进行点云检测。在此基础上,计算香蕉三维点云模型的体积和表面积,绘制黑斑的包络范围,求出黑斑的总面积。并通过人工测量计算与算法结果对比,以相对误差作为评价指标,验证算法的有效性,最后拟合香蕉性状参数变化模型。
1.2.1 数据预处理
数据预处理过程包括以下步骤:模型转换、数据读写、点云去噪和点云降采样。模型转换中通过使用Meshlab进行模型格式转换,将三维扫描仪保存记录的香蕉obj模型文件转换为三维点云格式并保存。接着使用Matlab软件读取保存的香蕉点云数据,香蕉点云数据中存在一些无意义且不规则的点,这跟环境干扰、扫描软件错误测量等因素有关,因此在处理点云数据时,需通过点云滤波去除背景点云数据,提取试验区香蕉点云数据。香蕉点云数据往往包含大量的冗余数据,如果直接进行计算和处理,计算量很大,消耗时间也很长,因此需要使用pcdownsample对三维点云模型进行降采样,减少点云数据量。降采样后,单个香蕉植物的外部轮廓几乎没有变化。
1.2.2 点云处理
在香蕉点云处理阶段,使用欧式聚类完成点云的降噪处理。在香蕉表征参数测量阶段,使用欧式聚类算法去除点云处理过程中遗留的杂质边界和噪点。欧式聚类算法首先从香蕉的三维点云空间选择某点M,然后使用KD-Tree搜索点M附近的点,共找到N个点。然后将N个点与试验设定的阈值进行比较,小于阈值则归于集合Q中,当Q中的元素不再增加的时候结束搜索,如果Q的元素还在增加则继续重复刚才的操作,从而实现点云去噪,接着设定RGB阈值实现香蕉表面黑斑分割。
1.2.3 香蕉表型参数测量
在香蕉表征参数测量阶段,通过Alpha Shapes获得香蕉的表面积和体积,通过设定RGB阈值分割得到香蕉表面的黑斑面积。香蕉形状的正确分割是直接影响表面积和体积等最终估计参数的关键步骤。Alpha Shapes是一种提取边界点的算法,用于描述平面上有限点集的形状。该算法能够从无序点集中提取物体边缘并形成包络,进而进行体积计算。基本的Alpha形状算法依赖于Delaunay三角剖分,其中每个三角形边的特征是包含该边或三角形的最小空心圆的半径。定义的α参数的Alpha形状输出是一组边,其特征是半径(i)满足i≤1/α。Alpha形状算法能够确定由一组具有异质分布和低密度的点表示的对象的边界[27]。Alpha Shapes通过在散点S上设置一个可以滚动的球体,球体的半径设置为Alpha,在图上进行滚动,通过滚球滚动进行遍历,遍历过程中的外部的线即为轮廓线,如果球体的半径过小,散点可能无法完全包围在球体内部。而此时球体将会在散点S内部,其中每一个点都将是边界。在球体半径足够大且趋近于无穷大时,滚动球体的点形成了外包,如图2所示。
计算圆心坐标的公式如图3所示。
假设点集中半径为α的圆由点集内任意2点 P1(x1,y1)、P2(x2,y2)唯一确定,若圆内无其他点,则 P1、P2 为边界点,线段 P1P2 为边界线段。并可以得到过这2点的圆的圆心 P3,即求出与 P1 点、P2 点距离为 α 的点 P3(x3,y3),其计算公式如下:
$$ \begin{aligned} & x_2=x+\left(x_1-x\right)/2-H \left(y_1-y\right), \end{aligned} $$ (1) $$y_2=y+\left(y_1-y\right)/2-H \left(x-x_2\right), $$ (2) $$x_3=x+\left(x_1-x\right)/2+H \left(y_1-y\right), $$ (3) $$y_3=y+\left(y_1-y\right)/2+H \left(x-x_1\right), $$ (4) 其中,
$$ {H}=\sqrt{{\alpha^2}/{S^2}-{1}/{4}} , $$ (5) $$S^2=\left(x-x_1\right)^2+\left(y-y_1\right)^2。 $$ (6) 使用Alpha Shapes后,散点被聚合成完整的香蕉点云,如图4所示。利用Matlab库函数中的surfaceArea计算出点云模型的表面积,利用函数Volume计算出体积。
在衰老的过程中,成熟香蕉表面的特征通常会发生变化,本研究采用阈值分割算法来识别和计算黑斑面积。传统使用SFM、CMVS和PMVS算法等进行图像处理,然后进行点云去噪融合[28]。在本研究中,由于黑斑部分的占比是随机的,并且在不同时间和不同温度条件下黑斑的模型无法确定,同时黑斑点云的识别需要定义阈值。因此,上述方法不适用于本研究。
本试验使用RGB阈值分割处理来提取黑斑部分,主要思想是通过设定1个阈值,利用Matlab计算香蕉表面像素点的灰度值,并将其与设定的阈值进行比较。在阈值范围内的像素点被识别为黑斑部分,超过阈值的像素点则被视为非黑斑部分,使用RGB阈值分割处理的结果如图5所示。
2. 结果与分析
首先,利用算法计算香蕉的黑斑面积、体积和表面积,其次,验证该算法的准确性和真实性。本文通过预试验实际测量香蕉的表面积和体积,利用记录的数据求取平均相对误差,以相对误差作为评价指标,验证算法的有效性。再次通过平均数据拟合出香蕉的黑斑变化拟合函数,接着利用提前准备的不同天数及新鲜度的香蕉检验评估模型,验证拟合函数的准确性。最后基于上述数据及多样本模型拟合香蕉黑斑、表面积、体积以及黑斑占比参数变化模型。
2.1 香蕉实际测量预试验
为验证本算法的准确性,进行了预试验以获取香蕉的真实表面积和体积信息,首先准备5根香蕉并编号1~5。准备1只黑色签字笔,准备1把尺子,准备1个1000 mL的量筒。使用黑色签字笔和尺子分别在1~5号香蕉表面较为平坦部分绘制一个边长分别为1.0、1.0、1.5、1.5和2.0 cm的正方形。
接着提前准备1000 mL的空量筒并加注600 mL纯净水。将5根香蕉依次放入量筒中,每次测量都需要重新加注600 mL纯净水,将香蕉完全淹没于水中,因香蕉具有一定的浮力,使用铁丝按压香蕉。试验中的铁丝较细,因此造成的误差可忽略不计。
本文使用相对误差(Er)来量化香蕉表面积和体积计算的准确性,以面积相对误差为例,如公式(7)所示。
$$ {E}_{{\rm{r}}} = \dfrac{\left|M_1-M_2\right|}{M_1}\times 100\mathrm{{\text{%}}} , $$ (7) 式中,M1、M2分别表示实际测量和算法算出的表面积。
通过溢水法、实际面积测量法以及本文算法计算统计的试验数据如表1所示。表面积计算的平均相对误差为0.67%,体积计算的平均相对误差为0.47%,平均相对误差均<1%,验证了本算法在计算表面积和体积时具有较高的精度。
表 1 不同香蕉样本的面积与体积1)Table 1. Areas and volumes of different banana samples样本
SampleM1/
mm2V1/
cm3M2/
mm2V2/
cm3相对误差/%
Relative errorM2 V2 1 100 189 98.87 189.21 1.13 0.11 2 100 203 98.93 202.16 1.07 0.42 3 225 187 224.46 188.16 0.24 0.62 4 225 174 224.65 171.13 0.16 1.65 5 400 186 397.17 184.16 0.71 0.99 1)M1 为实际测量的手绘正方形的表面积,V1 为溢水法记录的香蕉的体积;M2 为本文算法得出的手绘正方形的表面积,V2 为本文算法得出的香蕉体积
1)M1 is the actually measured surface area of the hand-drawn square, V1 is the volume of the banana recorded by the overflow method; M2 is the surface area of the hand-drawn square obtained by this algorithm, V2 is the volume of the banana obtained by this algorithm2.2 数据拟合试验
针对香蕉黑斑部分的面积,本研究采用傅里叶函数[29]进行数据拟合。
通过对10根香蕉的黑斑面积占比图像进行拟合,得到10条不同的曲线,且拟合走势基本相同(图6)。通过求取10根香蕉黑斑占比的像素点均值拟合出1条新的函数曲线,并且得到1个函数关系式(8)。
$$ f\left(x\right)={a}_0+{a}_1{\cos}\left({x}{w}\right)+{b}_1{\sin}\left({x}{w}\right)\text{,} $$ (8) 式中,
$ f\left(x\right) $ 代表1个周期函数,x代表角频率,a0、a1、b1为傅里叶系数,其中a0=0.4017(0.2986, 0.5047);a1=−0.4244(−0.5850, −0.2638);b1=−0.02019(−0.4613,0.4209);w=0.3070(0.1331, 0.4810)。误差平方和为0.0162;决定系数(R2)=0.9819;调整R2=0.9728;均方根为0.0520。R2表示回归直线对观测值的拟合程度,R2的最优值为1,越趋近于1说明拟合效果越好,通过多种函数拟合对比发现,最优拟合度为傅里叶函数拟合,R2=0.9819的傅里叶函数拟合图见图7。根据图7可以得出,香蕉表面黑斑面积与时间呈正相关,由R2可知,真实的黑斑变化图像与傅里叶函数拟合的图像拟合度较高,该拟合函数能够有效地解决采后香蕉所在周期不明的问题,可为香蕉表征变化过程中的性状参数变化预测及香蕉保鲜贮存提供数据支持。通过对黑斑部分面积的测量和估算,可以计算出香蕉所在的周期以及腐烂的时间,为香蕉的采后保鲜提供依据。2.3 评估试验模型
为了验证拟合函数的准确性,准备了2~6 d的香蕉作为本次验证集。利用本文算法求解出表面积、黑斑面积及黑斑占比数据总共5个测试集,测试集1~5依次为2~6 d通过三维扫描仪获取的三维香蕉点云数据。分别将5个测试集的黑斑占比数据代入拟合函数关系式(8)中,得到5个测试集的所处周期:x1=1.767,介于1~2 d;x2=2.702,介于2~3 d;x3=3.304,介于3~4 d;x4=4.674,介于4~5 d;x5=5.834,介于5~6 d。5个测试集都处于其存放的天数周期内,因此该拟合函数具有可行性。
2.4 多对象跟踪分析与验证
本文进行为期10 d的香蕉采集,共计100组试验数据,包含对象1~10的表面积、体积、黑斑面积和黑斑占比。其中,对10组对象各项平均数据利用Excel作图,结果如图8所示。由图8可知,香蕉的体积随着时间的变化逐渐减少,表面积与时间呈负相关,同时黑斑随着时间的延长越来越明显,占比越来越多,第10天香蕉的黑斑占比已接近90%。上述结果说明在腐烂过程中,香蕉的表面积、体积和黑斑等性状参数与时间都存在相关性,其中,黑斑变化拟合函数为:
$$ \begin{split} f\left(x\right)= & 0.401\;7-0.424\;4\mathrm{c}\mathrm{o}\mathrm{s}\left(0.307\;0 x\right)-\\ & 0.020\;2\mathrm{s}\mathrm{i}\mathrm{n}\left(0.307\;0x\right)\mathrm{。} \end{split} $$ (9) 3. 结论
本文提出了基于三维点云的采后香蕉表征褐变定量评估方法,克服了传统模拟物体复杂的三维建模过程,得出香蕉黑斑面积占比随时间延长的拟合函数,为香蕉的新鲜度预测提供了数据基础与技术支持。本文使用三维扫描仪获取香蕉的三维图像,并利用Meshlab软件将其转化为三维点云。然后,结合三维点云去噪、平面点云轮廓线计算、RGB阈值分割和欧式聚类点云检测等多种算法,得出香蕉的表面积和体积等物理参数。通过拟合不同的香蕉生长函数,并求取平均值进行傅里叶函数拟合达到模拟统一的目的。回归直线对观测值的拟合方程R2 =0.9816>0.75,说明了本研究的有效性。平均相对误差<1%,说明了本算法适用于计算香蕉表面积、体积和黑斑面积。该拟合函数能够有效地解决采后香蕉所处周期不明的问题,通过对黑斑部分的测量和估算,可以计算出香蕉周期以及腐烂的时间,为香蕉的采后保鲜提供参考。未来的研究将完善算法的多样性,将本文的算法拓展到其他水果的表征变化,拟合多种水果的表征褐变过程,以达到精准地预测估算。
-
表 1 兔源金黄色葡萄球菌毒力基因的检测结果1)
Table 1 PCR detection of virulence genes of Staphylococcus aureus isolated from rabbit
毒力
基因D01~D15 Y01~Y10 N01~N05 A01~A04 G01~G04 H01~H03 MSSA菌株 MRSA菌株 检出率/% 株数 检出率/% 株数 检出率/% 株数 检出率/% 株数 检出率/% 株数 检出率/% 株数 检出率/% 株数 检出率/% 株数 nuc 100.0 15 100.0 10 100.0 5 100.0 4 100.0 4 100.0 3 100.0 10 100.0 31 sea 13.3 2 0 0 40 2 0 0 0 0 0 0 20.0 2 6.5 2 seb 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 sec 93.3 14 100.0 10 100.0 5 50 2 25 1 100.0 3 90.0 9 83.9 26 sed 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 see 100.0 15 80 8 60 3 25 1 75 3 100.0 3 80.0 8 80.6 25 hla 100.0 15 100.0 10 100.0 5 100.0 4 100.0 4 100.0 3 100.0 10 100.0 31 hlb 86.7 13 100.0 10 80 4 75 3 100.0 4 100.0 3 100.0 10 87.1 27 TSST-1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 PVL 13.3 2 0 0 20 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 20.0 2 3.2 1 eta 100.0 15 100.0 10 100.0 5 100.0 4 100.0 4 100.0 3 100.0 10 100.0 31 etb 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 clfA 100.0 15 100.0 10 100.0 5 100.0 4 100.0 4 100.0 3 100.0 10 100.0 31 1) 检出率:指阳性检出率,株数:指革兰染色阳性的菌株数;菌株D01~D15来源于自贡,Y01~Y10来源于南充,N01~N05来源于乐山,A01~A04来源于成都,G01~G04来源于德阳,H01~H03来源于眉山。 表 2 金黄色葡萄球菌基本信息、等位基因编号及序列号
Table 2 Basic information, allele numbers and sequence types of Staphylococcus aureus strains
菌株 地点 分离
时间等位基因编号 ST arcC aroE glpF gmk pta tpi yqi D01~D15 自贡 2015 3 35 19 2 20 26 39 398 Y01~Y10 南充 2014 3 35 19 2 20 26 39 398 A01~A04 成都 2015 3 35 19 2 20 26 39 398 G01~G04 德阳 2015 3 35 19 2 20 26 39 398 H01~H03 眉山 2014 3 35 19 2 20 26 39 398 N01~N03、N05 乐山 2016 3 35 19 2 20 26 39 398 N04 乐山 2016 3 35 19 249 20 26 39 3 320 -
[1] SCHAUMBURG F, PAULY M, ANOH E, et al. Staphylococcus aureus complex from animals and humans in three remote African regions[J]. Clin Microbiol Infect, 2015, 21(4): 345.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2014.12.001
[2] LOWY F D. Staphylococcus aureus infections[J]. New Engl J Med, 1998, 339(27): 2026-2027. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199808203390806?query=prevarrow
[3] REN S Y, GENG Y, WANG K Y, et al. Streptococcus agalactiae infection in domestic rabbits, Oryctolagus cuniculus[J]. Transbound Emerg Dis, 2014, 61(6): e92-e95. doi: 10.1111/tbed.2014.61.issue-6
[4] KRUPA P, BYSTRO AN'U1 J, BANIA J, et al. Genotypes and oxacillin resistance of Staphylococcus aureus from chicken and chicken meat in Poland[J]. Poult Sci, 2014, 93(12): 3179-3186. doi: 10.3382/ps.2014-04321
[5] BREEN J E, HUDSON C D, GREEN M J, et al. Diagnosis and management of intramammary infection caused by Staphyiococcus aureus for dairy cows and herds[J]. Cattle Pract, 2014, 21:189-197.
[6] HIRAMATSU K, HANAKI H, INO T, et al. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus clinical strain with reduced vancomycin susceptibility[J]. J Antimicrob Chemoth, 1997, 40(1): 135-136. doi: 10.1093/jac/40.1.135
[7] YOUNGJU J, YOUNSUCK K, HONG S B, et al. Effect of vancomycin plus rifampicin in the treatment of nosocomial methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus pneumonia[J]. Crit Care Med, 2010, 38(1): 175-180. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0b013e3181b9ecea
[8] DZIEKIEWICZMRUGASIEWICZ M. Role of adhesion and biofilm formation by Staphyloccus aureus in bovine mastitis[J]. Med Weter, 2009, 65(2): 84-87. https://www.cabdirect.org/cabdirect/abstract/20093031739
[9] VALSESIA G, ROSSI M, BERTSCHY S, et al. Emergence of SCCmec type IV and SCCmec type V methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus containing the Panton-Valentine leukocidin genes in a large academic teaching hospital in central Switzerland: External invaders or persisting circulators?[J]. J Clin Microbiol, 2010, 48(3): 720-727. doi: 10.1128/JCM.01890-09
[10] MCHUGH E E. MLST analysis of Staphylococcus aureus isolates identified in a pediatric cohort in northwest Houston[D]. Houston: The University of Texas School of Public Health, 2012.
[11] GOLDING G R, CAMPBELL J, SPREITZER D, et al. Pulsed-field gel electrophoresis of Staphylococcus aureus[J]. Methods Mol Biol, 2015, 1301:85-93. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-2599-5
[12] O′HARA F P, SUAYA J A, RAY G T, et al. Spa typing and multilocus sequence typing show comparable performance in a macroepidemiologic study of Staphylococcus aureus in the United States[J]. Microb Drug Resist, 2015, 22(1): 88-96. doi: 10.1089/mdr.2014.0238
[13] ALIBAYOV B, BABA-MOUSSA L, SINA H, et al. Staphylococcus aureus mobile genetic elements[J]. Mol Biol Rep, 2014, 41(8): 5005-5018. doi: 10.1007/s11033-014-3367-3
[14] 熊咏民, 莫晓燕, 陈群, 等.聚合酶链反应检测耐甲氧西林金黄色葡萄球菌mecA和femB基因[J].中华微生物学和免疫学杂志, 2003, 23(6): 452. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DSDX201316032.htm [15] JARRAUD S, MOUGEL C, THIOULOUSE J, et al. Relationships between Staphylococcus aureus genetic background, virulence factors, agr groups (alleles), and human disease[J]. Infect Immun, 2002, 70(2): 631-641. doi: 10.1128/IAI.70.2.631-641.2002
[16] PEACOCK S J, MOORE C E, JUSTICE A, et al. Virulent combinations of adhesin and toxin genes in natural populations of Staphylococcus aureus[J]. Infect Immun, 2002, 70(9): 4987-4996. doi: 10.1128/IAI.70.9.4987-4996.2002
[17] GLASNER C, SABAT A J, DREISBACH A, et al. Rapid and high-resolution distinction of community-acquired and nosocomial Staphylococcus aureus isolates with identical pulsed-field gel electrophoresis patterns and spa types[J]. Int J Med Microbiol, 2013, 303(2): 70-75. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmm.2012.12.005
[18] GOMES-NEVES E, ANTUNES P, TAVARES A, et al. Salmonella cross-contamination in swine abattoirs in Portugal: Carcasses, meat and meat handlers[J]. Int J Food Microbiol, 2012, 157(1): 82-87. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2012.04.015
[19] 李建平. 奶牛乳房炎金黄色葡萄球菌脉冲场凝胶电泳分型及其主要毒力因子和耐药性的研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2009. [20] 陆军. 不同来源耐甲氧西林金黄色葡萄球菌毒力基因的研究[D]. 温州: 温州医学院, 2012. [21] 王英杰. 奶牛乳腺炎金黄色葡萄球菌相关毒力因子的研究[D]. 济南: 山东师范大学, 2008. [22] PRÉVOST G, CRIBIER B, COUPPIÉ P, et al. Panton-Valentine leucocidin and gamma-hemolysin from Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 49775 are encoded by distinct genetic loci and have different biological activities[J]. Infect Immun, 1995, 63(10): 4121-4129. http://iai.asm.org/content/63/10/4121.full.pdf
[23] PANTON P N, VALENTINE F C O. Staphylococcal toxin[J]. Lancet, 1932, 219(5662): 506-508. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(01)24468-7
[24] GILLET Y, ISSARTEL B, VANHEMS P, et al. Association between Staphylococcus aureus strains carrying gene for Panton-Valentine leukocidin and highly lethal necrotising pneumonia in young immunocompetent patients[J]. Lancet, 2002, 359(9308): 753-759. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(02)07877-7
[25] 童俊, 占志平.金黄色葡萄球菌毒力基因检测及分子分型研究[J].中华微生物学和免疫学杂志, 2015, 35(1):46-50. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZSSA201601126.htm [26] WINSTEL V, LIANG C, SANCHEZ-CARBALLO P, et al. Wall teichoic acid structure governs horizontal gene transfer between major bacterial pathogens[J]. Nat Commun, 2013, 4: 2345. http://eprints.gla.ac.uk/85584/1/85584.pdf
[27] XIA G, CORRIGAN R M, WINSTEL V, et al. Wall teichoic acid-dependent adsorption of staphylococcal siphovirus and myovirus[J]. J Bacteriol, 2011, 193(15): 4006-4009. doi: 10.1128/JB.01412-10
[28] VALENTINDOMELIER A S, GIRARD M, BERTRAND X, et al. Methicillin-susceptible ST398 Staphylococcus aureus responsible for bloodstream infections: An emerging human-adapted subclone[J]. PLoS One, 2011, 6(12): e28369. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0028369
[29] UHLEMANN A C, PORCELLA S F, TRIVEDI S, et al. Identification of a highly transmissible animal independent Staphylococcus aureus ST398 clone with distinct genomic and cell adhesion properties[J]. Mbio, 2012, 3(2):203-216. http://mbio.asm.org/content/3/2/e00027-12.short?related-urls=yesl3/2/e00027-12
[30] DE NEELING A J, VAN DEN BROEK M J, SPALBURG E C, et al. High prevalence of methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus in pigs[J]. Vet Microbiol, 2007, 122(3/4): 366-372. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17367960




 下载:
下载: