Effects of G418 treatment of donor cells on the in vitro developmental efficiency of cloned porcine embryos
-
摘要:目的
探索G418处理供体细胞对其核移植胚胎发育效率的影响。
方法利用G418单独处理猪成体成纤维细胞6 d后,收集细胞,利用荧光定量PCR的方法检测处理前后细胞中抗氧化应激、细胞凋亡相关基因的表达水平,运用亚硫酸盐结合测序法分别检测基因组重复序列LINE-1、微卫星的DNA甲基化状态,以及其核移植胚胎体外发育的能力。
结果经不同质量浓度G418处理的供体细胞的抗氧化应激酶相关基因及细胞凋亡基因表达发生显著变化(P<0.05),但其DNA甲基化水平没有发生改变(P>0.05);经G418处理的供体细胞的核移植胚胎的体外发育效率显著低于对照组(P<0.05)。
结论G418处理供体细胞可能对其克隆胚胎体外发育效率有抑制作用。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo explore the influence of G418 treatment of donor cells on the developmental efficiency of somatic cell nuclear transfer (SCNT) embryos.
MethodPorcine adult fibroblasts were collected after six days of G418 treatment. Expression levels of antioxidation and apoptosis-related genes were detected by quantitative RT-PCR before and after G418 treatment. The DNA methylation levels of LINE-1 repetitive sequences and microsatellites were analyzed using bisulfites sequencing analysis, and the in vitro developmental rates of SCNT embryos were investigated.
ResultG418 treatment of donor cells caused significant (P < 0.05) changes in expression levels of genes related to antioxidation and apoptosis, but did not significantly(P > 0.05) change DNA methylation levels. SCNT embryos cloned from G418-treated donor cells exhibited a significantly (P < 0.05) lower in vitro developmental rates compared with the control group.
ConclusionG418 treatment of donor cell may inhibit the development of SCNT embryo.
-
Keywords:
- G418 /
- porcine /
- cloning /
- nuclear transfer /
- transgene /
- embryonic development
-
在利用克隆技术生产转基因动物过程中,遗传霉素(Geneticin,G418)是最常用于细胞筛选的药物之一。G418是一种氨基糖苷类抗生素,具有抑制细胞增殖[1]、诱发细胞凋亡[2]等作用,并对原核和真核细胞等都有毒性。虽然有研究显示,G418筛选对转基因细胞核移植胚胎的发育效率有负面作用[3],但Liu等[4]统计分析了全世界至今已发表的克隆猪生产数据,比较了转基因和非转基因克隆胚胎的发育效率,发现2组之间胚胎的发育效率不存在显著差异。此外,广东温氏研究院动物克隆实验室在前期研究中还发现,利用G418筛选的转基因细胞作为核供体生产的克隆胚胎,其胚胎的发育效率显著高于未经G418处理的非转基因组。虽然上述研究所用的转基因细胞都是经过G418药物筛选处理,但它们同时还携带整合的外源基因,这导致其结果难以准确证明G418筛选供体细胞对转基因克隆胚胎发育效率的影响。
为了探索G418单独处理核供体细胞对克隆胚胎发育效率的影响,从而为将来优化体细胞克隆法制备转基因动物技术奠定基础,本研究利用不同质量浓度G418分别处理猪成体成纤维细胞6 d后,观察不同质量浓度G418处理的细胞生长情况,并检测超氧化物歧化酶(Superoxide dismutase, SOD)和过氧化氢酶(Catalase, CAT)等抗氧化酶相关基因、细胞凋亡基因、甲基化转移酶(DNA methyltransferase, Dnmt)相关基因的表达水平及细胞整体甲基化水平。随后,利用筛选得到的细胞进行核移植,对胚胎发育效率进行统计分析,研究G418处理核供体细胞对猪胚胎体外发育效率的影响。
1. 材料与方法
试验于2015年3—12月在华南农业大学动物科学学院/广东温氏研究院动物克隆实验室完成。
1.1 材料
菌株和细胞株:大肠埃希菌Escherichia coli DH5α感受态细胞,北京全式金生物技术有限公司;杜洛克公猪成体成纤维细胞由广东温氏研究院动物克隆实验室提供。
主要试剂:细胞DNA&RNA抽提试剂盒(QiagenAllPrepTM DMA/RNA Micro Kit)、反转录试剂盒(PrimeScriptTMRT reagent Kit with gDNA Eraser)为TaKaRa公司产品,实时定量PCR试剂盒(SYBR Select Master Mix)为Life公司产品,亚硫酸盐转化试剂盒(EZ DNA Methylation-GoldTM Kit)、甲基化特异PCR酶预混液(ZymoTaqTMPreMix)为ZYMO RESEARCH公司产品,TA连接试剂盒(InsTAcloneTM PCR Cloning Kit)、蓝白斑筛选试剂(X-Gal、IPTG)为Fermentas公司产品,PCR产物纯化试剂盒(E.Z.N.A.® Cycle-Pure Kit)为OMEGA公司产品,G418为GIBCO公司产品。
1.2 方法
1.2.1 猪成体成纤维细胞的复苏与培养
将冻存管从液氮罐中取出,立即投入37 ℃水浴中不停搅动(溶解时间尽量控制在1 min内),待要完全溶解后,将冻存管内冻存液转移到离心管中,加入3倍体积的DMEM培养液,离心(750 r·min-1,5 min)后,去除上清液。加入新鲜培养液(DMEM+体积分数为10%FBS)悬浮细胞,将细胞稀释到所需浓度并吹打为单层细胞,转入新的培养皿中培养,放置于37 ℃、体积分数为5% CO2的培养箱进行培养。当细胞汇合度达到90%左右时,可进行消化、传代培养。本试验所用细胞为第6代杜洛克公猪成体成纤维细胞。
1.2.2 猪成体成纤维对G418的耐受性试验
将传至第6代的猪成体成纤维细胞接种到24孔板内,待细胞生长至汇合度为50%~60%时,同时将终质量浓度分别为0、100、200、300、400、500、600、700、800、900和1 000 μg·mL-1的G418加入到培养孔内,每种质量浓度做3个平行对照。37 ℃连续培养14 d,每2 d换液1次,同时补加相同质量浓度的G418。每天在显微镜下观察细胞生长和死亡情况,确定猪成体成纤维细胞对G418的耐受程度。
1.2.3 G418处理供体细胞
将传至第6代的猪成体成纤维细胞接种于6孔板,放入37 ℃、体积分数为5% CO2培养箱中培养。细胞培养至汇合度为50%时,将G418按照0(对照)、100、200 μg·mL-1加入到细胞培养液中,每个质量浓度4个重复,每2 d换液1次,并每天观察细胞状况。细胞培养至第6天时,收集其中1孔细胞进行体细胞核移植,向另外3孔内加入350 μL RLT裂解液(Qiagen),涡旋振荡15 s,根据细胞DNA&RNA抽提试剂盒说明书进行细胞DNA和RNA的抽提。
1.2.4 细胞基因组DNA甲基化的测定
利用亚硫酸盐转化试剂盒对细胞基因组DNA进行亚硫酸盐转化,然后进行甲基化PCR扩增,重复序列LINE-1和微卫星引物序列来自许卫华等[5]。反应程序为95 ℃预变性10 min;95 ℃变性30 s,55 ℃复性25 s,72 ℃延伸30 s,40个热循环;72 ℃延伸7 min;4 ℃条件保存 > 4 min。PCR产物经过0.03 g·mL-1的琼脂糖凝胶电泳进行特异性鉴定,根据扩增特异性直接利用PCR产物纯化试剂盒进行纯化、浓度测定。利用TA连接试剂盒将纯化产物连接至pTZ57R/T载体,转化,涂板,挑取白斑进行菌液培养。阳性菌液经PCR鉴定后,送公司测序,每个样品至少要获得15个以上有效测序结果。测序结果经BiQ Analyzer软件分析后,在线(http://biqanalyzer.bioinf.mpiinf.mpg.de/tools/MethylationDiagrams/index.php)制作高分辨率的甲基化串珠图。
1.2.5 反转录及定量PCR
用反转录试剂盒对细胞RNA进行反转录。实时荧光定量PCR用实时荧光定量PCR试剂盒进行,10 μL PCR反应体系,每次3~4个技术重复。实时荧光定量PCR引物序列为β-actin-F:5′-CCACGAGACCACCTTCAACTC-3′,β-actin-R:5′- TGATCTCCTTCTGCATCCTGT-3′; p53-F:5′- GTACATGACCGAGGTGGTGAGG-3′, p53-R:5′- GGC-GTCTTCCAGTGTGATGATG-3′;CAT-F:5′- GAACCCAGCCCTGACAAGATGC-3′,CAT-R:5′- CCAAGGCCGAATGCGTCTGTT-3′;Cu.Zn-SOD-F:5′- CTCTCCCGCTGCTTCTGGTA-3′,Cu.Zn-SOD-R:5′- CGAAGTA-GATGGTGCCCTGC-3′;Mn-SOD-F:5′-GGACAA-ATCTGAGCCCTAACG -3′,Mn-SOD-R:5′- CCTTGTTGAAACCGAGCC -3′;DNMT1、DNMT3a、Bcl-2、Bax引物来自Kumar等[6],产物长度为100~300 bp。PCR反应参数为:95 ℃预变性、热启动5 min;95 ℃变性10 s,60 ℃复性15 s,72 ℃延伸20 s,45~50个循环。溶解曲线参数:95 ℃ 15 s,55 ℃ 15 s,95 ℃ 15 s。
1.2.6 克隆胚胎的构建
克隆胚胎的构建按照广东温氏研究院动物克隆实验室方法进行[7]。核移植24 h检测卵裂率,168 h后检测囊胚率,并用Hocchst33342对囊胚进行染色、压片,在荧光显微镜下检测囊胚细胞数。
1.2.7 数据处理及统计分析
基因组相对表达数据分析中,各基因Ct值经过内参基因(β-actin)和对照样品正态化处理后,用2-ΔΔCt方法计算相对表达量。用软件SPSS17.0进行数据处理,χ2检验进行差异显著性分析。
不同质量浓度G418处理组供体细胞获得的体细胞克隆胚胎的体外发育数据(分裂率、囊胚率和囊胚细胞总数)用χ2检验进行分析。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 猪成体成纤维细胞的G418耐受试验结果
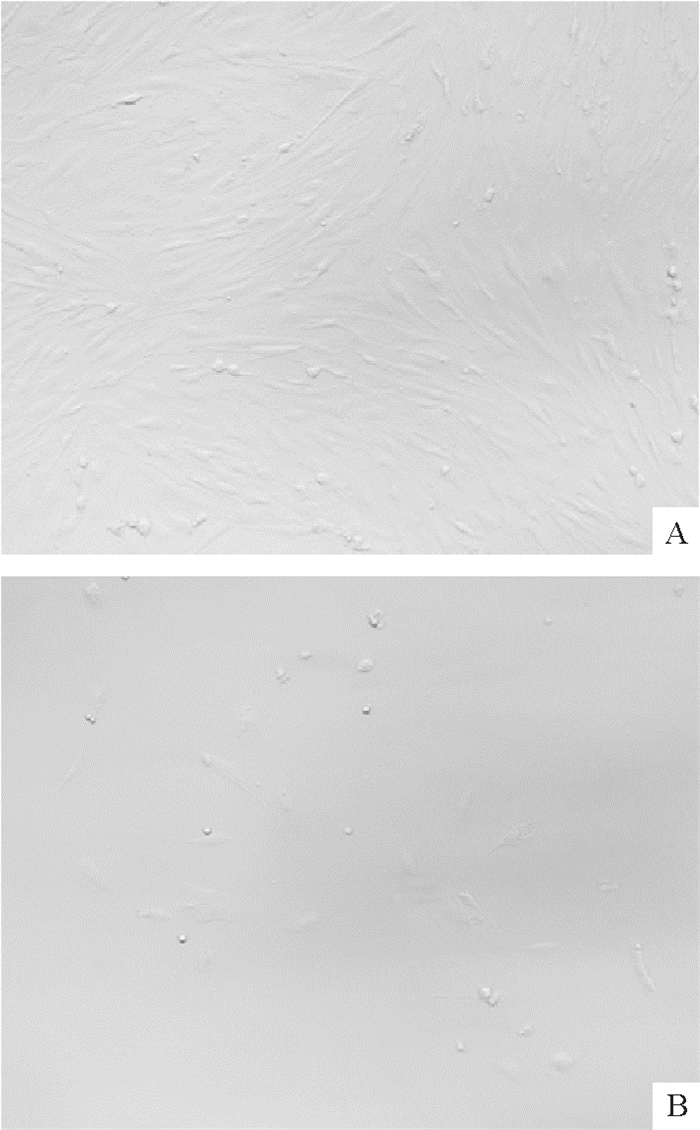
加入不同质量浓度的G418都会导致猪成体成纤维细胞的死亡,细胞死亡后收缩呈点状。G418筛选前后的细胞见图 1。为了摸索出最佳的G418处理质量浓度,分别用100、200、300、400、500、600、700、800、900和1 000 μg·mL-1 G418处理第6代猪成体成纤维细胞,检测细胞对G418的敏感度。常规试验流程中一般以10~14 d内使全部非阳性细胞死亡的G418质量浓度为筛选的最低适宜质量浓度[8],而本研究结果(表 1)显示,当G418质量浓度为100或200 μg·mL-1时,全部细胞死亡时间为9~11 d。这说明后续试验可用100或200 μg·mL-1作为G418处理细胞的适宜质量浓度。
表 1 不同质量浓度G418致死所有细胞所需时间Table 1. Cell death time under different concentrations of G418
2.2 G418处理猪成体成纤维细胞对特异基因表达的影响
2.2.1 抗氧化酶相关基因
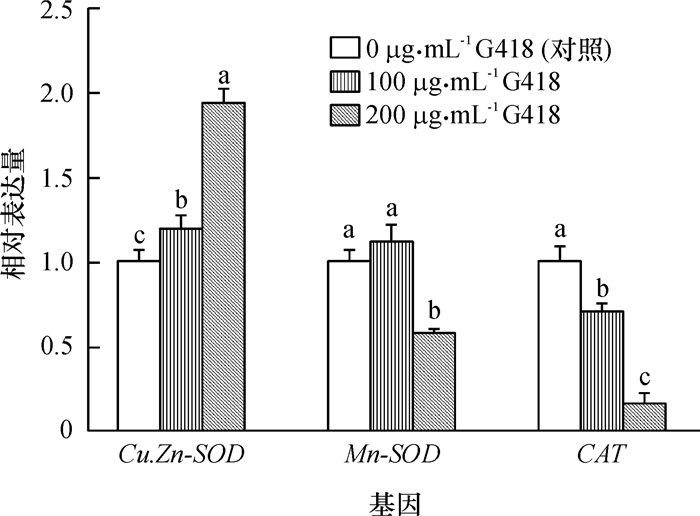
为了研究G418处理是否导致细胞产生氧化应激,收集0、100和200 μg·mL-1G418处理6 d的猪成体成纤维细胞,分别进行q-PCR,检测抗氧化酶相关基因(Cu.Zn-SOD、Mn-SOD和CAT)在mRNA水平的表达情况。由图 2可见,细胞经G418处理后, 随G418质量浓度的升高Cu.Zn-SOD基因的表达水平显著地升高(P<0.05),CAT基因则显著下降(P<0.05),200 μg·mL-1 G418处理组的Mn-SOD基因相对表达量也显著下降(P<0.05)。
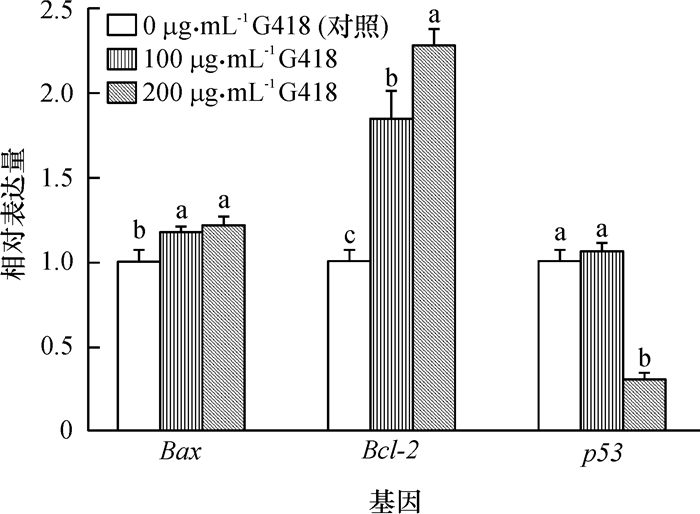
2.2.2 细胞凋亡相关基因
为了研究G418处理是否影响细胞凋亡相关基因表达,用荧光定量PCR检测细胞凋亡基因(Bax、 Bcl-2和p53)在0、100和200 μg·mL-1 G418处理6 d的猪成体成纤维细胞内的表达情况。由图 3可见,猪成体纤维细胞经G418处理后, 其促凋亡基因Bax的表达水平随G418质量浓度的升高显著升高(P < 0.05),抗凋亡基因 Bcl-2 的表达水平也随G418质量浓度显著升高(P < 0.05),且其升高幅度远大于Bax基因。200 μg·mL-1G418处理组的促凋亡基因 p53 表达量显著降低(P < 0.05)。说明经G418处理后存活的细胞抑制凋亡能力较强。
2.3 G418处理猪成体成纤维细胞对细胞甲基化水平的影响
2.3.1 G418处理猪成体成纤维细胞对细胞基因组DNA甲基化水平的影响
G418处理猪成体成纤维细胞6 d后,各组中重复序列LINE-1和微卫星的差异性甲基化区域(DMR)亚硫酸氢盐测序结果见图 4。猪成体成纤维细胞经0 (对照)、100和200 μg·mL-1 G418处理后,LINE-1的DMR甲基化率分别为62.73%、69.46%和69.98%;微卫星的DMR甲基化率分别为68.12%、65.15%和64.41%。同一个DMR与对照组之间的甲基化率差异性采用χ2检验。结果表明处理组与对照组中LINE-1和微卫星的DMR甲基化水平差异不显著(P > 0.05)。
![]() 图 4 不同质量浓度G418处理猪成体成纤维细胞基因组重复序列甲基化水平的影响图中1~3为3个处理组个体重复;1条链表示1个克隆测序结果,1个圈表示1个CpG,其中,黑色实心圆圈表示甲基化的CpG,白色空心圆圈表示未甲基化的CpG,串珠图中“ǀ ”表示该位点发生非CG或TG突变。A、B、C分别为LINE-1对照组0 μg·mL-1G418、100 μg·mL-1 G418处理组、200 μg·mL-1 G418处理组; D、E、F分别为微卫星对照组0 μg·mL-1G418、100 μg·mL-1 G418处理组、200 μg·mL-1 G418处理组。Figure 4. DNA methylation levels of genomic repeat sequences in porcine adult fibroblasts treated with different concentrations of G418
图 4 不同质量浓度G418处理猪成体成纤维细胞基因组重复序列甲基化水平的影响图中1~3为3个处理组个体重复;1条链表示1个克隆测序结果,1个圈表示1个CpG,其中,黑色实心圆圈表示甲基化的CpG,白色空心圆圈表示未甲基化的CpG,串珠图中“ǀ ”表示该位点发生非CG或TG突变。A、B、C分别为LINE-1对照组0 μg·mL-1G418、100 μg·mL-1 G418处理组、200 μg·mL-1 G418处理组; D、E、F分别为微卫星对照组0 μg·mL-1G418、100 μg·mL-1 G418处理组、200 μg·mL-1 G418处理组。Figure 4. DNA methylation levels of genomic repeat sequences in porcine adult fibroblasts treated with different concentrations of G4182.3.2 G418处理猪成体成纤维细胞对细胞DNA甲基化酶相关基因表达水平的影响
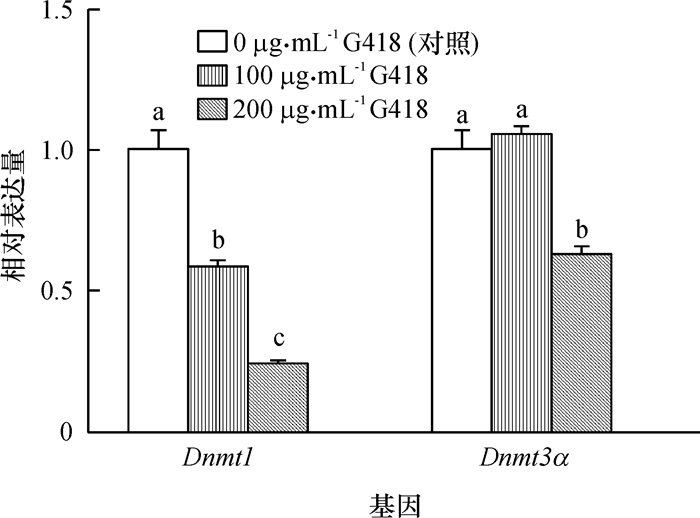
采用荧光定量PCR技术对不同质量浓度G418处理的猪成体成纤维细胞Dnmt1 和Dnmt3a 基因的mRNA表达进行相对定量分析,结果见图 5。随着G418质量浓度升高,Dnmt1 基因表达量显著降低(P<0.05);G418质量浓度为200 μg·mL-1处理组细胞的 Dnmt3a 基因表达显著低于(P<0.05)对照组和100 μg·mL-1处理组(图 5)。Dnmt1 和Dnmt3a 基因的表达量均有所降低,但并不影响细胞整体甲基化水平。
2.4 不同质量浓度G418处理对猪体细胞克隆胚胎体外发育的影响
采用100、200 μg·mL-1G418处理6 d后的猪成体成纤维细胞作为供体细胞进行核移植,并在体外培养克隆胚胎发育至囊胚阶段,检测胚胎的融合率、卵裂率、囊胚率及囊胚细胞数,结果见表 2。由表 2可见,随着G418质量浓度的升高,融合率、卵裂率显著降低(P < 0.05);囊胚率100、200 μg·mL-1 G418处理组显著低于(P<0.05)对照组,但100、200 μg·mL-1 G418处理组间差异不显著(P > 0.05);囊胚细胞数并没有显著变化(P > 0.05)。G418单独处理核供体细胞可能会使核移植胚胎体外发育能力下降。
表 2 G418处理猪成体成纤维细胞对猪体细胞克隆胚胎体外发育性能的影响1)Table 2. The effects of G418 on the in vitro development of porcine somatic cell nuclear transfer embryos
3. 讨论与结论
体细胞核移植技术被广泛应用于生产转基因动物,尤其是基因修饰大动物。供体细胞提供克隆胚胎的主要遗传物质,是体细胞克隆成功与否的关键因素之一。供体细胞的细胞形态、周期、活性以及供体的个体差异、性别年龄等都会对克隆效率有影响[9]。
正常机体的自由基氧化作用与抗氧化防御作用处于动态平衡状态。外界环境刺激和机体内氧化反应代谢过程中产生大量活性氧(Reactive oxygen species, ROS),对酶及转录因子的活化、mRNA表达等有较大的影响[10]。本研究结果显示SOD及CAT基因的mRNA表达水平出现改变,这可能与细胞抵抗外来刺激有关,但细胞的抗氧化能力是否发生改变,更准确的应该在翻译水平上对SOD及CAT基因的活性进行检测。ROS对细胞膜[11]或者DNA[12]产生伤害,促使凋亡相关基因表达的改变而引发细胞凋亡[13]。Bcl-2蛋白家族与 p53基因是重要的细胞凋亡调节因子,两者相互作用,调控细胞凋亡[14]。当Bcl-2和Bax 基因形成异源二聚体比例增加时,抑制细胞凋亡。本研究结果显示,G418处理后细胞 Bcl-2/Bax 基因的比例有所提高,促凋亡基因p53的表达量下调,这可能是细胞自身应对G418所带来的外来刺激而产生的一种自我保护,通过调节自身基因的表达,抑制细胞发生凋亡。
在体细胞核移植中,DNA甲基化是调控供体核内重编程的一种方式,对恢复细胞的全能性、提高体细胞核转移的效率具有重要意义[15]。哺乳动物基因组中,转座元件占到了50%左右,LINE是转座元件中所占比例最大的一种类型。LINE-1是LINE中的主要类型,在染色体中散在分布,约占小鼠和人类基因组的17%~20%[16]。微卫星是真核生物基因组重复序列中的主要组成部分,随机、广泛地分布于基因组中,大约占到猪全基因组的0.85%[17]。因此LINE-1和微卫星的甲基化水平基本可代表整个基因组的甲基化水平。Dnmt1和Dnmt3a分别是维持DNA甲基化和从头甲基化的关键酶。研究表明,敲除小鼠的Dnmt1 基因,会导致严重的基因组去甲基化或胚胎死亡;敲除Dnmt3a 基因,小鼠在出生后4周内死亡[18]。本研究中,经G418处理后,核供体细胞的Dnmt1 和Dnmt3a 基因的mRNA表达量均显著下调,表明G418会影响细胞内重要DNA甲基转移酶的mRNA表达,但不影响细胞整体甲基化水平。本研究经高质量浓度G418处理后的供体细胞进行核移植所获得的重构胚的融合率、卵裂率和囊胚率均显著低于对照组,而囊胚细胞总数没有显著差异。这说明供体基因组的整体甲基化水平与克隆胚胎的发育能力可能没有必然联系。这可能是核移植之后G418的毒性作用仍然存在于细胞内,从而影响了细胞生长及克隆胚胎的发育性能。顾晓龙等[19]利用RG108处理供体细胞并进行甲基化水平的检测,发现供体细胞整体甲基化水平的改变可能对提高核移植效率没有直接影响。Bonk等[20]使用低密度甲基化芯片技术检测克隆供体细胞、精子、克隆囊胚、体内囊胚等的甲基化水平,同样发现供体细胞整体甲基化水平的差异并非体外生产的囊胚发育率低下的主要原因,而某些区域特定的DNA甲基化修饰才是促进重构胚胎发育的关键。
转基因与非转基因细胞作为供体细胞进行体细胞核移植,两者之间克隆胚胎体外发育效率是否存在差异,当今的报道说法不一,这可能是由于不同类型的供体细胞、培养体系、筛选药物、培养时间、转基因片段大小以及转染方法等差异所造成。本研究经高质量浓度G418处理后的核供体细胞进行核移植所获得的重构胚的融合率、卵裂率和囊胚率均显著低于对照组,而囊胚细胞数没有显著差异,这可能是细胞刚经历外界的刺激后马上进行核移植,G418对细胞仍然存在毒性而影响细胞生长及克隆胚胎的发育性能。后续应在细胞进行G418处理后,撤走药物继续培养传代,使药物的毒性作用降至最低,再进行核移植,可能结果更加客观。
本研究发现经G418处理后的核供体细胞进行核移植,克隆胚胎体外发育效率显著下降。在制备转基因动物时,利用电转或脂质体方法进行转染会影响供体细胞膜,再加入G418进行筛选,会对细胞造成更大的损伤,从而影响转基因克隆胚胎体外发育效率。因此,进行转基因细胞系阳性克隆筛选时可考虑降低G418的质量浓度,或者利用套环法或刮除法结合有限稀释法,减少对供体细胞的伤害,这可能有利于转基因克隆胚胎的发育。
-
图 4 不同质量浓度G418处理猪成体成纤维细胞基因组重复序列甲基化水平的影响
图中1~3为3个处理组个体重复;1条链表示1个克隆测序结果,1个圈表示1个CpG,其中,黑色实心圆圈表示甲基化的CpG,白色空心圆圈表示未甲基化的CpG,串珠图中“ǀ ”表示该位点发生非CG或TG突变。A、B、C分别为LINE-1对照组0 μg·mL-1G418、100 μg·mL-1 G418处理组、200 μg·mL-1 G418处理组; D、E、F分别为微卫星对照组0 μg·mL-1G418、100 μg·mL-1 G418处理组、200 μg·mL-1 G418处理组。
Figure 4. DNA methylation levels of genomic repeat sequences in porcine adult fibroblasts treated with different concentrations of G418
表 1 不同质量浓度G418致死所有细胞所需时间
Table 1 Cell death time under different concentrations of G418

表 2 G418处理猪成体成纤维细胞对猪体细胞克隆胚胎体外发育性能的影响1)
Table 2 The effects of G418 on the in vitro development of porcine somatic cell nuclear transfer embryos

-
[1] 金其煌. 乙酰胆碱酯酶在细胞凋亡中的作用及G418诱导细胞凋亡的分子机制[D]. 上海: 中国科学院研究生院(上海生命科学研究院), 2004. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-80100-2004138063.htm [2] JIN Q H, ZHAO B, ZHANG X J. Cytochrome c release and endoplasmic reticulum stress are involved in caspase-dependent apoptosis induced by G418[J]. Cell Mol Life Sci, 2004, 61(14): 1816-1825. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK200502979316
[3] 李文哲. 体细胞核移植技术生产转人β-防御素3基因牛的研究[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2010. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/article/cdmd-10712-2010149414.htm [4] LIU Y, LI J, LOVENDAHL P, et al. In vitro manipulation techniques of porcine embryos: A meta-analysis related to transfers, pregnancies and piglets[J]. Reprod Fertil Dev, 2015, 27(3): 429-439. doi: 10.1071/RD13329
[5] 许卫华, 吴珍芳, 余波, 等.供体细胞系基因座位特异DNA甲基化多态性及其与猪克隆效率的关联分析[J].广东农业科学, 2014, 41(12): 165-170. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-874X.2014.12.036 [6] KUMAR B M, JIN H, KIM J, et al. Differential gene expression patterns in porcine nuclear transfer embryos reconstructed with fetal fibroblasts and mesenchymal stem cells[J]. Dev Dynam, 2007, 236(2): 435-446. doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1097-0177
[7] 周荣, 罗绿花, 石俊松, 等.胚胎培养液中能量底物对猪体细胞克隆胚胎体外培养的影响[J].广东畜牧兽医科技, 2015, 40(5): 28-31. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-8567.2015.05.009 [8] 潘登科. 影响猪体细胞克隆胚胎发育能力的因素研究[D]. 北京: 中国农业大学, 2005. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=degree&id=Y773675 [9] 张小建, 李键, 王蕊, 等.供体细胞对哺乳动物体细胞核移植的影响[J].动物医学进展, 2007, 28(3): 82-85. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-5038.2007.03.023 [10] 李武. 活性氧对生长抑素的调节与代谢综合征的关系研究[D]. 南京: 江南大学, 2010. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10295-2010075452.htm [11] AITKEN R J, CLARKSON J S, FISHEL S. Generation of reactive oxygen species, lipid peroxidation, and human sperm function[J]. Biol Reprod, 1989, 41(1): 183-197. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod41.1.183
[12] HALLIWELL B, ARUOMA O I. DNA damage by oxygen-derived species: Its mechanism and measurement in mammalian systems[J]. FEBS Lett, 1991, 281(1/2): 9-19. doi: 10.1016-0014-5793(91)80347-6/
[13] 王晓静.氧化应激相关的细胞凋亡过程中基因表达改变[J].国外医学(肿瘤学分册), 2004, 31(1): 10-14. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-422X.2004.01.003 [14] 周桔, 罗荣保, 汤长发, 等. Bcl-2蛋白家族和p53基因在细胞凋亡中的调控效应[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2007, 11(10): 1950-1952. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1673-8225.2007.10.048 [15] 颜昊. DNA甲基化修饰与体细胞核移植的关系[J].生命科学, 2009, 21(4): 542-548. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10126-1013293408.htm [16] ZAMUDIO S, TORRICOS T, FIK E, et al. Hypoglycemia and the origin of hypoxia-induced reduction in human fetal growth[J]. PLoS One, 2010, 5(1): e8551. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0008551
[17] 戚文华, 蒋雪梅, 肖国生, 等.猪全基因组中微卫星分布规律[J].畜牧与兽医, 2014, 46(8): 9-13. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/xmysy201408003 [18] OKANO M, BELL D W, HABER D A, et al. DNA methyltransferases Dnmt3a and Dnmt3b are essential for de novo methylation and mammalian development[J]. Cell, 1999, 99(3): 247-257. doi: 10.1016/S0092-8674(00)81656-6
[19] 顾晓龙, 张廷宇, 戴建军, 等. RG108对猪胎儿成纤维细胞甲基化水平及克隆胚胎发育的影响[J].核农学报, 2014, 28(1): 14-21. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hnxb201401003 [20] BONK A J, LI R, LAI L, et al. Aberrant DNA methylation in porcine in vitro, parthenogenetic, and somatic cell nuclear transfer-produced blastocysts[J]. Mol Reprod Dev, 2008, 75(2): 250-264. doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1098-2795



 下载:
下载: