Assessment of multi-function of Pinus tabulaeformis plantation in Qingyang area
-
摘要:目的
研究陇东地区甘肃省庆阳市油松人工林多功能发挥情况,构建评价模型,为该地区森林经营提供科学依据。
方法以庆阳市油松人工林为研究对象,在下属7县选取63块样地进行调查,采用层次分析法构建多功能评价指标体系,从油松人工林涵养水源、固碳放氧、生物多样性保护和优质种源保存4种功能中筛选11项评价指标,结合调查数据和专家打分的方式确定各指标权重,计算各样地的多功能贡献总分,采用正态等距划分将处于不同地区的油松林多功能评价指标划分为5个等级。
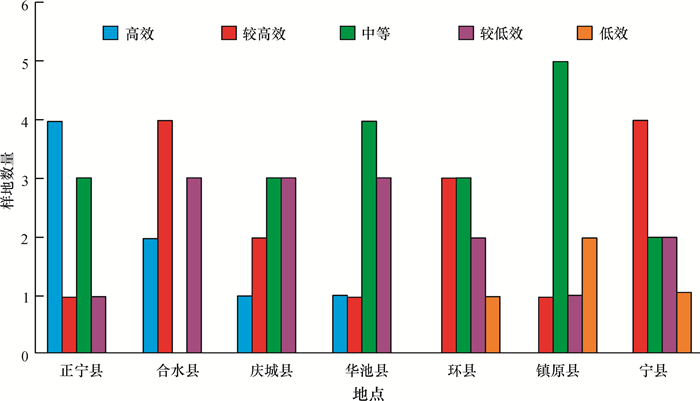
结果庆阳地区油松人工林多功能发挥水平最高的是水源涵养功能,其次是生物多样性保护功能;固碳放氧功能和优良种源保存功能发挥水平偏低。油松人工林多功能发挥高效、较高效、中效、较低效和低效的比例分别为12.7%、25.4%、31.75%、25.4%和4.76%,总体多功能发挥一般,发挥最好的地区是正宁县,最差的地区为镇原县。
结论运用层次分析法能有效进行森林多功能评价,应采取经营抚育措施提高庆阳市森林多功能的发挥。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo investigate the multi-function of Pinus tabulaeformis plantation in Qingyang, Gansu Province, establish an evaluation system, and provide a scientific basis for the forest management in Qingyang area.
MethodWe surveyed 63 sample plots of P. tabulaeformis plantations from seven counties of Qingyang, and used analytic hierarchy process(AHP) to establish the multi-function evaluation index system. Eleven indexes were chosen from four functions including water conservation, carbon fixation and oxygen release, biodiversity conservation and excellent provenance preservation. The weights of different indexes were determined using the surveyed data and expert scoring. The total scores for multi-functions of different sample plots were calculated. Using normal equidistant partition, evaluation indexes of plantations of different counties were divided into five categories.
ResultFor the P. tabulaeformis plantation in Qingyang, the water conservation function had the highest effect, followed by the biodiversity protection function. The functions of carbon fixation and oxygen release and excellent provenance preservation had relatively low effect. The proportions of sample plots that had high effect, moderate high effect, medium effect, moderate low effect and low effect for their multi-functions were 12.7%, 25.4%, 31.75%, 25.4% and 4.76% respectively. The performance was the best in Zhengning County and the worst in Zhenyuan County. The overall effect of multi-function of P. tabulaeformis plantation in Qianyang was ordinary.
ConclusionAHP can be used to effectively evaluate forest multi-function. We should take management measures to improve the multi-function of Qingyang forests.
-
亚甲基蓝(Methylene blue, MB)属噻嗪类的染料类化合物。在淡水鱼类养殖中,MB对水霉病、红嘴病、小瓜虫病等淡水鱼常见疾病都有较好的预防和治疗的效果[1-2]。但随着渔业养殖行业的快速发展,也产生了含有大量MB的养殖废水,而高浓度的MB溶液具有一定的毒性,对自然环境和人体健康均有严重的影响[3-5],因此对养殖废水中的MB进行有效处理显得尤为重要。普鲁士蓝(Prussian blue, PB)是一种配位聚合物,属于有机骨架类,由无机金属中心内配位层与桥连的有机结构外配位层配体相互连接而成的、具有周期性框架结构的晶体材料[6-7]。在普鲁士蓝晶体中,每相邻的铁呈现2种不同的价态:FeII和FeIII,并且与—CN—一起构建成有机骨架。当FeII/H2O2混合后发现,FeII可以催化H2O2分解,产生氧化性较强的羟基自由基(•OH),可将有机污染物快速氧化分解,同时FeII转变成FeIII,因此芬顿(Fenton)催化降解成为一种治理环境的高效方法[8]。与此同时发现,FeIII具有光芬顿(Photo-Fenton)催化效果,FeIII/H2O2的混合体系被光照射时,FeIII在光的作用下催化H2O2分解产生•OH,对污染物有相似的降解效果,并且FeIII转变成FeII[9]。PB的组成元素中富含FeII和FeIII,当PB/H2O2体系受到光照射后,PB中的FeII/H2O2发生芬顿、FeIII/ H2O2发生光芬顿、该过程中的2种催化反应耦合,使FeII与FeIII相互循环转化,加快了•OH产生,提高了有机污染物的降解速率[10]。
在催化降解过程中对体系加热,热会激发活性氧的连续形成[11]。虽然热可以提高降解速率,但额外引入的热源浪费自然资源,不利于可持续化发展[12]。运用催化材料的光热效应来促进催化降解已经成为一种重要的节能方式[13-14]。PB独特的金属有机框架结构在近红外区域有着较强的光吸收,使之具有优异的光热转化效率。Fang等[15]研究表明,缓慢结晶形成的立方晶形PB的光热转化效率达到73.9%。为了高效利用太阳能,快速处理养殖溶液中MB这类有机污染物,本文制备出亚微米尺寸类球形普鲁士蓝(Submicron Prussian blue,smPB),并对smPB进行了光热转化性能的研究,以期进一步提高污染物的降解速率和太阳能的利用率,同时达到节约能源目的。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料
体积分数为30%的H2O2溶液、盐酸(HCl)和聚乙烯亚胺(PEI)均为分析纯,购自上海国药集团化学试剂有限公司(中国,上海),十水合亚铁氰化钠[Na4Fe(CN)6·10H2O]购自上海阿拉丁生化科技股份有限公司(中国,上海),所有药品均未进一步纯化使用。扫描电子显微镜(SEM)在Hitachi S4800仪器上测试(产自日本;供应商:天美仪拓实验设备有限公司,中国,上海);透射电子显微镜(TEM)在FEI Tecnai F20仪器上测试(产自美国;供应商:FEI香港有限公司,中国,香港);XRD在BRUKER D8 ADVANCE X射线衍射仪上测定(产自德国;供应商:布鲁克科技有限公司,中国,北京),2θ范围为5°~50°;红外光谱在Thermo NICOLET 6700红外光谱仪上测试(产自美国;供应商:赛默飞世尔科技有限公司,中国,北京),测试范围4 000~400 cm−1,KBr压片法;电子顺磁共振在Bruker A300上测试(产自德国;供应商:布鲁克科技有限公司,中国,北京);亚甲基蓝的吸光度在TU-1810上测试(产自中国;供应商:苏州赛力威仪器设备有限公司,中国,苏州);紫外可见光漫反射在LAMBDA 950上测试(产自美国;供应商:珀金埃尔默仪器有限公司,中国,上海);太阳光经SAN-EIELECTRIC模拟照射(产自日本;供应商:巨力科技有限公司,中国,北京)。
1.2 亚微米尺寸类球形普鲁士蓝的制备
采用水热缓慢结晶法制备smPB。在温室条件下,称取0.3 g的Na4Fe(CN)6·10H2O溶解在100 mL去离子水中;随后,向溶液里滴加0.1 g聚乙烯亚胺(Polyethylenimine, PEI,相对分子质量为1 000),搅拌10 min后,向溶液里滴加6 mL浓盐酸(体积分数为5%);接着,在60 ℃油浴锅里加热6 h;然后,使用真空抽滤装置收集沉淀物,并分别用水和乙醇溶液(体积分数为50%)清洗若干次;最后,在60 ℃的真空烘箱里干燥4 h。
1.3 光热转化试验
取20 mg的smPB置于100 mL的去离子水中,放置在太阳光模拟器下,使用1个太阳光的功率对其进行1 h的照射,每隔2 min记录1次溶液温度。smPB在200~2 500 nm波长范围内的光热转化效率(
$ \eta $ )计算公式如下:$$ \eta =\frac{\displaystyle\sum A_{i}{\eta }_{i}}{\displaystyle\sum {\eta }_{i}}\times 100{\text{%}} ,$$ 式中,Ai表示特定波长下的吸光率,%;ƞi表示特定波长下的能量;
${{i}}=200\sim 2 \;500 $ 。1.4 芬顿、光芬顿以及光热芬顿催化试验
取20 mg的smPB置于100 mL的MB溶液(ρ=20 mg/L)中,黑暗中搅拌30 min,使smPB达到吸附饱和平衡。芬顿催化降解时,向体系中加入1 mL的 H2O2溶液(质量分数为30%),每隔5 min取出4 mL溶液,测量MB浓度;光分顿催化降解时,将体系置于通入循环水的双层烧杯中,保持溶液温度26 ℃恒定,在1个太阳光功率照射下,向体系中加入1 mL的H2O2溶液,每隔5 min取出4 mL溶液,测量MB浓度;光热芬顿催化降解时,将体系置于太阳光模拟器下,用1个太阳光的功率照射,然后向体系中加入1 mL的H2O2溶液,每隔5 min取出4 mL溶液,测量MB浓度。
MB浓度测量方法:测量前期,首先准备0、0.1、0.2、0.4、0.8、1.0、5.0、10.0、15.0、20.0、25.0、30.0 mg/L的MB溶液,分别在TU-1810上测量MB不同质量浓度的吸光度,并以吸光度为横坐标,MB质量浓度为纵坐标绘制标准曲线。催化降解MB时,在TU-1810上测量出MB实时吸光度后,通过标准曲线找到MB实时质量浓度。MB去除效率(E)按照下式计算:
$$ E=\frac{{\rho }_{t}}{{\rho }_{0}}\times 100{\text{%}} , $$ 式中,ρ0表示初始MB质量浓度,ρt表示t时刻MB质量浓度,mg/L。
采用伪一级反应速率方程对MB催化反应过程的反应动力学进行分析,伪一级动力学公式如下:
$$ {{C}_{t}}={{C}_{0}}{{\text{e}}^{(-kt)}}, $$ 式中,Ct为反应时间为t的MB质量浓度,C0为初始MB质量浓度,mg·L−1;k为伪一级反应速率常数,min−1;t为时间,min。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 形貌表征
根据文献中报道的合成Fe4[Fe(CN)6]3立方体微粒的方法[13],向溶液中添加PEI,在PEI链上的氨基基团作用下,控制PB的结晶过程形成smPB粒子。如图1a所示,smPB粒子直径范围在200~300 nm之间,形貌、尺寸大小较为均一。如图1b所示,smPB表面呈蜂窝状纹路,层层复合。溶液里的PEI会影响普鲁士蓝表面生长,当普鲁士蓝初期缓慢结晶形成一个晶种时,PEI会附着在晶种表面,普鲁士蓝在表面附着PEI的晶种上生长,当长到一定厚度时,溶液中的PEI又会附着在刚长成的晶体表面,以此方式循环生长,直到尺寸变为一定大小时停止生长,形成类层层堆叠的结构形状。如图1c所示,可以清晰地观察到,smPB中C、Fe、N和O等元素,且分布较为均匀。
2.2 红外光谱和XRD表征
图2为smPB的红外光谱图,其中,3 430 cm−1属于水分子的振动吸收峰,2066 cm−1属于氰基的振动吸收峰,表示—CN—的振动[16],表明smPB具有PB的特征峰。
图3为未经PEI调控所制备的PB标准XRD谱图和经过PEI调控后制备的smPB的XRD谱图。从图3中可以发现,PB和smPB均在17.5°、24.8°、28°、35.1°、39.5°出现衍射峰,这与Fang等[15]报道的立方晶形PB衍射峰基本相同,表明smPB具有Fe4[Fe(CN)6]3的晶体结构。
2.3 XPS表征
为了进一步分析smPB材料的表面特性,对其进行XPS表征分析。由图4的 XPS总谱图可以知道,smPB材料由C、N、O、Fe组成,无其他元素,这与XRD表征结果一致。
由图5的精细谱可以知道,Fe2P有6个主峰,分别为FeII2P3/2、FeIII2P3/2、FeII2P1/2、FeIII2P1/2以及2个卫星峰;706.5和719.9 eV处的结合能峰代表分别为FeII2P3/2和FeIII2P1/2,708.9和722.4 eV处的结合能峰代表分别为FeIII2P3/2和FeIII2P1/2,712.2和725.1 eV处的结合能峰代表2个卫星峰。XPS表征结果与XRD表征结果一致,证明smPB为Fe4[Fe(CN)6]3的材料。
2.4 全光谱吸光率
为了研究smPB的吸光性能,在波长为200~2 500 nm的范围内对其进行测试。如图6所示,在太阳能主要分布的近红外区域200~1 200 nm的范围内,smPB的吸光率较高,对近红外光的吸光率达到90%左右;在太阳能分布较弱的其他波段也维持较高的吸收率;全光谱太阳光的照射下,smPB光热转化率达到89.8%。
2.5 羟基自由基检测结果
在芬顿催化降解反应体系中,•OH对有机污染物的催化降解起到重要作用。图7的结果表明,当smPB与H2O2共存于反应溶液中,在有、无光照的条件下均可以清晰地观察到强度对比为1∶2∶2∶1的•OH特征信号,表明在芬顿以及光芬顿催化降解过程中,smPB有效激活H2O2产生•OH。在没有太阳光照射的情况下,smPB与H2O2共存的体系中产生•OH的量较少,催化能力弱;但在有光照的条件下,•OH的特征信号峰强度远高于黑暗条件下的强度,太阳光加速FeII/FeIII的循环转化并促进了•OH的产生,从而加快催化降解速率。芬顿以及光芬顿催化降解过程和最终产物如下[17]:
$$ {{\rm{[F}}{{\rm{e}}^{{\rm{II}}}}{\left( {{\rm{CN}}} \right)_{\rm{6}}}]^{{\rm{4 - }}}}{\rm{ + }}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{2}}} \to {[{\rm{F}}{{\rm{e}}^{{\rm{III}}}}{\left( {{\rm{CN}}} \right)_{\rm{6}}}{\rm{]}}^{{\rm{3 - }}}} + \bullet {\rm{OH + O}}{{\rm{H}}^{\rm{ - }}}, $$ (3) $$ {{\rm{[F}}{{\rm{e}}^{{\rm{III}}}}{\left( {{\rm{CN}}} \right)_{\rm{6}}}\left] {^{{\rm{3 - }}}{\rm{ + }}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{2}}} \to {\rm{ }}} \right[{\rm{F}}{{\rm{e}}^{{\rm{II}}}}{\left( {{\rm{CN}}} \right)_{\rm{6}}}{\rm{]}}^{{\rm{4 - }}}} + \bullet {\rm{OOH + }}{{\rm{H}}^{\rm{ + }}}, $$ (4) $$ \bullet {\rm{OOH + }}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{2}}} \to \bullet {\rm{OH + }}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{ + }}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{2}}}, $$ (5) $$ {{\rm{[F}}{{\rm{e}}^{{\rm{III}}}}{\left( {{\rm{CN}}} \right)_{\rm{6}}}{\rm{]}}^{{\rm{3 - }}}}{\rm{ + }}hv{\rm{ + }}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{O}} \to {\rm{ [F}}{{\rm{e}}^{{\rm{II}}}}{\left( {{\rm{CN}}} \right)_{\rm{6}}}{{\rm{]}}^{{\rm{4 - }}}} + \bullet {\rm{OH + }}{{\rm{H}}^{\rm{ + }}}, $$ (6) $$ \bullet {\rm{OH + MB}} \to 中间产物 {\rm{}} \to {\rm{ C}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{ + }}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{O}}。 $$ (7) 2.6 光热转化能力
smPB具有将光转化为热的能力。在1个太阳光的照射下,对有(无) smPB粒子的水溶液的温度进行了监测,结果见图8。由图8可见,纯水溶液在1个太阳光下照射1 h后,纯水的温度从26 ℃上升到31 ℃左右;含有smPB的水溶液,经过1 h的照射,温度由26.0 ℃上升到34.8 ℃左右。在纯水体系中,水对近红外光有一定的吸收能力,从而导致纯水温度上升。在0~15 min时,2条曲线重合,在这个阶段,2个体系中溶液温度的提升主要源自水对近红外光的吸收而产生的热;在15~60 min时,含有smPB粒子的溶液温度明显高于纯水溶液的温度,在此阶段,smPB进行光热转化作用产生的热远高于水吸收近红外产生的热,使含有smPB粒子体系的温度比纯水的温度高。
2.7 催化降解速率
为了考察光热、光以及无光等条件下,smPB对MB的催化降解情况,分别进行了光热芬顿催化降解、光芬顿催化降解以及芬顿催化降解,试验结果如图9所示。由图9可见,在可见光的照射且有光热产生的情况下,smPB的光热芬顿催化降解速率明显高于光芬顿和芬顿降解速率;在光热芬顿催化时,smPB在40 min时将20 mg/L的MB基本完全降解,而光芬顿催化降解率为50%、芬顿催化降解率为20%。没有加入smPB仅含有H2O2的对照组中,在有光照以及水吸收红外产生热的条件下,40 min时对MB的降解速率为40%(图9a);仅含有H2O2的对照组中,在光照且使用循环水装置去除热的条件下,40 min时的降解速率为10%(图9b);仅含有H2O2的对照组,在没有光照的条件下降解速率为0(图9c)。光热芬顿催化降解时,在光和热的作用下,加速FeII和FeIII的循环转化速率,加快•OH的产生,热会促进催化降解速率,光和热的耦合提高了有机污染物的催化降解速率。
采用伪一级反应速率方程进一步分析MB催化反应过程的动力学,结果见图10。从图10中可以看出,在光热条件下,smPB的反应速率常数达到0.058,高于其他条件下的反应速率常数。这是因为在光和热的作用下,加快了MB的催化降解速率。
3. 结论
采用Na4Fe(CN)6·10H2O与PEI为主要原料,通过水热缓慢结晶法,利用PEI链上的氨基基团,控制PB的结晶过程,研制出具有良好的光热转化性能以及光热芬顿催化性能的smPB催化剂。当自然界中最为丰富的清洁能源太阳能被smPB利用时,smPB可以将太阳能转化为热能,兼备光芬顿性能的smPB,将光和热2种功能耦合在一起,不仅提高了太阳能的利用率,同时加速对污染物的降解。在1个太阳光辐射1 h的情况下,含有smPB粒子的溶液温度提高8.8 ℃左右,比无smPB粒子的对照组溶液温度高3.8 ℃左右。在催化降解时,H2O2的降解能力较低,加入smPB催化剂后,对MB的催化降解速度有所提高;当利用太阳光对该体系进行光热芬顿催化降解时,在光和热的作用下,FeII和FeIII的循环转化速率加快,与光芬顿和芬顿条件下相比,MB的降解速度大大提升,40 min内可以将100 mL溶液(MB质量浓度为20 mg/L)中的MB污染物降解99%。
致谢: 党鹏在外业调查、土壤理化性质的测试以及数据分析中给予了帮助, 庆阳市各林业局的工作人员在试验的布设和调查中也给予了帮助,在此一并致谢! -
表 1 庆阳市油松人工林多功能评价指标体系
Table 1 Multi-function evaluation index system of Pinus tabularformis plantations in Qingyang
目标层(A) 准则层(B) 指标层(C) 编号 指标 编号 指标 油松人工林多功能评价 B1 水源涵养功能 C1 郁闭度 C2 枯落物厚度 C3 土壤厚度 C4 土壤孔隙度 C5 坡度 B2 固碳放氧功能 C6 林龄 C7 森林生物量 B3 生物多样性保护功能 C8 林下植被种类 C9 林下植被盖度 B4 优良种源保存功能 C10 单位面积蓄积量 C11 幼苗数量 表 2 专家打分矩阵1)
Table 2 The expert scoring matrix
A B1 B2 B3 B4 Wi B1 1 7 5 9 0.640 B2 1/7 1 7 7 0.144 B3 1/5 1/7 1 1 0.176 B4 1/9 1/7 1 1 0.041 1) CR=0.096 7,λmax=4.258 3。 B1 C1 C2 C3 C4 C5 Wi C1 1 3 5 8 8 0.498 C2 1/3 1 3 5 8 0.261 C3 1/5 1/3 1 3 7 0.144 C4 1/8 1/5 1/3 1 3 0.063 C5 1/8 1/8 1/7 1/3 1 0.034 1) CR=0.070 6,λmax=5.316 3。 表 3 庆阳市油松人工林多功能评价指标权重
Table 3 The weights of multi-function evaluation indexes of Pinus tabidaeformis plantations in Qingyang
目标层 准则层 分层权重 指标层 分层权重 指标权重 A B1 0.640 C1 0.498 0.318 C2 0.261 0.167 C3 0.144 0.092 C4 0.063 0.041 C5 0.034 0.022 B2 0.144 C6 0.167 0.037 C7 0.833 0.021 B3 0.176 C8 0.722 0.127 C9 0.278 0.049 B4 0.041 C10 0.722 0.030 C11 0.278 0.011 表 4 油松人工林多功能快速评价指标等级划分标准
Table 4 The grading standard of multi-function evaluation indexes of Pinus tabularformis plantations in Qingyang
评价指标1) 不同等级划分标准 好 较好 中等 较差 差 C1 [60, 80) ≥80 [40, 60) [20, 40) < 20 C2 ≥4 [3, 4) [2, 3) [1, 3) < 1 C3 ≥60 [50, 60) [40, 50) [30, 40) < 30 C4 [45, 65) [40, 45); [65, 70) [35, 40); [70, 75) [30, 35); [75, 80) < 30; ≥80 C5 ≥5 [5, 15) [15, 25) [25, 35) < 35 C6 [25, 35) [20, 25); [35, 40) [15, 20); [40, 50) [10, 15); [50, 60) [1, 10); ≥60 C7 ≥120 [90, 120) [60, 90) [30, 60) < 30 C8 ≥20 [15, 20) [10, 15) [5, 10) < 5 C9 ≥70 [50, 70) [30, 50) [10, 30) < 10 C10 ≥80 [60, 80) [40, 60) [20, 40) < 20 C11 ≥2 000 [1 600, 2 000) [1 200, 1 600) [8000, 1 200) < 800 1) C1为郁闭度(%),C2为枯落物厚度(cm),C3为土壤厚度(cm),C4为土壤孔隙度(%),C5为坡度(°),C6为林龄(a),C7为森林生物量(m3·hm-2),C8为林下植被种类(种),C9为林下植被盖度(%),C10为单位面积蓄积量(m3·hm-2),C11为幼苗数量(个·hm-2)。 表 5 样地多功能评价结果
Table 5 The evaluation scores of multi-functions of sample plots
样地编号1) 水源涵养功能 固碳放氧功能 生物多样性保护功能 优良种源保存功能 总贡献得分 P1 40.615 2.366 10.566 2.000 55.546 P2 41.046 1.952 13.110 2.000 58.106 P3 38.390 3.114 10.566 2.227 54.297 P4 49.885 3.114 9.001 2.227 64.227 P5 50.316 3.863 10.566 3.045 67.789 P6 55.924 4.277 14.088 2.681 76.971 P7 63.104 5.440 8.022 3.045 79.611 P8 60.448 5.440 8.022 3.863 77.773 P9 62.724 5.440 10.566 3.863 82.593 P10 37.713 1.952 10.566 2.000 52.230 P11 33.621 1.952 13.110 2.000 50.682 P12 40.666 2.700 9.588 1.409 54.362 P13 50.316 3.529 9.001 2.227 65.072 P14 47.845 3.863 10.566 3.045 65.319 P15 52.592 4.277 14.088 2.454 73.411 P16 63.104 5.026 4.500 3.045 75.675 P17 51.178 5.026 8.022 3.863 68.088 P18 57.719 5.026 10.566 3.045 76.355 P19 39.179 4.611 8.022 3.045 54.857 P20 39.558 1.952 13.110 2.000 56.619 P21 29.068 1.952 13.110 2.000 46.129 P22 38.390 3.114 11.544 1.636 54.684 P23 44.512 3.114 11.544 2.227 61.398 P24 47.414 3.863 10.566 3.045 64.888 P25 47.414 3.863 13.110 2.454 66.840 P26 51.557 5.026 7.044 3.045 66.672 P27 57.546 5.026 9.588 3.272 75.431 P28 40.666 5.026 10.566 3.045 59.302 P29 39.558 1.952 10.566 1.636 53.712 P30 30.914 1.952 13.110 2.000 47.974 P31 38.390 3.114 9.001 2.227 52.732 P32 44.512 3.114 11.544 2.227 61.398 P33 47.414 3.863 10.566 3.045 64.888 P34 47.414 3.863 13.110 2.454 66.840 P35 48.225 5.026 7.044 3.045 63.339 P36 57.115 5.026 9.588 3.272 75.000 P37 28.258 1.952 13.110 1.409 44.728 P38 30.914 1.952 14.088 2.000 48.953 P39 38.390 3.114 9.588 2.227 53.318 P40 44.512 3.114 10.566 2.227 60.420 P41 47.414 3.863 10.566 3.045 64.888 P42 47.414 3.863 10.566 2.454 64.297 P43 54.593 4.611 7.044 2.454 68.703 P44 51.178 5.026 9.588 2.681 68.472 P45 53.403 4.611 10.566 3.045 71.625 P46 29.499 1.952 13.110 1.409 45.969 P47 26.412 1.952 11.544 2.000 41.908 P48 37.713 3.114 11.544 2.227 54.599 P49 44.512 3.114 11.544 2.227 61.398 P50 44.758 4.277 10.566 3.045 62.646 P51 47.414 3.863 10.566 2.454 64.297 P52 48.225 4.611 7.044 2.227 62.107 P53 51.178 4.611 9.588 2.681 68.058 P54 46.603 4.611 10.566 2.818 64.598 P55 29.499 1.952 13.110 1.409 45.969 P56 28.258 3.114 11.544 2.000 44.916 P57 40.615 1.952 9.588 2.227 54.381 P58 44.512 3.863 11.544 2.227 62.146 P59 45.569 4.277 10.566 2.818 63.230 P60 50.747 3.863 10.566 2.227 67.402 P61 48.225 5.026 9.588 2.227 65.065 P62 49.332 4.611 9.588 2.681 66.212 P63 46.603 4.611 13.110 3.045 67.369 1) 正宁县样地编号为P1~P9,合水县样地编号为P10~P18,庆城县样地编号为P19~P27,华池县样地编号为P28~P36,环县样地编号为P37~P45,镇原县样地编号为P46~P54,宁县样地编号为P55~P63。 -
[1] HARRISON P, VANDEWALLE M, SYKES M, et al. Identifying and prioritising services in European terrestrial and freshwater ecosystems[J]. Biodivers and Conserv, 2010, 19(10): 2791-2821. doi: 10.1007/s10531-010-9789-x
[2] 王兵, 魏文俊, 冷泠.宁夏六盘山不同森林类型土壤贮水与入渗研究[J].内蒙古农业大学学报(自然科学版), 2006, 27(3):1-5. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NMGM200603000.htm [3] 赵红宇.林业在生态建设中的特殊地位[J].内蒙古林业调查设计, 2011, 34(6):6. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NMLD201106005.htm [4] 侯元兆, 王琦.中国森林资源核算研究[J].世界林业研究, 1995(3):51-56. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GTLH201411004.htm [5] LOVELL S, MENDEZ V, ERICKSON D, et al. Extent, pattern, and multi-functionality of treed habitats on farms in Vermont, USA[J]. Agroforest Syst, 2010, 80(2): 153-171. doi: 10.1007/s10457-010-9328-5
[6] 李金良, 郑小贤.北京地区水源涵养林健康评价指标体系的探讨[J].林业资源管理, 2004(1): 31-34. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LYZY200401007.htm [7] 鲁绍伟, 余新晓, 刘凤芹, 等.北京市八达岭林场森林生态系统健康性评价[J].水土保持学报, 2006, 20(3): 79-82. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQS200603019.htm [8] 赵学明, 刘东兰, 郑小贤.北京八达岭林场森林多功能评价指标体系探讨[J].林业资源管理, 2010(3):45-48. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LYZY201003010.htm [9] 蔡永茂, 许兰霞, 张咏.八达岭林场的分类经营评价[J].北京林业大学学报, 2003, 25(12): 57-62. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJLY2003S1014.htm [10] 朱绍文, 张立, 孙春林.八达岭林场森林资源价值评估及生态效益经济补偿的初步探讨[J].北京林业大学学报, 2003, 25(12): 71-74. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJLY2003S1017.htm [11] COSTANZA R, D′ARGE R, DE GROOT R. The value of the world's ecosystem services and natural capital[J].Nature, 1997, 387(15): 253-260. http://mro.massey.ac.nz/handle/10179/5983
[12] COSTANZA R. Ecosystem services: Multiple classification systems are needed[J]. Biol Conserv, 2008, 141(2): 350-352. doi: 10.1016/j.biocon.2007.12.020
[13] 殷鸣放, 郑小贤, 殷炜达.森林多功能评价与表达方法[J].东北林业大学学报, 2012, 40(6):23-26. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DBLY201206008.htm [14] 张永利, 杨锋伟, 王兵, 等, 中国森林生态系统服务功能研究[M].北京:科学出版社, 2010. [15] 周彬. 太岳山油松林人工林水文特征研究[D]. 北京: 北京林业大学, 2013. [16] 鲍文, 包维楷, 丁德蓉, 等.岷江上游人工油松林凋落量及其持水特征[J].西南农业大学学报(自然科学版), 2004, 26(5):567-571. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XNND200405014.htm [17] 莫菲, 于澎涛, 王彦辉, 等.六盘山华北落叶松林和红桦林枯落物持水特征及其截持降雨过程[J].生态学报, 2009, 29(6) :2868-2876. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STXB200906015.htm [18] 杨学军, 姜志林.溧阳地区森林景观的生物多样性评价[J].生态学报, 2001, 21(4):671-675. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STXB200104025.htm [19] 贾振声, 骆永菊, 徐文权.关于正态分布的等距分组[J].数学的实践与认识, 2010, 40(20):238-244. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YBSF201005005.htm [20] 王礼先.水土保持学[M].北京:中国林业出版社, 1995:10-15. [21] 彭道黎, 张志华, 靳云燕.北京市生态公益林经营目标及指标体系的研究[J].林业调查规划, 2006, 31(6):16-19. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LDGH200606003.htm [22] 张邦文, 欧阳杰, 金苏蓉, 等.兴国县飞播马尾松林多功能经营评价[J].林业科技开发, 2014, 28(1):50-54. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10410-1013130755.htm [23] 张彦雷. 山西太岳山油松人工林多功能快速评价研究[D]. 北京: 北京林业大学, 2014.









 下载:
下载: