Degradation dynamics of bifenthrin in cabbage and soil
-
摘要:目的
建立残留联苯菊酯的检测方法,研究质量分数1%联苯菊酯·噻虫咹颗粒剂中联苯菊酯在甘蓝Brassica oleracea和土壤中的残留及消解动态。
方法在广东广州市、广西南宁市和湖北潜江市进行田间试验,联苯菊酯在0.01~1.00 mg·kg-1水平范围内取0.01、0.10、0.50 mg·kg-1添加,样品中的联苯菊酯经乙腈超声波辅助提取,弗罗里硅土固相萃取柱净化,气相色谱(GC-ECD)检测,外标法定量,得到联苯菊酯在甘蓝和土壤中的残留及消解动态。
结果联苯菊酯在甘蓝中的平均回收率为83.64%~96.44%,相对标准偏差为3.26%~7.24%;在土壤中平均回收率为86.76%~90.09%,相对标准偏差为2.17%~4.94%。联苯菊酯在土壤中的残留半衰期为6.77~13.51 d,在甘蓝中未检出。
结论联苯菊酯属易降解农药;该施药方法安全,值得借鉴。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo establish a detection method of bifenthrin, and to study the residue and degradation dynamics of bifenthrin in the form of 1% bifenthrin·clothianidin granules in cabbage and soil.
MethodField experiments were conducted in Guangzhou of Guangdong, Nanning of Guangxi and Qianjiang of Hubei.Bifenthrin was added at three levels of 0.01, 0.10, 0.50 mg·kg-1 in the range from 0.01 to 1.00 mg·kg-1. Bifenthrin was extracted from cabbage and soil using ultrasonic-assisted acetonitrile extraction, cleaned up using a florisil solid phase extraction column, then detected by GC with ECD detector, and quantified by external standard method.
ResultThe average recovery rates of bifenthrin in cabbage were 83.64 %-96.44% with 3.26%-7.24%RSD, and the average recovery rates in soil were 86.76%-90.09% with 2.17%-4.94%RSD. The half-life of bifenthrin in soil was 6.77-13.51 d.No bifenthrin residue was detected in cabbage at harvest.
ConclusionBifenthrin is an easily degradable pesticide. Using 1% bifenthrin·clothianidin granules as pesticide is safe and recommended.
-
Keywords:
- bifenthrin /
- granular formulation /
- cabbage /
- soil /
- residue detection
-
联苯菊酯,化学名称为(1R, S)-顺式-(Z)-2, 2-二甲基-3-(2-氯-3, 3, 3-三氟-1-丙烯基)环丙烷羧酸-2-甲基-3-苯基苄酯,是由FMC公司开发的一种低毒、广谱、高效的拟除虫菊酯类杀虫剂,又称氟氯菊酯、天王星、虫螨灵或毕芬宁[1]。常用于防治白粉虱Trialeurodes vaporariorum、烟粉虱Bemisia tabaci、茶小绿叶蝉Empoasca pirisuga等常见害虫[2]。联苯菊酯在市场上常见的剂型有乳油、水乳剂、悬浮剂等[3]。国内外有很多关于联苯菊酯在茶叶Camelli sinensis、棉花Gossypiums spp.、番茄Solanum lycopersicum等作物上的消解动态的报道[4-8],但鲜见关于颗粒剂的报道。
联苯菊酯·噻虫胺为美国富美实公司最新研发的一种新型混配杀虫剂,主要用于防治黄曲条跳甲Phyllotreta striolata,兼治蝼蛄Gryllotalpa、小地老虎Agrotis ypsilon等地下害虫,对作物的生长没有影响[9]。该混配颗粒制剂在甘蓝Brassica oleracea苗期沟施或撒施,整个生育期只需用药1次,省时省力。但一次性大量用药,在作物、土壤和水体中残留的联苯菊酯会对人类健康和生态环境造成危害[10-12]。因此,建立对联苯菊酯颗粒剂中联苯菊酯在甘蓝田中的残留消解试验及检测分析方法是必要的。用于联苯菊酯的检测分析方法主要有气相色谱法(GC-ECD)、高效液相色谱法、毛细管电泳[13-15]等。本研究采用有较好精确性和灵敏度的GC-ECD检测甘蓝和土壤中残留的联苯菊酯。本研究根据《农药登记残留田间实验标准操作规程》[16]设计田间试验,检测联苯菊酯·噻虫咹颗粒剂施用于甘蓝田后,联苯菊酯在甘蓝及土壤中的消解动态和最终残留,并对该施药方法进行安全风险评估, 为规避农药残留风险提供依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 仪器与试剂
岛津GC-2010Plus气相色谱仪(配ECD检测器、自动进样器、化学工作站);组织捣碎机MJ-25BM02C(常州博远实验分析仪器厂);超声波清洗器KH-500型(昆山创超声仪器有限公司);旋转蒸发器EYELA N-1100(日本EYELA公司);氮吹仪(上海安普科学仪器有限公司);循环水真空泵SHB-Ⅲ;烘箱S.C.101型(上海试验仪器厂);电子天平(万分之一) BS210S型(德国SaRtoRius公司);精密移液枪(德国艾本德公司)。
联苯菊酯标准品:100 μg·mL-1(农业部环境保护科研监测所);1% (w)联苯菊酯·噻虫胺颗粒剂(肇庆市真格生物科技有限公司);乙腈、正己烷、丙酮、氯化钠均为分析纯(天津富宇精细化工有限公司), 甲醇和乙腈为色谱纯(美国MREDA); SPE小柱(Florisil,标准样品为1g);超纯水,电阻值≥18.0 MΩ。
1.2 田间试验方案及样品采集
联苯菊酯在甘蓝和土壤中消解动态和最终残留试验在广东广州市、广西南宁市、湖北潜江市进行。试验小区面积均为20 m2,设空白对照区,每个处理设3个重复。各小区间设保护间隔。
消解动态试验在甘蓝移栽后,制剂以高剂量有效成分1 200 g·hm-2 (2倍最高推荐剂量)于苗期(作物生长状态对应BBCH编号18~20)均匀撒施于沟(穴)中,并覆土,施药1次。土壤残留消解动态试验另选未种植甘蓝的空白地进行。于药后0(2 h)、1、3、5、7、14、21、30、45 d,采集甘蓝植株及土壤样品。甘蓝样品每次每小区以随机采样法采集不少于1 kg生长正常、无病害的植株,去除根部及腐烂叶。土壤样品每小区随机多点采集0~10 cm的土壤不少于1 kg。样品装入采样袋中,贴好标签,贮存于-20 ℃冰柜中。
最终残留试验设低剂量有效成分600 (最高推荐剂量)和1 200 g·hm-2 (2倍最高推荐剂量),施药1次,于药后7、15、30 d分别采集甘蓝样品不少于2 kg和地表以下0~15 cm的土壤样品。样品分装后贴好标签,-20 ℃冰柜中保存。
1.3 联苯菊酯残留分析方法
1.3.1 甘蓝和土壤中联苯菊酯提取
准确称取10 g甘蓝试样放入匀浆机中,加入100 mL乙腈,在匀浆机中高速匀浆2 min后滤纸过滤,滤液收集到装有5~7 g氯化钠的100 mL具塞量筒中,盖上塞子,剧烈震荡1 min,在室温下静置30 min,使乙腈相和水相分层。从具塞量筒中吸取50 mL上清液,放入150 mL的平底烧瓶中,40 ℃下减压浓缩至近干,待净化。准确称取20 g土壤试样放入三角瓶中,加入40 mL乙腈,在超声波清洗器中超声提取30 min,减压抽滤,准确吸取滤液5 mL于氮吹仪上蒸发近干,5 mL正己烷定容,待进样测定。每处理重复3次。
1.3.2 样品净化
由于甘蓝中有较多的杂质,需要进样前净化样品。依次用5 mL正己烷-丙酮(体积比90: 10)、5 mL正己烷活化Florisil柱,5 mL正己烷上样,10 mL正己烷-丙酮(体积比90: 10)淋洗,15 mL洗脱正己烷-丙酮(体积比90: 10)。收集洗脱液,浓缩后5 mL正己烷定容,待进样测定。
1.3.3 气相色谱分析条件
色谱柱:DB-5(30.00 m× 0.25 mm×0.25 μm)石英毛细管柱;柱初始温度:170 ℃,保留2 min,10 ℃·min-1升至250 ℃,保留6 min; 进样口温度:260 ℃,不分流;检测器温度:300 ℃,尾吹气:30 mL·min-1;载气为氮气(φ为99.99%):3.0 mL·min-1;进样量:1 μL。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 联苯菊酯在甘蓝和土壤中的添加回收率及检出限
在线性范围(0.01~1.00 mg·kg-1)内,分别在空白甘蓝和空白土壤中,准确添加3个浓度(0.01、0.10、0.50 mg·kg-1)的联苯菊酯标准溶液,每个浓度重复5次,测定回收率。气相色谱试验显示联苯菊酯峰形及重现性较好且无杂质干扰。联苯菊酯在甘蓝中的平均回收率为83.64 %~96.44%,相对标准偏差为3.26%~7.24%,在土壤中平均回收率为86.76%~90.09%,相对标准偏差为2.17%~4.94%(表 1)。方法的准确度和精密度均符合农药残留分析的要求。该方法的最小检出量为6.10×10-3ng,联苯菊酯的最低检出浓度为0.01 mg·kg-1。
表 1 联苯菊酯在甘蓝和土壤的添加回收率Table 1. Recovery rates of bifenthrin in cabbage and soil samples
2.2 联苯菊酯在甘蓝和土壤的消解动态
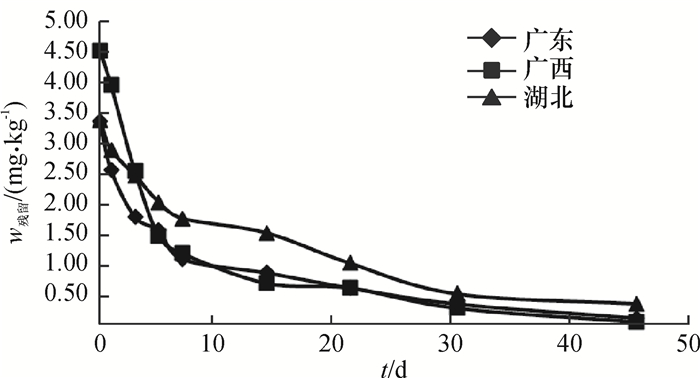
结果表明,当施药量为1 200 g·hm-2时,联苯菊酯在土壤中的原始沉积量为3.327 2~4.506 1 mg·kg-1,药后45 d残留量为0.025 7~0.327 9 mg·kg-1,消解率为90.19%~99.43%。在甘蓝中未检出。联苯菊酯在土壤中降解动态曲线见图 1,降解半衰期为6.77~13.51 d(表 2)。
表 2 联苯菊酯在土壤中的残留消解动态Table 2. Degradation dynamics of bifenthrin in soil
2.3 联苯菊酯在甘蓝和土壤中的最终残留
最终残留试验研究了施药1次后7、15、30 d甘蓝样品和土壤样品中联苯菊酯的残留量。结果(表 3)表明,推荐使用最高剂量(有效成分含量600 g·hm-2)下,甘蓝收获时,联苯菊酯在广东土壤中残留量为0.055 3 mg·kg-1,广西、湖北土壤中均未检出。2倍(有效成分含量1 200 g·hm-2)施药剂量时,甘蓝收获时在广东、广西、湖北土壤中联苯菊酯残留量分别为0.274 3、0.593 5和0.259 4 mg·kg-1。甘蓝均未检出残留联苯菊酯。
表 3 联苯菊酯在甘蓝和土壤中的最终残留Table 3. Final residue amounts of bifenthrin in cabbage and soil
3. 结论
建立了较为简便的联苯菊酯在甘蓝和土壤中残留的检测方法。试验结果表明:样品中的联苯菊酯经乙腈超声辅助提取,弗罗里硅土固相萃取柱净化,正己烷定容,在气相色谱程序升温的分析条件下有良好的峰形。该方法的添加回收率、灵敏度及准确度均符合农药残留分析的要求。
农药有效成分在作物上的降解与作物种类和农药制剂剂型相关。联苯菊酯乳油在绿豆Vigna radiata、豌豆Pisum sativum、辣椒Capsicum annuum和甘蓝上的半衰期分别为3.3、2.1、9.6、7.7 d[17-18]。联苯菊酯可溶液剂在棉花上的半衰期为4.2 d。本试验研究表明1% (w)联苯菊酯·噻虫胺颗粒剂,在甘蓝试验田以2倍最高推荐剂量(有效成分1 200 g·hm-2)施用,联苯菊酯在土壤中的消解半衰期为6.77~13.51 d, 降解较快,属于易降解农药, 且在土壤中不移动,对非靶标生物安全。该混配颗粒剂中的联苯菊酯不具有内吸性,不能通过内吸传导到地上植株[19]。最终残留结果表明,最高推荐使用剂量(有效成分600 g·hm-2)下,甘蓝收获时土壤中联苯菊酯的最大残留量为0.055 3 mg·kg-1,基本完全消解,不会造成土壤污染,且在甘蓝上未检出,低于我国制定的结球甘蓝上联苯菊酯MRL值0.2 mg·kg-1[20]。该商品制剂使用较为安全,这种省时省力的1次性大量施药的方法值得借鉴,在防治蔬菜类害虫方面有广阔的应用前景。
-
表 1 联苯菊酯在甘蓝和土壤的添加回收率
Table 1 Recovery rates of bifenthrin in cabbage and soil samples

表 2 联苯菊酯在土壤中的残留消解动态
Table 2 Degradation dynamics of bifenthrin in soil

表 3 联苯菊酯在甘蓝和土壤中的最终残留
Table 3 Final residue amounts of bifenthrin in cabbage and soil

-
[1] 刘长令.世界农药信息手册[M].北京:化学工业出版社, 2000: 12-14. [2] 张海伟, 冯慧, 文一, 等.联苯菊酯在干茶中的残留和降解行为研究[J].河南农业科学, 2013, 42(10): 84-87. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-3268.2013.10.021 [3] 邹文娟, 尹红.联苯菊酯3种剂型对台湾乳白蚁的药效研究[J].中华卫生杀虫药械, 2009, 15(3): 197-199. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WSSC200903011.htm [4] GAO N, GUO X, ZHANG K, et al. High-performance liquid chromatography and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry methods for the determination of imidacloprid, chlorpyrifos, and bifenthrin residues in tea leaves[J]. Instrum Sci Technol, 2014, 42(3): 267-277. doi: 10.1080/10739149.2013.862629
[5] YOU X, JIANG N, LIU F, et al. Dissipation and residue of bifenthrin in wheat under field conditions[J]. B Environ Contam Tox, 2013, 90(2): 238-241. doi: 10.1007/s00128-012-0903-5
[6] CHAUHAN R, MONGA S, KUMARI B. Dissipation and decontamination of bifenthrin residues in tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum Mill)[J]. B Environ Contam Tox, 2012, 89(1): 181-186. doi: 10.1007/s00128-012-0629-4
[7] 方丽萍, 邬元娟, 李瑞菊, 等.联苯菊酯在棉花和土壤中的残留和降解行为研究[J].生态环境学报, 2012, 21(8): 1493-1497. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/tryhj201208022 [8] 吴光远, 曾明森, 夏会龙, 等.联苯菊酯茶园残留与使用安全性[J].福建农业学报, 2013, 28(4): 366-371. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0384.2013.04.013 [9] 吴燕君, 王道泽, 洪文英, 等.联苯·噻虫胺对小白菜黄曲条跳甲的控制作用[J].浙江农业科学, 2012(2): 194-197. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0528-9017.2012.02.027 [10] JIN M, ZHANG X, WANG L, et al. Developmental toxicity of bifenthrin in embryo-larval stages of zebrafish[J]. Aquat Toxicol, 2009, 95(4): 347-354. doi: 10.1016/j.aquatox.2009.10.003
[11] CHEN S, LUO J, HU M, et al. Microbial detoxification of bifenthrin by a novel yeast and its potential for contaminated soils treatment[J/OL]. Plos one, 2012, 7(2): e30862[2015-06-10]. http://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0030862
[12] JIANG W, KON R T, OTHOUDT R A, et al. Method development, validation, and analysis of bifenthrin residues in fresh and dry cilantro foliages and cilantro seeds using GC-ECD[J]. B Environ Contam Tox, 2004, 73(1): 9-16. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=JJ028031968
[13] 张丹, 张进忠, 骆云中, 等.高效液相色谱同时测定果园土壤中的乐果、甲基托布津和联苯菊酯残留[J].西南师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2012, 37(3): 91-95. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5471.2012.03.018 [14] 董振霖, 杨春光, 薛大方, 等.气相色谱-质谱法测定植物源性食品中残留的联苯菊酯[J].色谱, 2009, 27(1): 82-85. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-8713.2009.01.016 [15] HERNANDEZ-BORGES J, FRIAS-GARCIA S, CIFUENTES A, et al. Pesticide analysis by capillary electrophoresis[J]. J Sep Sci, 2004, 27(12): 947-963. doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1615-9314
[16] 王运浩, 季颖, 龚勇, 等.农药登记残留田间试验标准操作规程[M].北京:中国标准出版社, 2007: 68-72. [17] BLETSOU A A, HANAFI A H, DASENAKI M E, et al. Development of specific LC-ESI-MS/MS methods to determine bifenthrin, lufenuron, and iprodione residue levels in green beans, peas, and chili peppers under Egyptian field conditions[J]. Food Anal Method, 2013, 6(4): 1099-1112. doi: 10.1007/s12161-012-9515-2
[18] 陈丽霞, 韩丙军, 彭黎旭.热带气候下联苯菊酯在甘蓝和土壤中的残留降解动态[J].现代农药, 2008, 7(5): 32-35. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-5284.2008.05.009 [19] 王爱芬, 李小鹰.联苯菊酯的应用开发研究综述[J].白蚁科技, 2000, 17(2): 3-10. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK200000677236 [20] 农业部, 国家卫生计生委. 食品中农药最大残留限量: GB 2763—2014[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2014.



 下载:
下载: