Establishment of an evaluation system for field resistance against sugarcane pokkah boeng
-
摘要:目的
探讨甘蔗梢腐病田间分级标准和品种(系)区域性抗病差异。
方法以11个甘蔗新品种(系)和广西当前主栽品种ROC22在南宁、柳州、河池、百色、北海和崇左6个试验点梢腐病的发病情况为依据,建立甘蔗梢腐病田间病害分级标准及品种(系)抗性评价体系。
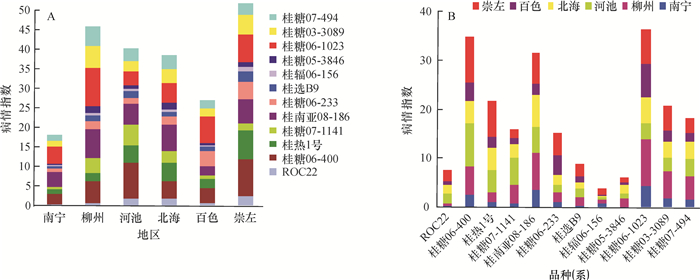
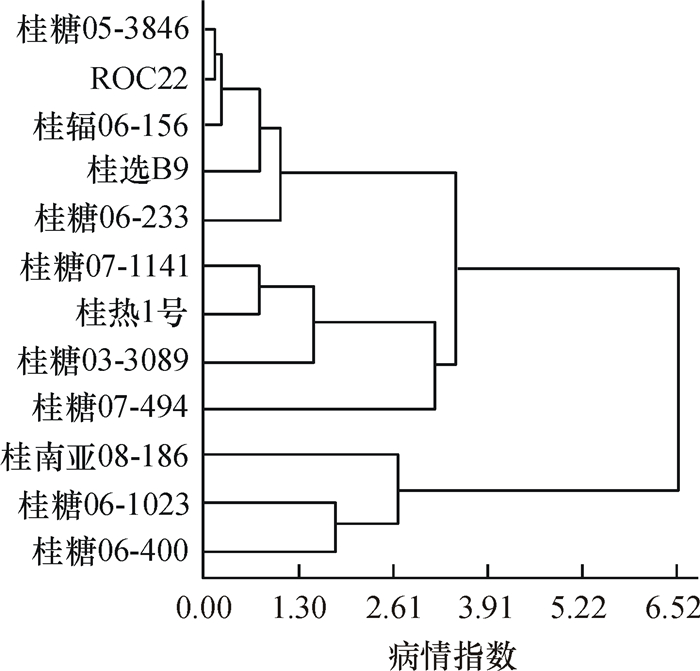
结果参试点新植蔗梢腐病发病率为0.16%~23.82%(平均为3.51%),病情指数为0.03~16.48(平均为3.45),宿根蔗梢腐病发病率为0~25.89%(平均为4.27%),病情指数为0~17.37(平均为4.61)。建立了田间抗性评价标准,并将抗性水平划分为高抗、抗病、中抗、中感、感病和高感6个不同抗性等级。研究的12个品种(系)中没有发现高抗和高感材料,其中桂辐06-156、桂糖05-3846、桂选B9和ROC22抗性最好,表现为抗性;桂糖06-1023和桂糖06-400抗性最差,均表现为感病。根据病情指数对12个材料进行聚类分析,结果显示,不同甘蔗品种(系)的聚类与抗性等级划分的结果一致。梢腐病在广西蔗区的发生呈现区域性,崇左、柳州和河池3个试验点属于梢腐病重发区;北海次之;百色和南宁2个试验点属于轻发区。
结论不同甘蔗种植区域、不同品种(系)以及不同植期存在感抗梢腐病差异性。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo discuss the field grading standard on sugarcane pokkah boeng disease severity, and study regional and varietal(clonal) differences in occurrence of pokkah boeng disease.
MethodThe occurrence of pokkah boeng disease on 11 new sugarcane varieties (lines) and the dominant cultivar ROC22 in Guangxi was investigated in six sites including Nanning, Liuzhou, Hechi, Baise, Beihai and Chongzuo cities. The grading standard on sugarcane pokkah boeng disease and the resistance evaluation system were established.
ResultThe incidence and disease severity index (DSI) of new-planting sugarcane were 0.16%-23.82% (average 3.51%) and 0.03-16.48 (average 3.45) respectively, and those of ratoon cane were 0-25.89% (average 4.27%) and 0-17.37 (average 4.61). According to the new standard, six resistance grades were established, including high resistance (HR), resistance (R), medium resistance (MR), medium susceptible (MS), susceptible (S) and high susceptible (HS). HR and HS sugarcane varieties (clones) were not found in the 12 tested materials. Among the 12 varieties, Guifu06-156, Guitang05-3846, GuixuanB9 and ROC22 belonged to R grade and demonstrated the highest resistance against pokkah boeng disease, and Guitang06-1023 and Guitang06-400 were S grade with the lowest resistance. The 12 tested sugarcane varieties(clones) were clustered according to the DSI, and the result agreed with that of resistance grading. The incidence of pokkah boeng disease showed regional difference in Guangxi. The sugarcane areas of Chongzuo, Liuzhou and Hechi were the most serious, followed by Beihai, and Baise and Nanning were the least serious.
ConclusionThere were distinct differences among different sugarcane areas, among varieties(lines)and among planting seasons regarding the susceptibility and resistance against pokkah boeng disease.
-
Keywords:
- sugarcane /
- pokkah boeng /
- grading standard /
- resistance evaluation /
- cluster analysis
-
甲型流感病毒可引起包括人、猪、马、鸟类及海洋动物感染的病毒性传染病,其主要宿主是水禽。猪呼吸道上皮细胞具有 2种流感病毒受体,能够同时感染人流感病毒和禽流感病毒,被认为是流感病毒的中间宿主或流感病毒的“混合器”。在猪体内同时感染的多种流感病毒有可能通过重组,或在对哺乳动物的适应过程,产生新的变异毒株[1]。1993年Fan等[2]在中国南方以及东南亚地区分离出类禽(Eurasian avian-like,EA)H1N1 SIV,现该类病毒已在亚洲多个地区猪群中广泛流行。2009年甲型H1N1/2009流感(Pdm09H1N1)在墨西哥暴发,并且迅速蔓延感染至其他国家地区。Pdm09H1N1流感病毒来源于猪,是一种人、猪、禽三源重组的病毒[3]。Chen等[4]在对华南地区流感病毒血清学调查中发现,同1份血清中可以同时检测到3种亚型流感病毒抗体,表明H1N1猪流感的流行状况复杂。欧亚类禽H1N1、Pdm09H1N1、经典H1N1等亚型猪流感病毒长期共存在我国猪群中[5],严重影响猪群的健康和公共卫生安全。
本研究对华南农业大学兽医学院分离到的猪流感病毒SWSS1株、SWL6株和Pdm091057株,进行生物信息学分析,并制备全病毒灭活疫苗,免疫雌性新西兰大白兔,采用血凝抑制试验方法,对流行于我国猪群中的H1N1亚型猪流感病毒不同分支之间的血清学交叉特性进行分析,以期为血清学诊断提供参考依据,同时也为流感病毒的通用疫苗的研制及防控奠定基础。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料
7株流感病毒株由华南农业大学兽医学院传染病实验室提供,分别为SWSS1:A/swine/Guangdong/SS1/2012(HINI)、SWL6:A/swine/Guangdong/L6/2012(HINI)、Pdm091057:A/Guangdong/1057/2010(H1N1)、A/swine/Guangdong/ l22/2010(H3N2)、A/Chicken/Shanghai/ 10/2001(H9N2)、A/Duck/Anhui/1/2006/(H5N1)、A/Pigeon/Shanghai/S1421/2013(H7N9),其中,A/swine/Guangdong/SS1/2012(HINI)、A/swine/Guangdong/L6/2012(HINI)和A/Guangdong/1057/2010(H1N1)作为免疫原用于制备灭活疫苗。12只雌性新西兰大白兔购自南方医科大学动物实验中心;SPF鸡胚购自广州市华南农业大学生物药品有限公司。
1.2 方法
1.2.1 病毒的增殖 病毒增殖按照文献[6]的方法进行。
1.2.2 病毒血凝效价、EID50及病毒的鸡胚生长曲线的测定 待检病毒液的血凝试验按照世界卫生组织的标准进行,病毒株的EID50按照文献[6]的方法进行测定。将100 EID50的原始病毒接种9日龄的SPF鸡胚,分别在24、36、48、60和72 h收集尿囊液进行血凝效价测定,并绘制鸡胚生长曲线。
1.2.3 遗传和抗原相关性分析 在GenBank中选择具有代表性的H1N1猪流感病毒不同分支参考毒株,利用生物信息学软件分析SWSS1、SWL6和Pdm091057病毒株的遗传进化情况。
1.2.4 疫苗制备 收获107 EID50以上的病毒液,按照体积比1∶1,加入体积分数为0.2%的甲醛溶液做灭活抗原。置37 ℃恒温摇床内灭活24~48 h,并在10日龄SPF鸡胚上连续传3代安检。分别取3株灭活病毒抗原液,分别用弗氏佐剂制备上述3种病毒的全病毒灭活疫苗,油水体积比为2∶1。
1.2.5 免疫试验 将12只新西兰大白兔分成4组,每组3只,第1、2、3组为免疫组,分别腹腔注射SWSS1、SWL6和Pdm091057的全病毒灭活疫苗,0.1 mL·只–1,第4组为PBS对照组。免疫后每周采血检测血凝抑制(Hemagglutination inhibition, HI)抗体滴度,2次免疫后待抗体水平达到稳定时,收获血清备用。
1.2.6 血清学交叉反应试验 进行SWSS1、SWL6和Pdm091057病毒株之间的血清学交叉反应试验以及与H3、H5、H7、H9亚型流感病毒的血清学交叉反应试验。HI试验参照文献[7]的方法进行。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 HA基因片段遗传信息和抗原位点分析
SWSS1、SWL6和Pdm091057病毒株及在GenBank中所选参考毒株的遗传进化分析表明,SWSS1株属于欧亚类禽分支,SWL6属于经典H1N1分支,Pdm091057属于Pdm09H1N1分支(图1)。病毒抗原位点所在的HA基因片段的氨基酸序列相似性对比结果显示,SWSS1株与SWL6株的HA基因片段的氨基酸序列相似性为70.3%,SWSS1株与Pdm091057株的HA基因片段的氨基酸序列相似性为69.4%,SWL6株与Pdm091057株的HA基因片段的氨基酸序列相似性为89.1%。
进一步分析3株病毒株HA基因片段的抗原位点[7],SWSS1毒株与SWL6、Pdm091057毒株的HA基因片段的抗原位点比较结果见图2,SWSS1毒株与SWL6毒株在Sa位点有4个氨基酸位点的不同,与Pdm091057毒株有2个氨基酸位点的不同;SWSS1毒株与SWL6毒株Sb抗原位点有4个氨基酸位点的不同,与Pdm091057毒株Sb抗原位点有2个氨基酸位点的不同;SWSS1毒株与SWL6 毒株Cb抗原位点有2个氨基酸位点的不同,与Pdm091057毒株Cb抗原位点有1个氨基酸位点的不同;SWSS1毒株与SWL6毒株、Pdm091057毒株Ca1抗原位点各有3个氨基酸位点的不同;SWSS1毒株与SWL6毒株、Pdm091057毒株Ca2抗原位点各有5个氨基酸位点的不同。
2.2 病毒血凝效价、EID50及病毒的鸡胚生长曲线
SWSS1、SWL6和Pdm091057病毒株分别接种鸡胚收集尿囊液,检测病毒的红细胞凝集效价分别为211、29和210;计算SWSS1、SWL6和Pdm091057 病毒株的鸡胚半数感染量,其lgEID50·mL–1分别为9.0、8.2和8.5;将100 EID50的原始病毒液接种9日龄的SPF鸡胚,收集尿囊液进行血凝效价测定,结果如图3所示,3株病毒株在鸡胚中均表现出高复制能力,具有较高的鸡胚适应性。
2.3 灭活疫苗免疫后病毒株的HI抗体滴度
采用血凝抑制试验检测免疫2次后兔血清中HI抗体滴度,以评价SWSS1、SWL6和Pdm091057病毒株的免疫效果,结果如图4所示,首免第3周HI抗体滴度可达到1 280以上,第3周再次免疫后,3株病毒株均可诱导较高的HI抗体滴度,且SWSS1的HI平均抗体滴度高达2 560以上。
2.4 血清学交叉反应
上述试验制备的阳性抗SWSS1血清、抗SWL6血清和抗Pdm091057血清为标准血清,H1、H3、H5、H7、H9亚型流感病毒株血清学交叉反应如表1所示,SWSS1毒株制备的抗体与类人季节性H3N2亚型流感病毒具有较低水平的血清学交叉反应,与其他亚型无血清学交叉反应,SWL6与Pdm091057毒株制备的抗体相互之间具有较低的血清学反应,与其他亚型流感病毒无血清学反应。
表 1 不同亚型抗原对标准血清抗体滴度检测结果Table 1. The titers of different subtypes of the influenza virus against the standard serums毒株(四单位抗原) HI抗体滴度 抗SWSS1血清 抗SWL6血清 抗Pdm091057血清 A/swine/Guangdong/SS1/2012(H1N1)1) 2 560 <20 <20 A/swine/Guangdong/L6/2012(H1N1)2) <20 1 280 40 A/Guangdong/1057/2010(H1N1)3) <20 40 1 280 A/swine/Guangdong/l22/2010(H3N2) 40 <20 <20 A/Duck/Anhui/1/2006/(H5N1) <20 <20 <20 A/Chicken/Shanghai/10/2001(H9N2) <20 <20 <20 A/Pigeon/Shanghai/S1421/2013(H7N9) <20 <20 <20 1) 为SWSS1; 2) 为SWL6;3) 为Pdm091057。 3. 讨论与结论
近年来随着流感病毒的变异,猪流感病毒感染人的现象时有发生,流感病毒可通过不断变异和进化,逃避宿主的免疫保护,引起新的暴发和流行[8]。Liu等[9]对华南地区猪群流感的发生和流行情况进行的研究表明多数猪场存在H1、H3亚型猪流感病毒感染情况,一些猪群还存在禽源H4、H5、H7、H9等亚型流感病毒抗体[10]。目前在世界猪群中流行的H1N1流感病毒主要分为3类:经典H1N1、类禽H1N1、类人H1N1。有研究报道[11],类禽H1N1 在华南地区猪群中较为活跃,随着变异和重组,感染人的风险逐步增强。
本试验分析了甲型H1亚型流感病毒的HA基因遗传进化关系,SWSS1株属于欧亚类禽分支,SWL6属于经典H1N1分支,Pdm091057属于Pdn09H1N1分支。3株病毒的HA基因片段的氨基酸序列相似性为69.4%~89.1%。同时,HA基因抗原表位分析揭示了SWSS1、SWL6和Pdm091057 毒株之间抗原位点的差异,这些差异会导致流感病毒表面蛋白构象的理化特性不同[11],这可能是H1亚型病毒之间的无血清学交叉反应的原因。同时,近年来的血清学调查显示[12],猪群中有多种亚型共感染的情况,在同一份血清中能同时检测到H1、H3等多种亚型的流感抗体,且HI抗体效价相对较高,而本研究表明,SWSS1毒株制备的抗体与类人季节性H3N2亚型流感病毒具有较低水平的血清学交叉反应,与其他亚型无血清学交叉反应,SWL6株与Pdm091057株制备的抗体相互之间具有较低的血清学反应,而与其他亚型流感病毒无血清学反应,以上也证明了流感病毒在猪群中的共感染现象的存在,并且为流感病毒在猪“混合器”作用下发生流感病毒重组的可能提供了试验依据。另外,本试验抗SWSS1血清与人季节性H3N2亚型流感病毒之间及SWL6 株与Pdm091057株制备的抗体相互之间血清学交叉反应均较低,尽管其交叉反应机制尚不清楚,但Pdm091057株的HA基因来源于经典H1亚型流感病毒的重组病毒,有研究表明流感病毒HA蛋白在病毒交叉反应的过程中起决定性作用[13-14],理论上解释了在进化关系上SWL6 株与Pdm091057株存在着一定的亲缘关系,推测可能是其具有较低的血清学交叉反应的原因。
本试验中3株病毒株在鸡胚中均表现出高的复制能力,具有较高的鸡胚适应性。首免后HI抗体滴度达到1 280以上,再次免疫后3株病毒株均可以诱导较高的HI抗体滴度,且SWSS1的平均HI抗体滴度高达2 560以上,有研究表明类禽H1N1流感病毒能降低同源异源H1亚型流感病毒对小鼠上致病性[15],其保护机制有待进一步研究。本试验结果显示,类禽SWSS1株、SWL6株、Pdm091057 株病毒诱导机体产生高水平的抗体滴度,且平均HI抗体滴度达1 280以上,可以作为理想的疫苗候选株。另外普遍认为注射疫苗是抵抗流感病毒感染的有效方法,本研究初步分析了3株H1亚型流感病毒的HA蛋白的抗原表位,为下一步流感病毒致病机制的研究及基因工程通用表位疫苗的研制奠定基础。
致谢: 感谢广西农业科学院甘蔗研究所刘晓燕、柳州市农业科学研究所韦开军、百色市农业科学研究所李文教、河池市农业科学研究所陆文娟、北海市农业科学研究所朱斌及广西南亚热带农业科学研究所邱文武对甘蔗的日常管理和协助调查! -
表 1 参试甘蔗品种(系)信息
Table 1 The information of tested sugarcane varieties (lines)

表 2 甘蔗梢腐病田间调查分级标准
Table 2 The grading standard of sugarcane pokkah boeng disease severity in the field

表 3 甘蔗梢腐病田间抗性评价标准
Table 3 The grading standard of sugarcane resistance to pokkah boeng disease in the field

表 4 参试品种(系)梢腐病抗性评价1)
Table 4 The resistance evaluation of tested varieties (lines) to sugarcane pokkah boeng disease

-
[1] 洪伟雄. 甘蔗梢腐病病原菌: 串珠镰刀菌分子生物学研究初探[D]. 福州: 福建农林大学, 2011. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10389-1011164813.htm [2] SINGH A, CHAUHAN S S, SINGH A, et al. Deterioration in sugarcane due to pokkah boeng disease[J]. Sugar Tech, 2006, 8(2): 187-190. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2fb00bb8a3395ab97615b8f612ec73ee&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[3] 黄鸿能.浅谈甘蔗病害在广东蔗区的为害及其主要防治对策[J].甘蔗糖业, 1993(3):13-17. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK000005392363 [4] 刘梦林, 黄冬发, 李德健, 等.广西甘蔗梢腐病的发生和防治研究初报[J].广西农业科学, 1991(4):175-178. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK000000919830 [5] 张玉娟. 甘蔗梢腐病病原分子检测及甘蔗组合、品种的抗病性评价[D]. 福州: 福建农林大学, 2009. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10389-2009170509.htm [6] VISHWAKARMA S K, KUMAR P, NIGAM A, et al. Pokkah boeng: An emerging disease of sugarcane[J]. J Plant Pathol Microb, 2013, 4(3): 170. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=b31c0e5eec6a08defc8b1eefce5b3251&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[7] 沈万宽, 邓海华.引进甘蔗品种黑穗病抗性鉴定及结果分析[J].中国农学通报, 2011, 27(19): 234-238. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgnxtb201119045 [8] 李朝生, 霍秀娟, 韦绍龙, 等. 5份香蕉种质对枯萎病的抗性评价[J].南方农业学报, 2012, 43(4): 449-453. doi: 10.3969/j:issn.2095-1191.2012.04.449 [9] HSUAN H M, SALLEH B, ZAKARIA L. Molecular identification of Fusarium species in Gibberella fujikuroi species complex from rice, sugarcane and maize from Peninsular Malaysia[J]. Int J Mol, 2011, 12(10): 6722-6732. doi: 10.3390/ijms12106722
[10] ABU AHMAD Y, RASSABY L, ROYER M, et al. Yellow leaf of sugarcane is caused by at least three different genotypes of sugarcane yellow leaf virus, one of which predominates on the island of Réunion[J]. Arch Virol, 2006, 151(7): 1355-1371. doi: 10.1007/s00705-005-0712-9
[11] 单红丽, 李文凤, 黄应昆, 等.国家甘蔗体系繁殖和示范新品种(系)病虫害调查[J].中国糖料, 2014, 36 (2):50-53. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgtl201402020 [12] 黄庆裕, 朱来佳, 黎达境, 等.水稻纹枯病病情指数与病株率关系数学模型的研究及应用[J].广西植保, 2010, 23 (1): 1-3. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8779.2010.01.001 [13] 路银贵, 曹永胜, 田兰芝, 等.玉米粗缩病病情严重度分级标准及病情指数与产量损失率关系的研究[J].华北农学报, 2006, 21(4): 87-90. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-7091.2006.04.022 [14] 郭云忠, 段双科, 张涛.病情指数划分小麦品种(系)赤霉病抗病性类型方法的改进研究[J].河南农业大学学报, 1999, 33(4): 336-338. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2340.1999.04.006 [15] VISWANATHAN R, RAO G P. Disease scenario and management of major sugarcane diseases in India[J]. Sugar Tech, 2011, 13(4): 336-353. doi: 10.1007/s12355-011-0102-4
[16] AOKI T, O'DONNELL K, GEISER D M. Systematics of key phytopathogenic Fusarium species: Current status and future challenges[J]. J Gen Plant Pathal, 2014, 80(3):189-201. doi: 10.1007/s10327-014-0509-3
[17] 沈万宽, 姜子德, 邓海华, 等.甘蔗黑穗病及其病原菌研究进展[J].热带作物学报, 2013, 34(10): 2063-2068. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2561.2013.10.036 [18] PETROVIC T, BURGESS L W, COWIE I, et al. Diversity and fertility of Fusarium sacchari from wild rice (Oryza australiensis) in Northern Australia, and pathogenicity tests with wild rice, rice, sorghum and maize[J]. Eur J Plant Pathol, 2013, 136(4): 773-788. doi: 10.1007/s10658-013-0206-7
[19] 黄梅燕, 廖锦鹏, 李勋, 等.国家第8轮甘蔗品种区试广西崇左市农业科学研究所试验点结果分析[J].甘蔗糖业, 2013 (3): 1-5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9695.2013.03.001 [20] 刘晓燕, 梁强, 李毅杰, 等. 2012—2013年广西甘蔗品种区试南宁点试验报告[J].中国糖料, 2015, 37(2):10-12. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=ZGTI201502005&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ




 下载:
下载: