Center of genetic diversity and core collection of common wild rice, Oryza rufipogon Griff., in Guangxi
-
摘要:目的
确定广西普通野生稻Oryza rufipogon Griff.遗传多样性中心,构建普通野生稻核心种质资源,为广西普通野生稻资源保护利用提供参考资料。
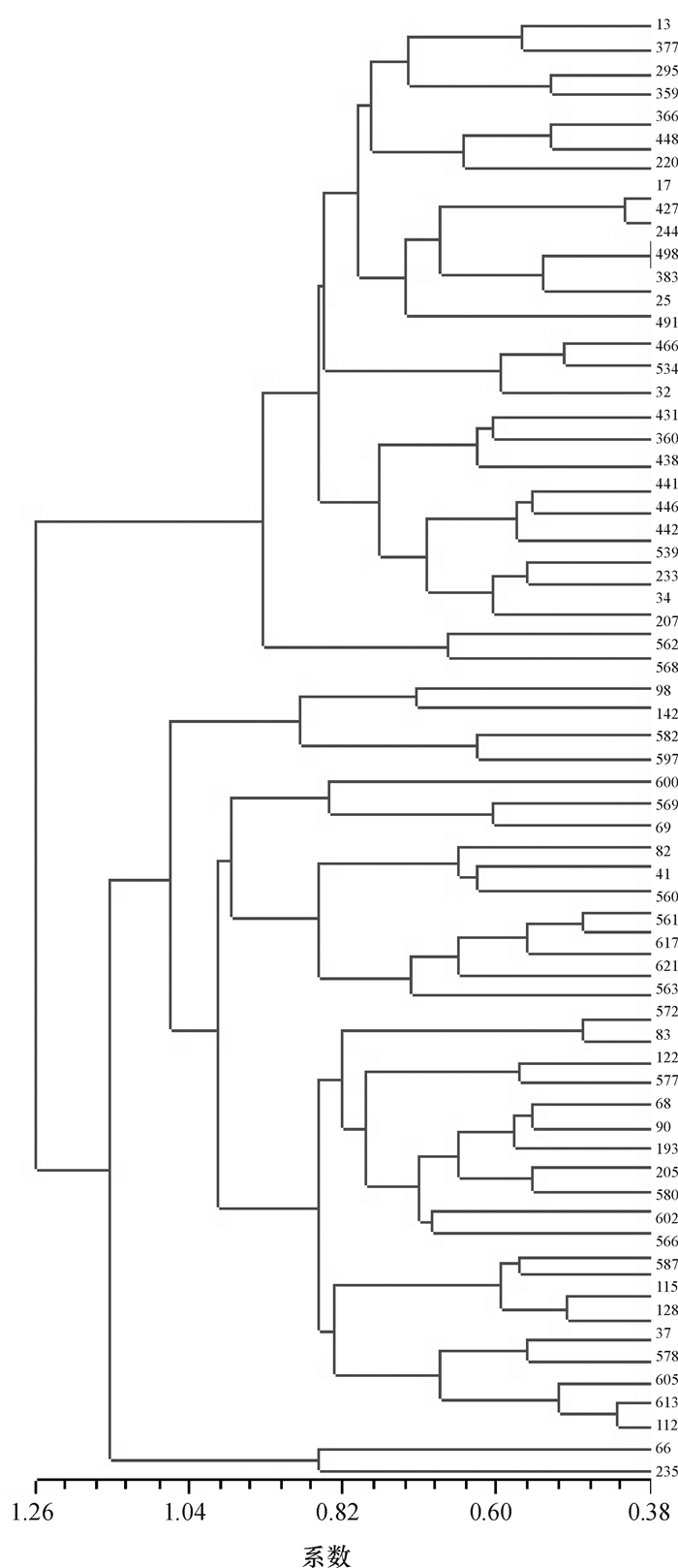
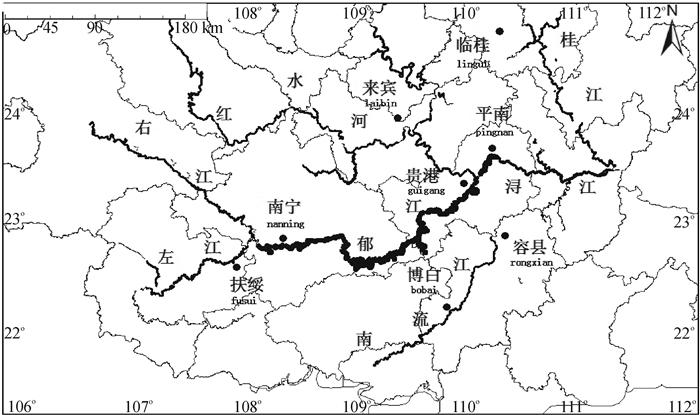
方法利用24对微卫星标记分析来自郁江流域、红水河流域、南流江流域和桂北山区的普通野生稻623份材料的遗传多样性;采用逐步聚类法构建10%和5%的广西普通野生稻核心种质。
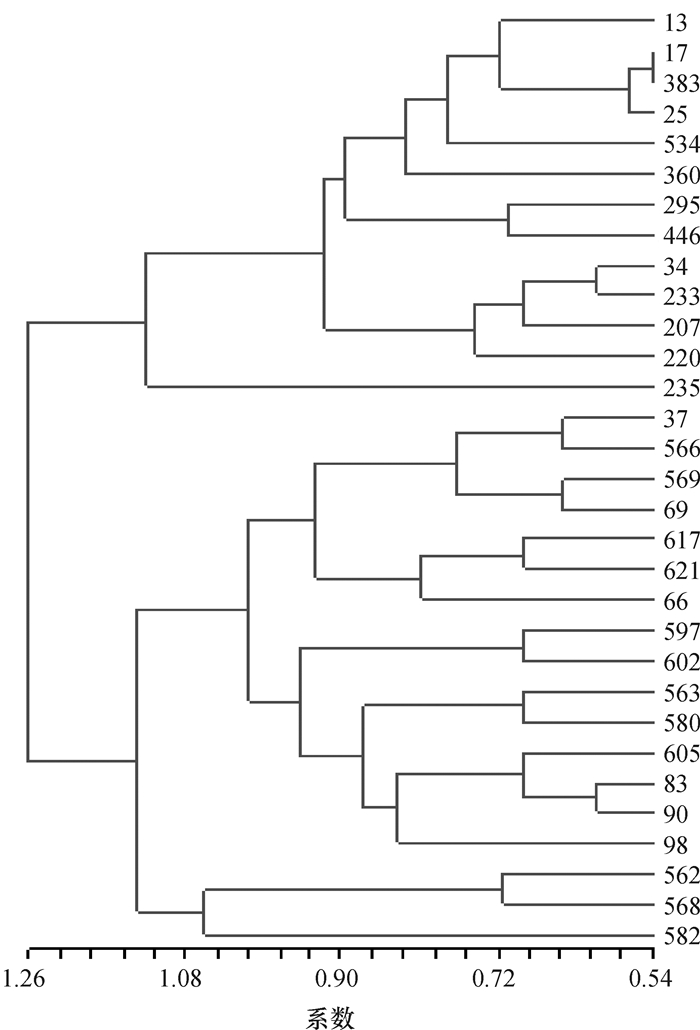
结果24个SSR位点总共检测到114个等位基因。平均等位基因数为4.75,平均有效等位基因数为3.000 1,Shannon信息指数为1.180 1,平均期望杂合度为0.638 8。9个居群遗传多样性指数为:邕宁居群 > 临桂居群 > 扶绥居群 > 容县居群 > 贵港居群 > 平南居群 > 古棚居群 > 五里塘居群 > 博白居群。4个区域的多样性指数为:郁江流域 > 桂北山区 > 南流江流域 > 红水河流域。广西普通野生稻资源5%的核心样本共31份,其中邕宁居群有14份,扶绥居群有12份;邕宁居群和扶绥居群分别占本居群分析样本的5.76%和18.75%,是核心样本的主要来源。
结论郁江流域是广西普通野生稻多样性中心;邕宁居群的普通野生稻地理分布广、种类丰富,而扶绥居群遗传多样性异常丰富,它们是核心样本的主要来源,也是值得特别关注和重点保护的重要区域。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo confirm genetic diversity distribution center of common wild rice, Oryza rufipogon Griff., in Guangxi, and construct the core collection which will provide a reference for protecting and utilizing wild rice resources in Guangxi.
MethodA total number of 623 common wild rice resources from Yujiang River Basin, Hongshui River Basin, Nanliujiang River Basin and Guibei Mountain were used to study the genetic diversity with 24 SSR markers. The stepwise cluster analysis was used to construct 10% and 5% core collections of common wild rice in Guangxi.
ResultThere were 114 alleles to be detected at 24 SSR loci. The number of alleles per locus (A) was 4.75, the average number of effective alleles (Ae) was 3.000 1, the Shannon-weaver information index (I) was 1.180 1 and the average expected heterozygosity (He) was 0.638 8. The order of genetic diversity of 9 regional populations was Yongning (YN) > Lingui (LG) > Fusui (FS) > Rongxian (RX) > Guigang (GG) > Pingnan (PN) > Gupeng (GP) > Wulitang (WLT) > Bobai (BB). The order of genetic diversity of four regions was Yujiang River Basin>Guibei Mountain > Nanliujiang River Basin > Hongshui River Basin. There were 31 copies belong to 5% core collection, including 14 copies of Yongning population and 12 copies of Fusui population which accounted for 5.76% and 18.75% of analyzed samples respectively.
ConclusionThe genetic diversity center of Guangxi common wild rice is Yujiang River Basin. Wild rice of Yongning is widely distributed and presents various types. Wild rice of Fusui shows great rich genetic diversity. Yongning and Fusui regional populations, which are main sources of the core collection samples, are considered to be the most important populations of Guangxi common wild rice, and should be paid particular attention to their protection and exploitation.
-
Keywords:
- Oryza rufipogon /
- SSR /
- genetic diversity /
- core collection /
- Guangxi
-
-
表 1 来自广西4个区域的普通野生稻材料
Table 1 Materials of common wild rice from four regions in Guangxi

表 2 广西普通野生稻遗传多样性参数1)
Table 2 Parameters of genetic diversity of common wild rice in Guangxi

表 3 广西普通野生稻9个居群的遗传多样性1)
Table 3 Genetic diversities of nine regional populations of common wild rice in Guangxi

表 4 不同核心样本的遗传多样性比较1)
Table 4 Comparisons of genetic diversities of different core samples

表 5 各居群占核心样本的比例1)
Table 5 Ratios of core samples from each original populations

-
[1] FULLER D Q, SATO Y I, CASTILLO C, et al. Consilience of genetics and archaeobotany in the entangled history of rice[J]. Archaeol Anthropol Sci, 2010, 2(2):115-131. doi: 10.1007/s12520-010-0035-y
[2] 杨庆文, 黄娟.中国普通野生稻遗传多样性研究进展[J].作物学报, 2013, 39(4): 580-588. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zuowxb201304002 [3] 王美兴, 张洪亮, 张冬玲, 等.中国普通野生稻(O. rufipogon Griff.)的地理多样性与分化[J].科学通报, 2008, 53(22):2768-2775. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2008.22.015 [4] 韩东飞. 中国普通野生稻(Oryza rufipogon Griff. )的遗传多样性研究及栽培稻起源探讨[D]. 北京: 中国农业科学院, 2006. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/article/cdmd-82101-2006110840.htm [5] ZHOU H F, XIE Z W, GE S. Microsatelite analysis of genetic diversity and population genetic structure of a wild rice( 0ryza rufipogon Gril1.)in China[J]. Theor Appl Genet, 2003, 107(2):332-339.
[6] SONG Z P, XU X, WANG B, et al.Genetic diversity in the northernmost 0ryza rufipogon populations estimated by SSR markers[J]. Theor Appl Genet, 2003, 107(8):1492-1499. doi: 10.1007/s00122-003-1380-3
[7] 陈玲, 殷富有, 李维蛟, 等.云南三种野生稻遗传多样性和系统进化研究[J].中国稻米, 2014, 20(3):30-35. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-8082.2014.03.006 [8] 齐兰, 王效宁, 张吉贞, 等.利用SRAP标记研究海南野生稻的遗传多样性与遗传分化[J].植物遗传资源学报, 2015, 14(3):402-406. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zwyczyxb201303006 [9] 李杜娟, 陈雨, 潘大建, 等.粤东地区普通野生稻表型多样性分析[J].广东农业科学, 2012(2):13-17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-874X.2012.02.005 [10] 孙希平, 杨庆文, 李润植, 等.海南三种野生稻遗传多样性的比较研究[J].作物学报, 2007, 33(7):1100-1107. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0496-3490.2007.07.009 [11] 余萍, 李白超, 张洪亮, 等.广西普通野生稻(Oryza rufipogon Gril1.)表型性状和SSR多样性研究[J].遗传学报, 2004, 3l(9):934-940. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=ycxb200409008&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ [12] 黄娟, 杨庆文, 陈成斌, 等.广西普通野生稻的遗传多样性及分布特征[J].中国农业科学, 2009, 42(8):2633-2642. doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2009.08.001 [13] 盖红梅, 陈成斌, 沈法富, 等.广西武宣濠江流域普通野生稻居群遗传多样性及保护研究[J].植物遗传资源学报, 2005, 6(2):156-162. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-1810.2005.02.007 [14] 任民, 陈成斌, 荣廷昭, 等.桂东南地区普通野生稻遗传多样性研究[J].植物遗传资源学报, 2005, 6(1):31-36. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-1810.2005.01.006 [15] 黄金艳, 陈淼, 梁燕理, 等.广西来宾市五里塘普通野生稻(Oryza rufipogon Griff.)居群遗传多样性与核心种质研究[J].西南农业学报, 2008, 21(2):245-249. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4829.2008.02.001 [16] 梁燕理, 陈淼, 刘驰, 等.广西邕宁普通野生稻(Oryza rufipogon Griff.)种群遗传多样性及核心种质构建研究[J].安徽农业科学, 2008, 36(11) : 4439- 4441. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2008.11.032 [17] 李亚非, 陈成斌, 张万霞, 等.我国北回归线区域普通野生稻遗传多样性和遗传结构研究[J].植物遗传资源学报, 2007, 8(3):280-284. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-1810.2007.03.006 [18] HUANG X H, NORI KURATA, WEI X H, et al.A map of rice genome variation reveals the origin of cultivated rice[J].Nature, 2012, 490(7421):497-501. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=JJ0228073450
[19] CHEN D H, RONALD P C. A rapid DNA minipreparation method suitable for AFLP and other PCR applications[J].Plant Mol Biol Rep, 1999, 17(1):53-57. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=JJ022725656
[20] HU J, ZHU J, XU H M. Methods of constructing core collections by stepwise clustering with three sampling strategies based on the genotypic values of crops[J]. Theor Appl Genet, 2000, 101(1/2): 264-268. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=JJ0215091619
[21] 邓国富, 张宗琼, 李丹婷, 等.广西野生稻资源保护现状及育种应用研究进展[J].南方农业学报, 2012, 43(9):1425-1428. doi: 10.3969/j:issn.2095-1191.2012.09.1425 [22] 徐志健, 陈成斌, 梁世春, 等.广西野生稻自然资源濒危现状评估报告[J].广西农业科学, 2010, 41(3):281-285. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1191.2010.03.024 [23] ZHANG J W, XIE J K, WAN Y. et al. Research progresson the protection of wild rice resources in China[J].Agr Sci Technol, 2010, 11(2):95-97. http://www.cabdirect.org/abstracts/20103342943.html
[24] 章琦, 赵炳宇, 赵开军, 等.普通野生稻的抗水稻白叶枯病(Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae)新基因 Xa-23(t)的鉴定和分子标记定位[J].作物学报, 2000, 26(5):535-542. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zuowxb200005004 [25] HUANG D, QIU Y, ZHANG Y, et al. Fine mapping and characterization of BPH27 , a brownplanthopper resistance gene from wild rice(Oryza rufipogon Griff)[J].Theor Appl Genet, 2013, 126(1):219-229. doi: 10.1007/s00122-012-1975-7
[26] WANG Y, CAO L M, ZHANG Y X. et al. Map-based cloning and characterization of BPH29 , a B3 domain-containing recessive gene conferring brownplanthopper resistance in rice[J]. J Exp Bot, 2015, 66(19):6035-6045. http://pubmedcentralcanada.ca/pmcc/articles/PMC4566989/
[27] 覃惜阴, 韦仕邦, 黄英美, 等.杂交水稻恢复系桂99的选育与应用[J].杂交水稻, 1994(2):1-3. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199400780386 [28] 莫永生, 韦政, 黎志方, 等.杂交水稻强优广谱恢复系测253的选育与应用[J].作物杂志, 2003(6):46-47. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7283.2003.06.024 [29] 张月雄, 颜群, 黄大辉, 等.利用单片段代换系鉴定水稻稻瘟病抗性座位[J].西南农业学报, 2014, 27(4):1478-1482. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4829.2014.04.025 [30] 覃宝祥, 刘立龙, 韩飞怡, 等.普通野生稻染色体片段代换系的孕穗期耐冷性研究[J].基因组学与应用生物学, 2015, 34(6):1283-1289. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/97024C/201506/71887866504849534854485157.html



 下载:
下载: