Isolation and identification of phosphate solubilizing bacteria from rice rhizosphere soil, and promoting effect on rice plant growth
-
摘要:目的
为明确水稻根际溶磷菌株溶磷能力及其对水稻植株及根际土壤磷含量的影响。
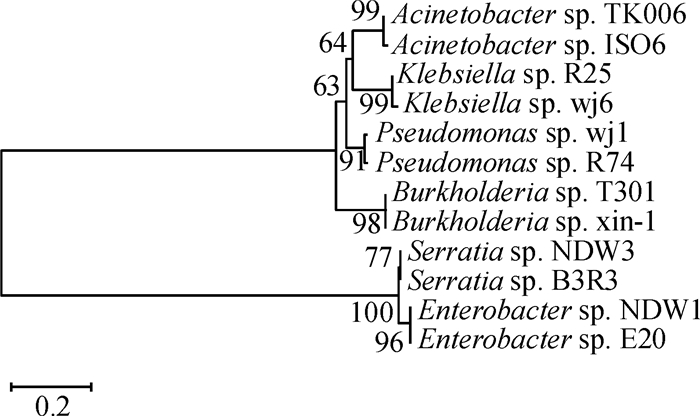
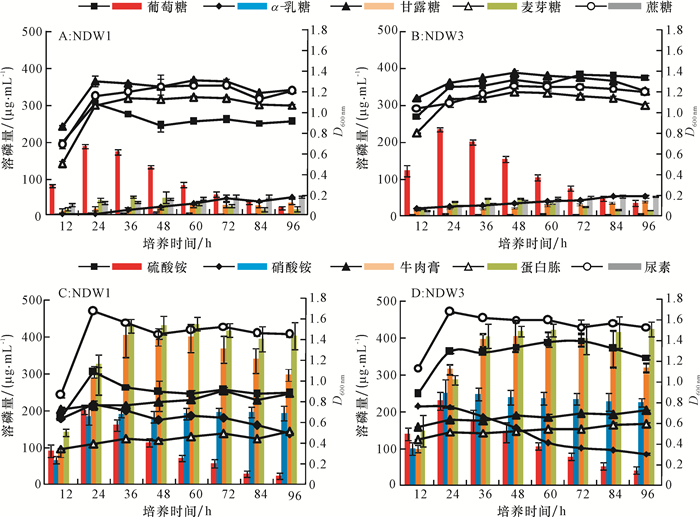
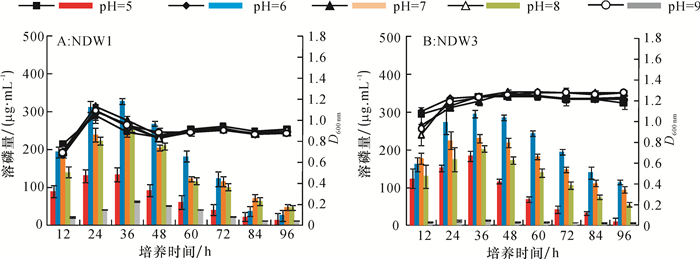
方法利用溶磷圈法从水稻根际土壤中分离获得具有较强溶解Ca3(PO4)2能力的2株细菌NDW1和NDW3,根据16S rDNA对菌株进行鉴定。以NBRIP为基础培养基,通过正交试验对2株菌株利用氮源、碳源及初始pH进行优化,鉴定菌株的吲哚乙酸(IAA)分泌量,研究溶磷菌对水稻的促生作用,以及对土壤速效磷和水稻幼苗全磷含量的影响。
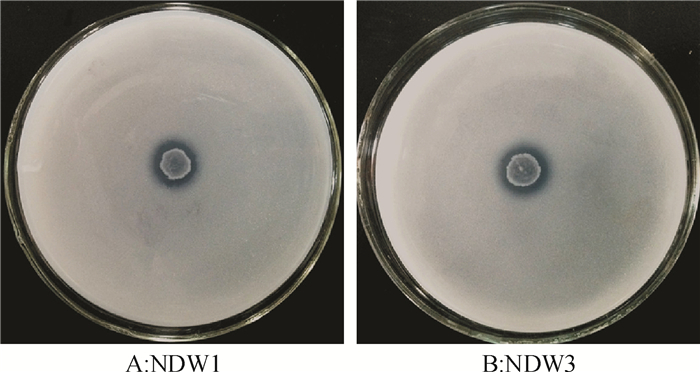
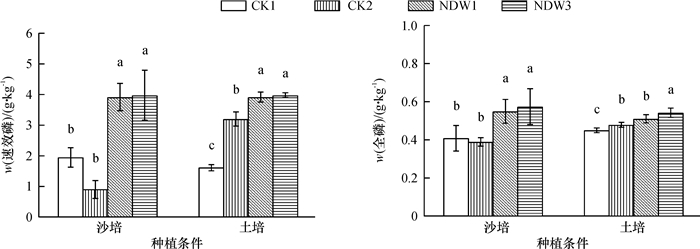
结果菌株NDW1和菌株NDW3分别被鉴定为Enterobacter sp.和Serratia sp.,2株菌株溶磷的最佳条件组合均为葡萄糖、蛋白胨及初始pH 6。2株菌株24 h内最高溶磷量分别为294.95和312.93 μg·mL-1,且都可分泌IAA。土培和沙培条件下,溶磷菌NDW3对水稻株高、根长、最大叶长及地上干质量都有明显的促进作用,并且NDW3在2种种植条件下均显著增加了根际土壤速效磷及水稻植株全磷含量。
结论从水稻根际土壤分离获得2株溶磷能力较好的细菌菌株Enterobacter sp. NDW1和Serratia sp. NDW3,菌株NDW3对水稻的促生作用强于菌株NDW1。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo determine the ability of phosphate dissolving of phosphate solubilizing bacteria(PSB)in rice rhizosphere, and study the effect of PSB on soluble phosphorus contents in rice plants and rhizosphere soil.
MethodTwo bacteria strains NDW1 and NDW3 with strong ability of dissolving Ca3(PO4)2 were isolated from rice rhizosphere soil based on the halo zone formation on media due to phosphate solubilization, and identified by 16S rDNA method. Phosphorus dissolving conditions of two strains were optimized by orthogonal test with NBRIP as the basic medium. The production of indole-3-acetic acid(IAA) were determined. The effects of NDW1 and NDW3 on promotion of rice growth, the soil available phosphorus contents and plant total phosphorus contents were studied.
ResultNDW1 and NDW3 were identified as Enterobacter sp. and Serratia sp.. The best combination of carbon, nitrogen source and pH for phosphate solubilition by NDW1 and NDW3 were both the combination of glucose, peptone and pH 6. The highest phosphorus contents dissolved by NDW1 and NDW3 were 294.95 and 312.93 μg·mL-1 after 24 h incubation, respectively. Both PSB could produce IAA. NDW3 significantly increased the shoot height, root length, maximum leaf length and above-ground dry mass of rice plant in both soil culture and sand culture. NDW3 also significantly increased the contents of soil available phosphorus and rice total phosphorus under both culture conditions.
ConclusionEnterobacter sp. NDW1 and Serratia sp. NDW3 isolated from rice rhizosphere soil have strong ability of phosphate dissolving. The growth promoting effect of NDW3 for rice plant is better than that of NDW1.
-
Keywords:
- soil phosphate solubilizing bacteria /
- IAA /
- growth promoting effect /
- phosphorus content /
- rice /
- rhizosphere
-
细胞水平生物进化的一个明显特征是从相对均匀的细胞质环境中发展出不同的细胞器结构,这些细胞器可以隔离生物大分子以提高特定生化过程的反应速率。真核细胞有2种细胞器,即膜结合的细胞器和无膜细胞器。无膜细胞器因缺失膜结构而更具灵活性,其蛋白质和核酸分子能够根据细胞微环境的变化动态地进行组装和解聚[1]。在受到外界环境刺激时,细胞通过一系列信号传导途径、改变基因表达等来快速抵抗压力并维持稳态,这个细胞重编程的过程被称为细胞应激反应[2]。而无膜细胞器的动态特性使得其在快速响应细胞变化方面具有独特的优势。如图1所示,本文以4种无膜细胞器(应激颗粒、P–小体、核仁、卡哈尔体)为代表总结无膜细胞器的特点、在应激反应中发挥的作用、以及其与疾病的关系。
1. 无膜细胞器简介
1.1 无膜细胞器的特点
在细胞水平生物进化过程中,真核细胞为了更好地实现对细胞组分、代谢过程和信号传导的时空控制,细胞发生区室化形成了许多细胞器。真核细胞有2种细胞器,一种是膜结合细胞器(细胞核、溶酶体、内质网和突触小泡等),另一种是无膜细胞器(应激颗粒、P–小体、核仁、卡哈尔体等)[3]。膜结合细胞器的脂质双分子层膜结构可以将特定的蛋白质、核酸和其他分子封闭在有限的空间内,这种现象使细胞器能够更有效地发挥功能。这些蛋白质或核酸从细胞器中泄漏可能会导致严重的后果,例如,细胞色素 c 释放到细胞质中导致细胞凋亡,而核酸释放到细胞质中导致先天免疫途径的激活[4-5]。相比之下,无膜细胞器没有任何膜结构的限制,可以经常与周围的细胞质交换各种分子物质。近几十年来,多种新型无膜细胞器被发现,它们的结构与组成也逐渐被解析。然而,关于这些无膜结构的形成机制以及它们如何发挥生物学功能仍然有待解答,这也是近年来细胞生物学研究的热点问题。
1.2 无膜细胞器的形成驱动力
液−液相分离 (Liquid-liquid phase separation,LLPS) 是聚合物化学中众所周知的现象,在结晶试验中经常观察到此现象,液滴的形成降低了成核的自由能[6]。近年来,越来越多的证据表明,相分离可能是无膜细胞器形成的潜在机制[7]。细胞内蛋白质–蛋白质、蛋白质–RNA 和 RNA-RNA 间的相互作用以及内在无序区域(Intrinsically disordered regions,IDR)间的弱、瞬时、多价相互作用,包括π-π 相互作用、阳离子−阴离子相互作用、偶极−偶极相互作用和 π−阳离子相互作用,这些多价相互作用促使某些蛋白质和RNA相互聚集转变为具有不同理化性质的另一相,从而形成无膜细胞器[8-9]。无膜细胞器表现出比周围介质更高的蛋白质密度和更弱的分子运动,从而提高了生化反应的速率[7]。在大多数情况下,这些结构表现出液体特征,因此被描述为小体、颗粒、液滴等。
1.3 无膜细胞器的特性与应激响应的关系
无膜细胞器生理功能的探索一直是备受关注的研究方向,它在各种细胞生化过程中发挥作用,包括应激反应、基因表达的调节和信号转导的控制等[10]。根据无膜细胞器的物理性质,推测其主要从4个方面发挥功能,包括调节生化反应的浓度、隔离有害成分、生物分子的储存和信号放大[11]。这些无膜细胞器的形成可以帮助细胞快速响应环境信号,从而促进存活。尽管不同类型细胞中无膜细胞器的数量有所差异,细胞在感受到外界环境变化时,其转录和翻译过程也会相应发生变化,而某些无膜细胞器的快速形成可以确保细胞中可溶性分子的浓度保持恒定,维持稳态平衡。并且,某些细胞成分如蛋白质与mRNA可以暂时储存在无膜细胞器中,更快地响应压力。近年来,已有不少研究表明,无膜细胞器在细胞应激响应中发挥重要作用[12]。细胞质中的应激颗粒在细胞受到刺激时快速形成,而在压力消失时解聚,被认为可以帮助细胞抵抗外部环境变化。而P–小体在一些细胞类型中是一直存在的,只是在受到压力时颗粒的大小和数量都会有所增加,但其成分也会发生变化,在压力解除时也会同应激颗粒一样消失。核仁和卡哈尔体则是细胞核中的重要无膜细胞器,参与核糖体合成等,其在细胞受到刺激时也会发生相应变化,并且它们的功能维持也对细胞存活至关重要,但其与应激响应的具体联系还需进一步探究。
2. 应激颗粒与P−小体
2.1 压力响应下的组装机制
应激颗粒 (Stress granule,SG) 是最具特征的细胞质无膜细胞器之一,在受到氧化应激、热应激、渗透压力、病毒感染、蛋白酶体抑制、内质网应激、紫外线照射、缺氧、能量消耗等不同的刺激时形成[13]。刺激早期,细胞的整体翻译受到抑制,mRNA 从多聚核糖体中解离并在核糖核蛋白(Ribonucleoprotein,RNP)复合物中积累。细胞质中RNP 的浓度增加,并且与一些 RNA 结合蛋白 (RNA-binding proteins,RBPs) 结合,例如激活 SH3 结构域结合蛋白 1 (Ras-GTPase activating SH3 domain-binding protein 1,G3BP1) 和 T 细胞内部抗原−1 (T-cell internal antigen-1,TIA-1) ,触发了更多种蛋白质的募集,这些蛋白的共同特征在于其结构中存在IDR[14]。IDR 介导蛋白质和 RNA 成分间的多价相互作用,其中, G3BP1 作为促进 RNA–蛋白质、蛋白质–蛋白质和 RNA-RNA 相互作用的关键节点,最终促进 LLPS 和 SG 形成。SG呈现高度动态的特征,在压力恢复后快速解聚,释放存储的 mRNAs 使其再次进入翻译过程[15]。不同条件下的SG组装通过不同的相互作用。例如,在氧化应激中,G3BP1 和 G3BP2 通过自身相互作用和与caprin的相互作用诱导哺乳动物细胞的 SG 形成[16-17]。然而,在渗透压力期间,G3BP1/2 和 caprin 并不是 SG 形成所必需的[18]。同样,在葡萄糖饥饿期间,酵母中的 Gtr1、Rps1b 和 Hgh1 促进 SG 的形成,但在热休克期间却抑制 SG 的形成[19]。这表明颗粒可以根据特定的细胞条件进行不同的组装,并且 SG 可能在不同的环境刺激下具有不同的功能。
压力会触发翻译停滞诱导SG形成,其中的作用途径主要分为2种:一种是真核翻译起始因子2亚基α(Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2 subunit alpha,eIF2α)的激酶响应不同刺激而磷酸化eIF2α,抑制翻译;另一种是一些药物以不依赖磷酸化eIF2α的方式诱导SG形成。eIF2α的激酶有4种:蛋白质激酶R(Double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase,PKR),一种由病毒感染、热和紫外线照射激活的双链RNA依赖性激酶;蛋白激酶R样内质网激酶 (Protein kinase R-like ER kinase, PERK),一种驻留在内质网膜上的蛋白,当未折叠的蛋白质在内质网腔中积聚时被激活;一般性调控阻遏蛋白激酶2(General control nonderepressible 2,GCN2),一种监测细胞中氨基酸水平并对氨基酸剥夺作出反应的蛋白质;血红素调节起始因子 2α 激酶(Heme-regulated initiation factor 2α kinase,HRI),一种红细胞成熟过程中确保珠蛋白链和血红素的平衡并感知亚砷酸盐产生的氧化应激的蛋白质。这些激酶会磷酸化 eIF2α,诱导SG形成[20-23]。然而,有些情况下SG的形成也与 eIF2α 磷酸化无关,例如Pateamine A 破坏 eIF4A 解旋酶和 H2O2 破坏 eIF4F 复合物,导致翻译抑制,从而诱导 SG 的形成[24-25]。而在响应渗透压力时,SG 核心蛋白由于分子拥挤作用而局部浓度升高,从而诱导 SG 形成[26]。
P–小体(Processing body,PB)是细胞质RNP颗粒,主要由一些与翻译抑制和 5'→3' mRNA 衰变相关的蛋白质和mRNA 组成[7]。这些 RNP 颗粒在真核生物中是保守的,和 SG 一样,它们也依赖于蛋白质–RNA 相互作用、低复杂性蛋白质序列和LLPS形成。PB在某些细胞系中组成型存在,在应激诱导下,其大小和数量会增加。一些蛋白质的敲除会使组成型和应激诱导的 PB 减少,主要包括ATP 依赖性 RNA 解旋酶6 (ATP-dependent RNA helicase 6,DDX6)、蛋白质 LSM14 同源物 A (LSM14A) 和真核翻译起始因子 4E 转运蛋白 (Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E transporter,EIF4ENIF1;也称为 4E-T)[27-28]。SG 和 PB 共享一些蛋白质成分,它们可以相互接触,并且都可以由细胞应激诱导[29]。而就 mRNAs 而言,SG 含有闭环的多聚腺苷酸化的 mRNAs,而 PB 含有去腺苷酸化的线性 mRNAs[30]。PB 是在研究与 5′→3′ mRNA 衰变途径相关蛋白质的定位过程中发现的,最初假设其是 mRNA 衰变的细胞位点。然而,mRNA 衰变过程不需要 PB,并且 mRNA 可以从 PB 中释放出来重新进行翻译[31-32]。因此,又有专家认为PB其实是翻译停滞的 mRNA 和无活性 mRNA 衰变酶的储存位点,是mRNA 衰变因子在无多核糖体转录本积累时所形成的结果[33-34]。但是,PB 在 mRNA 衰变中的功能仍然是一个悬而未决的问题。
2.2 在细胞抵抗压力中的作用
2.2.1 mRNA分选
基因表达的转录后调控对于发育、分化、免疫信号和神经元可塑性至关重要。转录后,mRNA 还需经过加帽、剪接、多聚腺苷酸化、核输出、与核糖体的结合和最终衰变,而这些都需要相应的 RNA 结合蛋白来协助完成。热应激、氧化应激、缺血或病毒感染,会引发翻译停滞,导致多聚核糖体快速解体[35]。从多聚核糖体中释放出来的 mRNA 在许多蛋白质的帮助下进行分流,该过程决定了 mRNA 的命运。细胞质 SG 是这种分选过程的形态学结果[36]。有研究发现,SG和PB还含有 RNA 诱导的沉默复合物 (RNA-induced silencing complexes,RISCs) ,表明这些 RNA 颗粒与 microRNA (miRNA) 诱导的翻译沉默途径整合在一起[37-38]。
关于哪些特定的 mRNA 包含或不包含在 SG 中,我们知之甚少。只有 50% 的细胞质 poly(A) RNA 被招募到 SG 中,这表明 SG 的 mRNA 具有一定选择性[35]。编码甘油醛−3−磷酸脱氢酶 (Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase,GAPDH)、β−肌动蛋白(β-actin)、c-MYC、胰岛素样生长因子 II (Insulin-like growth factor II,IGF-II) 和 H19 被募集到 SG 中,而编码热休克蛋白 70 (HSP70) 和热休克蛋白 90 (HSP90) 的 mRNA 基本被排除在外[39]。HSP90 和 HSP70的 mRNAs 在热激时转录激活,与 SG 组装同时进行,并且在这种刺激条件下都被优先翻译,而其他 mRNAs 则不然。MLN51 是参与剪接的重要蛋白,它位于 SG 中,而 HSP70 的 mRNA 缺乏内含子,避免了剪接过程,也就不会因为与 MLN51 结合而被招募到 SG 中[40]。同时,HSP70 的 mRNA 拥有一个长且结构化的 5' 非翻译区 (UTR),不需要 eIF4F 依赖的 mRNA 扫描,因此eIF4F 失活促进 SG 组装的过程并不影响 HSP70 mRNA 的翻译[41-42]。而且有研究采用绿色荧光蛋白 (Green fluorescent protein,GFP) 标记mRNA,发现其可以定位于 SG 和 PB中[43]。以上这些发现提示 SG 募集 mRNA 不是依靠序列特异性,而更可能是依据与该 mRNA 有关的蛋白组分。
PB的特征在于其含有参与 mRNA 衰变或沉默的蛋白质。典型的 mRNA 衰变开始于蛋白质脱帽复合物从 mRNA 的 5' 端去除帽,该复合物包含几种定位于PB的蛋白质,即 mRNA 脱帽酶亚基 1A 或 2(分别为 DCP1A 或 DCP2)、增强子mRNA 脱壳蛋白(EDC4,也称为 Hedls)和DDX6。最近的研究认为,mRNAs 被招募到PB中取决于其翻译程度,在PB中的mRNA 可以响应细胞环境变化重新进入翻译阶段[32, 44]。而且,检测 mRNA 衰变中间体的单分子研究表明,衰变发生在整个细胞,而不只是在PB中[45-46]。其次,对酵母脱帽突变体的研究表明,mRNA 衰变甚至可能在PB内受到抑制[47]。最后,在体外重建 LLPS 系统时发现,脱帽酶 DCP2的活性显著降低,一般认为在凝聚的液滴环境中酶的活性会受到抑制,但是这种现象的具体机制还不清楚[48]。以上这些结果说明 PB 形成是mRNA衰变的结果,而不是 mRNA 衰变的介质[31]。 因此,在细胞响应环境刺激时,PB可以储存翻译停滞的 mRNA,来帮助细胞优先考虑某些蛋白的翻译或衰减。
2.2.2 信号传导
除了作为 mRNA 分选中心外,SG还构成了以 RNA 为中心的信号枢纽[49]。许多信号蛋白被招募到 SG,但这个过程是短暂的,只持续到细胞适应压力而存活或不适应压力而死亡。作为信号中心,SG传达一种“紧急状态”,它们短暂存在,通过拦截和隔离信号成分来改变多个信号通路。在体外和体内试验中,多价信号蛋白的浓度依赖性聚集促进了它们从可溶性到不混溶液态的分层相变[9]。因此,液相 RNA 颗粒中信号蛋白的隔离可以整合多个应激信号级联反应来协调细胞对压力的反应。
被招募到 SG 的信号蛋白和酶种类繁多,包括接头/支架蛋白、蛋白质和脂质激酶、磷酸酶、核糖核酸酶、解旋酶、核糖基转移酶、葡糖基转移酶、GTP 酶、甲基转移酶和泛素修饰酶等[49]。SG 通过隔离促凋亡因子如活化蛋白 C 激酶 1的受体 (Receptor of activated protein C kinase 1,RACK1) 来抑制细胞凋亡[50]。同样,最近的一项研究发现,SG 通过招募 RNA 解旋酶 DDX3X 来抑制细胞焦亡,这是一种与炎症相关的细胞死亡形式[51]。真核细胞中高度保守的 TORC1 蛋白激酶复合物,控制细胞生长和代谢[52]。在最佳生长条件下,来自生长因子受体和环境营养物质的信号使 TORC1 在液泡或溶酶体膜上发挥活性,促进蛋白质合成并抑制自噬。氨基酸剥夺使 TORC1 失活后从溶酶体膜中释放出来[53]。失活的 TORC1 在应激诱导下聚集在 SG 中,酵母和人类细胞中的 SG 通过隔离 TORC1 和下游激酶来改变 TORC1 信号传导,从而影响应激过程[54-55]。在从压力中恢复期间,TORC1 随着分解的 SG 被释放出来,又重新被激活。
许多信号分子也被发现与 PB 相关,包括对细胞生长调节很重要的几种蛋白激酶和磷酸酶[56]。除了可能跟 SG 类似,将一些信号通路上的关键分子隔离,从而抑制信号传导外,还可以通过保护信号分子免受蛋白降解的途径来稳定信号分子。PB 通常是由对蛋白质稳态产生负面影响的外界刺激引起的。因此,未能与 PB 结合可能导致相关蛋白质的错误折叠和/或更新。酿酒酵母 Hrr25,是哺乳动物 CK1 的 δ/ε 同种型的酵母直系同源物[57]。这种蛋白激酶在核糖体成熟、囊泡运输、DNA 修复、网格蛋白介导的内吞作用和减数分裂中具有保守作用[58-62]。 Hrr25 的激酶活性是其定位到 PB 所必需的,未能定位到 PB 会导致 Hrr25 以蛋白酶体依赖的方式降解[63]。在减数分裂早期,Hrr25与 PB 的结合能够确保在随后的2次减数分裂中使细胞存在临界水平的 Hrr25[64]。与 PB 的结合不仅可以保护 Hrr25 免受降解,还可能影响 Hrr25 底物的磷酸化,从而对细胞生理学产生重大影响。
2.2.3 抗病毒应激反应
SG 的形成在抗病毒防御和恢复细胞稳态中起重要作用。SG 在功能层面上具有潜在的抗病毒作用,因为 SG 隔离和结合对病毒复制至关重要的细胞成分。例如,SG 通过结合与负链 RNA 互补的 3' 茎环来隔离 TIA-1 和 TIAR,这是病毒 RNA 复制所必需的[65]。任何病毒的有效复制都需要翻译起始因子,因此 40S 亚基、 eIF4G、eIF4A、eIF4B 和 eIF3 的隔离会对病毒复制产生负面影响。此外,刺激小RNA病毒翻译的内部核糖体进入位点(Internal ribosome entry site,IRES)的反式激活因子(如PTB、PCBP2和UNR)也被发现隔离在 SG 中[66]。PKR 在病毒诱导的 SG 形成中至关重要,其通过 eIF2α 磷酸化抑制病毒复制,并促进I 型干扰素 (Interferon,IFN) 产生[67-68]。IFN 的诱导代表了抵御病原体的第1道防线,并且多个 IFN 信号分子也被招募到 SG 中,来调节它们的活性。因此,SG 的形成也是对病毒感染的先天免疫反应。
一些病毒在感染早期诱导SG 的形成,但在后期通过阻断 eIF2α 的磷酸化或切割 SG 支架蛋白如 G3BP1 来抑制 SG 的形成;而另一些病毒则通过将 SG 蛋白转变为非典型颗粒以促进病毒复制,例如 HCV、RSV、轮状病毒、哺乳动物正呼肠孤病毒 (Mammalian orthoreovirus,MRV) 和小鼠肝炎冠状病毒 (Mouse hepatitis virus,MHV)[67, 69-76]。SG 的形成在病毒复制周期的不同阶段或通过不同的信号通路被诱导或抑制,表明感染期间SG 与病毒在互相博弈。
PB组分还包括RISCs、miRNA 相关的 Argonaute (Ago) 蛋白、以及为 RISCs 发挥功能提供支架活性的 GW182 蛋白[77]。而且,在病毒感染期间,人们发现干扰素刺激基因(Interferon stimulated genes,ISG)也可以定位于 PB[78]。HIV-1 mRNA 与 RISC 蛋白相互作用使病毒 mRNA 在 PB 上积聚,并且在破坏 PB 结构的情况下,可观察到病毒的产量增多、感染性增强,这表明 PB 具有抗病毒感染的能力[79]。而某些研究发现,病毒也会反过来抑制 PB 的形成。脊髓灰质炎病毒(Poliovirus,PV)是一种正链 RNA 病毒,病毒蛋白酶3C会降解 PB 的几种成分,包括 Xrn1 和 DCP1A,但不影响其他成分,如 GW182、Edc3 和 Edc4,在感染4h后细胞中的 PB 被破坏[80]。轮状病毒则是通过使用病毒 RNA 作为 RNA 结合蛋白的海绵来分解 PB, 使 PB 中的Ago2、GW182 和 DCP1重新定位[81]。不仅如此,轮状病毒的 NSP1 蛋白可以降解 PB的成分 Pan3,同时重新定位其他2种成分(Xrn1 和 DCP1A)[82]。还有研究指出轮状病毒会干扰正常的 SG 和 PB 组装,但会选择性排除一些成分来促进非典型 SG-PB 结构的形成,并似乎与病毒质(Viroplasm,VM)共同构成更复杂的超分子结构以促进病毒生长[83]。
3. 核仁与卡哈尔体
3.1 功能特点
核仁的主要功能是快速产生大、小核糖体亚基,这个过程受到严格的调控以维持正常的细胞增殖和生长。 核仁内发生的3个主要事件,包括pre-rRNA 转录、加工和核糖体 RNP 组装[84]。RNA 聚合酶 I负责rDNA 基因转录生成的47S 前核糖体 RNA 转录物 (pre-rRNA) 的合成。pre-rRNA 由小核仁核糖核蛋白(snoRNP)加工和修饰,以生成 28S、18S 和 5.8S rRNA,它们与核糖体蛋白 (Ribosomal protein,RP) 组装形成大、小核糖体亚基的前体,再分别输出到细胞质并经过最后的加工步骤生成成熟的 40S 和 60S 核糖体亚基。上述核糖体生成过程中所涉及的分子,都集中在3个不同的亚核仁区室中,称为原纤维中心 (Fibrillar center,FC)、致密原纤维成分 (Dense fibrillar component,DFC) 和颗粒成分 (Granular component,GC)。人们普遍认为,pre-rRNA 是在 FC 或 FC 和 DFC 之间的边界从 rDNA 转录的。 FC 富含 RNA Pol I 机制的成分,如 UBF,而 DFC 含有 pre-rRNA 加工因子,如 snoRNA、snoRNP 蛋白、原纤维蛋白和 Nop58。 FC 和 DFC 被 GC 包围进行前核糖体亚基组装。核仁是通过LLPS形成的,具有液滴状的移动特征[85]。由于没有脂质膜的限制,核仁成分在核仁和核质间以及核仁内高速移动。
卡哈尔体(Cajal body,CB)是 Cajal 在哺乳动物神经元中发现的核结构[86],集中了许多分子成分,包括前 mRNA、前 rRNA 加工所需的线圈蛋白、存活运动神经元 (Survival motor neuron,SMN) 蛋白、核仁蛋白原纤维蛋白、小核 (snRNPs) 和核仁核糖核蛋白 (snoRNPs)[87]。CB的主要结构成分是 p80-coilin 蛋白,通常用作特征标记。CB 在物理和功能水平上都与核仁密切相关。CB 最初被称为“核仁附属体”,因其与神经元中的核仁密切相关。此外,CB 参与 snoRNPs 的成熟过程。一般来说,核仁和CB都参与了与细胞生长紧密相连的非多聚 (A) 尾 RNA 的产生,包括组蛋白 mRNA、CB中的 snRNA 和 snoRNA、以及核仁中的 rRNA。 总之,这些发现都表明 CB 和核仁存在密切联系。
3.2 压力影响下的结构功能变化
各种刺激会破坏或重塑核仁组织,导致核仁功能受损,包括pre-rRNA 转录和加工。DNA 损伤会引起核仁分离[88]。病毒感染还可引起核仁形态大小的特定变化[89-90]。快速增殖的动物细胞需要 rDNA 基因的高转录率和3种 RNA 聚合酶的活性,以满足细胞对核糖体的需求。在影响细胞周期进程/细胞内能量状态的刺激条件下,核糖体亚基生物合成的改变是一种可以保持细胞能量稳态的策略。调节核糖体合成以响应细胞外条件的关键参与者是哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白(Mammalian target of rapamycin,mTOR),它通过调节 TIF-1A、SL1 和 UBF 的定位和活性来促进pre-rRNA 合成,以及 RPs 的翻译[91]。而1 型单纯疱疹病毒 (HSV-1)感染则会影响 rRNA 加工,与pre-rRNA 合成无关[92]。
越来越多的证据表明,核仁可以作为压力感应细胞器来选择性地激活转录因子 p53。核仁改变会导致核仁成分从核仁快速重新分布到核质,反之亦然。这种重新分布的蛋白质对抑制 MDM2(也称为 HDM2,E3 泛素连接酶,用于在稳态下降解 p53) 起着至关重要的作用,而这一个过程有助于p53 的稳定。NPM1(也称为核磷蛋白或 B23)从核仁到核质的易位是核仁应激的标志之一,NPM1 通过与MDM2互作直接抑制 MDM2。研究表明,核仁中的氧化是各种应激条件下的常见现象,会导致 NPM1 的 S–谷胱甘肽化,而这是 NPM1 易位所必需的[93]。此外,有报道称由核仁的重要组分RPL5 (uL18)、RPL11 (uL5) 和 5S rRNA 组成的 5S RNP 复合物直接与 MDM2 结合以在压力下稳定 p53[94-96]。
在一些刺激情况下(热应激、DNA 损伤、生理性酸中毒和蛋白酶体抑制),核质和细胞溶质蛋白会被隔离到核仁中[97]。这些被限制在核仁的蛋白质包括参与应激反应、DNA 修复、细胞周期进程和蛋白质折叠的酶。例如,E3 泛素连接酶的隔离可防止其底物降解。许多核仁靶向蛋白含有携带正电荷的核仁定位信号,这对携带负电荷的核仁 RNA 或几种核仁中枢蛋白的相互作用很重要[98-99]。 未折叠或错误折叠的蛋白质和 HSP(例如 HSP70) 在某些刺激条件下进入核仁[100-101]。未折叠蛋白质被限制在核仁中,流动性减慢,便于在恢复期间被HSP 伴侣重新折叠或降解。然而长时间的压力会导致核仁区室的液相转变为固相,引发不可逆的淀粉样蛋白生成和核蛋白稳态的失调。
卡哈尔体的结构也会因不同类型的刺激而改变,例如UV照射、热应激、转录抑制、渗透压力、饥饿和病毒感染。营养剥夺导致卡哈尔体数量减少[102],而 UV照射可逆地破坏卡哈尔体,线圈蛋白会重新分布[103]。在 HSV-1 感染的细胞中,ICP0(病毒蛋白感染的细胞蛋白 0)的表达诱导着丝粒的不稳定以及随后线圈蛋白、SMN 和原纤维蛋白向受损着丝粒的重新分布[104]。而腺病毒诱导线圈蛋白和其他卡哈尔体成分向病毒复制中心外围募集,参与晚期病毒转录物的加工[105]。泛素蛋白酶体系统的功能障碍导致错误折叠的蛋白质聚集体的积累,从而引起毒性反应。在用硼替佐米(蛋白酶体抑制剂)处理后,作为对蛋白毒性应激的补偿反应,神经元中核仁的数量和大小,以及CB的数量都有所增加,这2种细胞器产生 snRNA、snoRNA 和 rRNA 的协调活性可能有助于蛋白酶体抑制后的神经元存活[106]。
4. 无膜细胞器与疾病的关系
因高流动性的物理特性,无膜细胞器具有快速适应细胞外部环境变化的能力,其中 SG 和 PB 在压力期间参与翻译调控、信号传导,抗病毒感染等过程。因此,这些颗粒的功能异常似乎会影响细胞正常生理活动从而导致疾病。目前,SG与疾病的关系已有不少研究报道,通常认为SG会促进疾病进展,或者它们的异常形成与疾病有关。
4.1 SG与肿瘤的关系
在面对缺氧、营养缺乏、活性氧和高渗透压等诸多不利条件时,肿瘤细胞可能会促进SG的生成,选择性地进行 mRNA 翻译,从而调节细胞信号传导途径、代谢和应激反应,促进自身存活[107]。例如,在肝癌细胞中,PI3K 和 MAPK/p38信号通路被激活后,mTOR活化导致下游效应激酶S6K1磷酸化eIF2α从而促进SG的形成,并且另一亚型S6K2参与SG的维持,从而促进肝癌的发展[108-109]。癌症治疗中常用的化疗药物,如硼替佐米、顺铂或依托泊苷,可能会刺激肿瘤细胞产生依赖于 eIF2α 磷酸化的 SG,从而抵抗药物的作用[110-111]。抗代谢药物5–氟尿嘧啶(5-Fu)广泛用于治疗实体瘤,但肿瘤通常在治疗后期对 5-Fu 产生耐药性。有研究指出在 5-Fu 诱导癌细胞 SG产生的过程中,RACK1被限制在SG中,抑制 MTK1-SAPK 及下游肿瘤凋亡信号通路,导致 5-Fu 的作用减弱[112]。对人肉瘤细胞SG的研究表明,G3BP1与Y-box结合蛋白(YB-1)相互作用,共同促进SG的产生;同时,G3BP1 和 YB-1 的表达增强提示肿瘤患者的预后较差[113] 。因此,SG或许有希望成为一种新型的癌症治疗靶点,可能通过抑制SG的形成来降低肿瘤的发生率、提高抗肿瘤药物的疗效、降低癌症患者的死亡率。
4.2 SG与心血管疾病的关系
一项临床研究表明,在先天性扩张型心肌病患者的重编程心肌细胞中发现了人类 RNA 结合基序蛋白 20 (RNA-binding motif protein 20,RBM20) 致病性的R636S等位基因突变,并且含有RBM20 变体的 mRNP 颗粒在患者心肌细胞的肌浆中异常积聚,表现出液体状特性,促进心脏生物大分子相分离并与SG融合[114]。这种慢性病可能引起细胞内蛋白翻译异常、RBP失调和SG的持续存在,从而促进心血管疾病的发展。
4.3 SG与神经退行性疾病的关系
伴随着脑老化、缺血、脑外伤等继发性神经炎症等因素引起的慢性脑病,老年人的神经系统易发生慢性应激,而慢性应激的发生又与神经退行性疾病密切相关。脑衰老、脑缺血、脑损伤和神经炎症,可能会诱导神经元中 SG 的产生。体外研究结果表明,在病理条件下,SG从液体转变为黏性/固体淀粉样蛋白并引起 tau 沉积,从而促进神经退行性疾病[115]。当危机消除时,SG 也通过自噬被消除并恢复正常的翻译过程。然而,在持续的刺激下,C9orf72突变导致 SG 自噬途径被阻断,并促进 TDP-43 在细胞质的积累,导致肌萎缩侧索硬化症(Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis,ALS)和额颞叶痴呆(Frontotemporal dementia,FTD)[116-117]。此外,蛋白质精氨酸甲基转移酶 5 在 R218 处对 FUS 精氨酸的甲基化是维持 SG 清除机制的先决条件。在急性应激期间,DJ-1(蛋白质/核酸脱糖酶) 能够与 SG 结合,共同调节 RNA 代谢和分流,发挥神经保护作用[118]。然而,在慢性应激条件下,DJ-1 突变促进了 SG 转化为病理性 SG,促进了帕金森病(Parkinson’s disease,PD)的发生。
5. 总结与展望
细胞内无膜细胞器可能会诱导一些适应性和可逆反应,这些反应对细胞外环境的变化非常敏感,包括转录或翻译过程的改变。此外,无膜细胞器通过隔离分子和提高生物分子局部浓度来控制内源性细胞活动,从而影响多种生物过程,例如酶促反应或信号转导。当细胞面临外界刺激时,适应环境维持体内平衡至关重要。压力会导致翻译的全局抑制,从而触发 SG和 PB 的形成,它们是 RNA 和蛋白质的瞬时细胞质无膜区室,没有膜结构限制和相分离的形成特点赋予了其快速响应环境压力而维持细胞稳态的能力。值得关注的是,最近有研究发现,拟南芥中的2个新应激颗粒蛋白质组分,RBGD2(RNA-binding glycine-rich group D 2)和RBGD4通过酪氨酸阵列(Tyr residue array, TRA)形式诱导蛋白液–液相分离,进而增强了拟南芥的耐热性[119]。由此可见,应激颗粒是真核细胞响应各种刺激的一种保守机制。而核仁和卡哈尔体是细胞核中重要的无膜细胞器,参与协调增殖细胞中的主要 RNA 蛋白组装和修饰过程。核仁和卡哈尔体似乎都是由细胞应激反应激活的信号通路的主要目标,这2个细胞器的组织、大小和蛋白质含量在刺激下发生一系列复杂的变化。但关于无膜细胞器在应激反应中的功能和作用仍然存在许多悬而未决的问题。破译无膜细胞器的存在如何改变细胞乃至个体的生物学过程,可能会进一步阐明这些RNA 颗粒的特性,以及它们在细胞稳态中发挥的作用。因此,揭示蛋白质–蛋白质相互作用网络的动力学和刺激下关键成核蛋白的翻译后修饰变化可能是未来研究方向的重点。而针对这些无膜细胞器的生理功能研究有可能为相关疾病的发病机制和防治提供新的见解。
-
图 5 不同处理对水稻根际土壤速效磷含量及幼苗全磷含量的影响
沙培条件下,CK1:加全磷营养液,CK2:加Ca3(PO4)2和无磷营养液;土培条件下,CK1:不加Ca3(PO4)2,CK2:加Ca3(PO4)2; 2种种植条件下,NDW1和NDW3处理分别在CK2处理的基础上接种相应菌株。相同种植条件不同柱子上相同小写字母表示不同处理间差异不显著(P>0.05, Duncan’s法)。
Figure 5. Effects of different treatments on soil available phosphorus contents and total phosphorus contents of rice seedlings
表 1 菌株溶磷的正交试验结果1)
Table 1 Results of the orthogonal test of phosphate solubilizing by bacteria strains
序号 NDW1 序号 NDW3 碳源 氮源 pH 溶磷量/(μg·mL-1) 碳源 氮源 pH 溶磷量/(μg·mL-1) 1 1 1 1 281.60 1 1 1 1 278.12 2 1 2 2 294.95 2 1 2 2 312.93 3 1 3 3 207.35 3 1 3 3 245.02 4 2 1 2 2.07 4 2 1 2 5.40 5 2 2 3 4.55 5 2 2 3 4.55 6 2 3 1 39.34 6 2 3 1 37.60 7 3 1 3 7.76 7 3 1 3 6.94 8 3 2 1 5.34 8 3 2 1 19.05 9 3 3 2 32.50 9 3 3 2 30.50 k1 261.30 97.14 108.76 k1 278.69 96.82 111.59 k2 15.32 101.61 109.84 k2 15.85 112.18 116.28 k3 15.20 93.06 73.22 k3 18.83 104.37 85.50 R 246.10 8.55 36.62 R 262.84 15.36 30.77 最优组合 1 2 2 最优组合 1 2 2 主次顺序 碳源>pH >氮源 主次顺序 碳源>pH >氮源 1)碳源1、2、3分别表示葡萄糖、麦芽糖、蔗糖;氮源1、2、3分别表示牛肉膏、蛋白胨、硝酸铵;pH 1、2、3分别表示pH为5、6、7。 表 2 溶磷菌产IAA的测定
Table 2 Measurements of IAA production of two phosphorus solubilizing strains
King培养液 菌株 ρ定量(IAA)/(μg·mL-1) 定性 加色氨酸 NDW1 11.37± 0.36 粉色 NDW3 15.62± 0.83 粉色 不加色氨酸 NDW1 5.41± 0.71 浅粉色 NDW3 5.60± 0.24 浅粉色 表 3 不同处理对水稻幼苗性状的影响1)
Table 3 Effects of different treatments on traits of rice seedlings
种植条件 处理 株高/cm 根长/cm 最大叶长/cm 地上干质量/mg 地下干质量/mg w(叶绿素)/(μg·g-1) 沙培 CK1 31.67±4.58b 9.50±0.10b 21.57±0.72b 29.00±7.21ab 8.33±0.58b 81.64±7.43b CK2 32.03±0.80b 9.46±0.23ab 19.27±0.83c 27.67±4.04b 8.67±1.53ab 79.27±0.17ab NDW1 34.20±1.91ab 9.73±0.11ab 20.93±1.00b 30.67±3.79ab 9.67±1.15ab 88.90±9.53ab NDW3 37.53±1.00a 9.83±0.25a 23.47±0.58a 39.00±5.57a 11.00±2.00a 103.57±9.37a 土培 CK1 31.20±1.11b 9.73±0.31b 19.73±0.23c 44.67±4.04b 17.67±5.86b 37.82±2.36b CK2 31.80±0.87b 9.83±0.25b 21.40±1.60bc 47.67±2.08b 18.33±3.51ab 54.82±0.39a NDW1 32.93±0.42ab 10.03±0.21ab 22.47±0.31ab 49.33±2.08b 26.67±5.50ab 56.67±0.18a NDW3 34.87±1.70a 10.37±0.20a 23.93±1.92a 58.00±5.29a 18.00±3.00a 59.72±2.81a 1) 沙培条件下,CK1:加全磷营养液,CK2:加Ca3(PO4)2和无磷营养液;土培条件下,CK1:不加Ca3(PO4)2,CK2:加Ca3(PO4)2; 2种种植条件下,NDW1和NDW3处理分别在CK2处理的基础上接种相应菌株。相同种植条件同列数据后相同小写字母表示不同处理间差异不显著(P>0.05, Duncan’s法)。 -
[1] KHAN M S, ZAIDI A, AHEMAD M, et al. Plant growth promotion by phosphate solubilizing fungi-current perspective[J]. Arch Agron Soil Sci, 2010, 56(1): 73-98. doi: 10.1080/03650340902806469
[2] 胡莹莹, 张民, 宋付朋.控释复肥中磷素在马铃薯上的效应研究[J].植物营养与肥料学报, 2003, 9(2): 174-177. doi: 10.11674/zwyf.2003.0208 [3] SHARMA S B, SAYYED R Z, TRIVEDI M H, et al. Phosphate solubilizing microbes: Sustainable approach for managing phosphorus deficiency in agricultural soils[J]. Springer Plus, 2013, 2(1): 587-601. doi: 10.1186/2193-1801-2-587
[4] 谢亚萍, 李爱荣, 闫志利, 等.不同供磷水平对胡麻磷素养分转运分配及其磷肥效率的影响[J].草业学报, 2014, 23(1): 158-166. doi: 10.11686/cyxb20140119 [5] 刘聪, 林维, 孙珑, 等.黑土区林地土壤高效解磷细菌的分离、筛选及其解磷效果[J].东北林业大学学报, 2013, 41(11): 83-86. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5382.2013.11.020 [6] HARIPRASED P, NIRANJANA S R. Isolation and characterization of phosphate solubilizing rhisobacteria to improve plant health of tomato[J]. Plant Soil, 2009, 316(1/2): 13-24.
[7] 冯瑞章, 姚拓, 周万海, 等.溶磷菌对燕麦生物量及植株氮、磷含量的影响[J].水土保持学报, 2009, 23(2): 188-192. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQS200902040.htm [8] AHMAD F, AHMAD I, KHAN M S. Screening of free-living rhizospheric bacteria for their multiple plant growth promoting activities[J]. Microbiol Res, 2008, 163(2): 173-181. doi: 10.1016/j.micres.2006.04.001
[9] 臧威, 孙剑秋, 王鹏, 等.东北地区四种农作物根际磷细菌的分布[J].中国生态农业学报, 2009, 17(6): 1206-1210. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGTN200906032.htm [10] MADER P, KAISER F, ADHOLEY A, et al. Inoculation of root microorganisms for sustainable wheat rice and wheat black gram rotations in India[J]. Soil Biol Biochem, 2011, 43(3): 609-619. doi: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2010.11.031
[11] 赵小蓉, 林启美.小麦根际与非根际解磷细菌的分布[J].华北农学报, 2001, 16(1) :111-115. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HBNB200101020.htm [12] 赵小蓉, 林启美.玉米根际与非根际解磷细菌的分布[J].生态学杂志, 2001, 20(6): 62-64. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STXZ200106015.htm [13] LIU Z, LI Y, ZHANG S, et al. Characterization of phosphate-solubilizing bacteria isolated from calcareous soils[J]. Appl Soil Ecol, 2015, 96:217-224. doi: 10.1016/j.apsoil.2015.08.003
[14] 刘江, 谷洁, 高华, 等.秦岭山区无机磷细菌筛选及其Biolog和分子生物学鉴定[J].干旱地区农业研究, 2012, 30(1): 184-189. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GHDQ201201033.htm [15] 陶涛, 叶明, 刘冬, 等.无机解磷细菌的筛选、鉴定及其溶磷能力研究[J].合肥工业大学学报, 2011, 34(2): 304-308. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HEFE201102035.htm [16] 杨春武. 虎尾草和水稻抗碱机制研究[D]. 长春: 东北师范大学, 2010. [17] AUSUBEL F, BRENT R, KINGSTON R E, et al. Short protocols in molecular biology[M]. 3 ed. Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons Inc, 1995.
[18] BAKERMANS C, MADSEN E. Diversity of 16S rDNA and naphthalene dioxygenase genes from coal-tar-waste-contaminated aquifer waters[J]. Microb Ecol, 2002, 44(2):95-106. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12087425
[19] MEHNAZ S, LAZAROVITS G. Inoculation effects of Pseudomonas putida, Gluconacetobacter azotocaptans, and Azospirillum lipoferum on corn plant growth under greenhouse conditions[J]. Microb Ecol, 2006, 51(3): 326-335. doi: 10.1007/s00248-006-9039-7
[20] 冯月红, 姚拓, 龙瑞军.土壤解磷菌研究进展[J].草原与草坪, 2003(1): 3-7. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CYCP200301001.htm [21] 鲍士旦.土壤农化分析[M].3版.北京:中国农业出版社, 2000:83-86. [22] 赵月华.植株全磷测定方法[J].科技与管理, 2012, 391(2):64. http://youxian.cnki.com.cn/yxdetail.aspx?filename=STXB20170601005&dbname=CAPJ2015 [23] KUNDU B S, GAUR A C. Inoculant carriers for phosphate-solubilizing micro-organisms[J]. Indian J Agr Sci, 1981, 51(4): 252-255.
[24] 祖元刚, 李冉, 王文杰, 等.我国东北土壤有机碳、无机碳含量与土壤理化性质的相关性[J].生态学报, 2011, 31(18): 5207-5216. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STXB201118013.htm [25] 戴沈艳, 贺云举, 申卫收, 等. 1株高效解磷细菌的紫外诱变选育及其在红壤稻田施用效果[J].生态环境学报, 2010, 19(7): 1646-1652. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRYJ201007025.htm [26] 刘文干, 何园球, 张坤, 等. 1株红壤溶磷菌的分离、鉴定及溶磷特性[J].微生物学报, 2012, 52(3): 326-333. http://youxian.cnki.com.cn/yxdetail.aspx?filename=JLNY20170921004&dbname=CAPJ2015 [27] HAMEEDA B, REDDY Y, HARISH K R. Effect of carbon substrates on rock phosphate solubilization by bacteria from composts and macrofauna[J]. Curr Microbiol, 2006, 53(4): 298-302. doi: 10.1007/s00284-006-0004-y
[28] 周毅, 汪建飞, 邢素芝, 等.解磷微生物有机肥对冬小麦产量形成的影响[J].麦类作物学报, 2013, 33(3): 526-529. doi: 10.7606/j.issn.1009-1041.2013.03.021 [29] 胡晓峰, 郭晋云, 张楠, 等. 1株溶磷抑病细菌的筛选及其溶磷特性[J].中国农业科学, 2010, 43(11): 2253-2260. doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2010.11.008 [30] XIE H, PASTERNAK J J, GLICK B R. Isolation and characterization of mutants of the plant growth-promoting rhizobacterium Pseudomonas putida GR12-2 that over produce indoleacetic acid[J]. Curr Microbiol, 1996, 32(2): 67-71. doi: 10.1007/s002849900012
[31] 郑文波, 申飞, 闫小梅, 等.红壤中产吲哚乙酸并具解磷作用的促生菌筛选鉴定及促生效果研究[J].土壤, 2015, 47(2): 361-368. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TURA201502026.htm [32] 谯天敏, 李姝江, 韩珊, 等.温哥华假单胞菌菌株PAN4解磷能力及对核桃的促生作用[J].华南农业大学学报, 2015, 36(5): 117-124. doi: 10.7671/j.issn.1001-411X.2015.05.020




 下载:
下载: