Effects of Mn application amounts on physiological characteristics and Mn content of aromatic rice
-
摘要:目的
探究硫酸锰(MnSO4)不同施用量对香稻生理特性和糙米中锰(Mn)元素含量的影响,为香稻的优质栽培提供理论依据。
方法以常规香稻美香占和农香18为材料,通过盆栽试验,采用随机区组排列,设置4个基施MnSO4 处理,即分别施入MnSO4 6.67 (Mn1)、10.00 (Mn2)、13.33 (Mn3)、16.67(Mn4) mg·kg-1,以不施入MnSO4 作为对照(CK)。
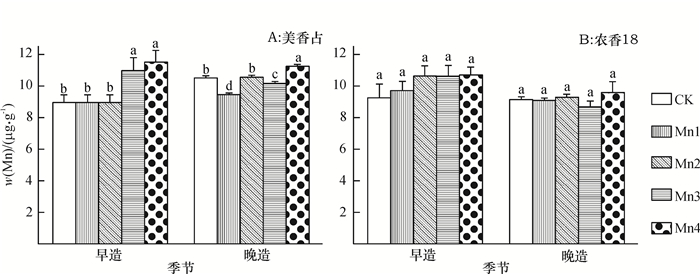
结果与CK相比,Mn4处理更有利于提高香稻糙米中Mn含量,美香占早、晚造增幅分别为22.02%和6.75%;农香18早、晚造增幅分别为1.48%和4.26%。基施MnSO4能较好地增加早、晚造香稻孕穗期及后期的茎秆和叶片中全Mn含量,2个品种均以Mn4处理的结果较好。基施MnSO4,以Mn4处理最有利于早、晚造香稻不同生育期叶片净光合速率(Pn)的提高和植株干物质积累量的增加;Mn4处理更有利于增强早、晚造各生育期叶片超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)和过氧化物酶(POD)活性,降低叶片丙二醛(MDA)含量。
结论适量基施MnSO4有利于提高香稻的Pn,增强香稻对外界环境的抗逆性和适应性,促进香稻的生长,提高香稻茎叶中全Mn含量,最终促进糙米中锰元素的积累;本研究最佳施用量为基施MnSO4 16.67 mg·kg-1。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo investigate the effects of MnSO4 basal applications on physiological characters and Mn content of aromatic rice, and to provide a theoretical basis for cultivating high-quality aromatic rice.
MethodPot experiment was carried out using Meixiangzhan and Nongxiang 18 as planting materials. Four basal applications of MnSO4 were employed with the concentrations of 6.67 (Mn1), 10.00 (Mn2), 13.33 (Mn3) and 16.67 (Mn4) mg·kg-1 respectively. There was a control treatment (CK) with none MnSO4 application. The experiment was arranged in a randomized block design. The Mn contents of leaves, stems and brown rice grains were measured. The enzyme activities of superoxide dismutase (SOD) and peroxidase (POD), and the content of malondialdehyde (MDA) in rice leaf were investigated.
ResultCompared to the control, Mn4 was more beneficial to increase the Mn content of brown rice grains in early and late seasons by 22.02% and 6.75% respectively for Meixiangzhan, and 1.48% and 4.26% respectively for Nongxiang18. Mn4 treatment was better to increase the Mn content in the stems and leaves of early and late aromatic rice varieties after booting stages. Mn4 treatment improved the net photosynthetic rate of leaf and dry mass of above-ground of early and late aromatic rice varieties. Moreover, Mn4 treatment was more effective to improve the SOD and POD activities and decrease the MDA content in the leaves of early and late aromatic rice varieties.
ConclusionAppropriate basal application of MnSO4 would be more effective to improve the net photosynthetic rate and the Mn contents of stem, leaf and brown rice grains, enhance the resistance, adaptability and growth of aromatic rice variety. The optimal application amount of MnSO4 is 16.67 mg·kg-1 in this study.
-
-
表 1 基施MnSO4对早、晚造香稻茎秆中全Mn含量的影响1)
Table 1 Effect of MnSO4 basal application on Mn content of aromatic rice stem in early and late seasons

表 2 基施MnSO4对早、晚造香稻叶片中全Mn含量的影响1)
Table 2 Effect of MnSO4 basal application on Mn content of aromatic rice leaf in early and late seasons

表 3 基施MnSO4对早、晚造香稻叶片净光合速率(Pn)的影响1)
Table 3 Effect of MnSO4 basal application on net photosynthetic rate (Pn) of aromatic rice leaf in early and late seasons

表 4 基施MnSO4对早、晚造地上部干物质积累量的影响1)
Table 4 Effect of MnSO4 basal application on dry matter accumulation of above-ground plant of aromatic rice in early and late seasons

表 5 基施MnSO4对早、晚造香稻叶片SOD活性的影响1)
Table 5 Effect of MnSO4 basal application on SOD activity of aromatic rice leaf in early and late seasons

表 6 基施MnSO4对早、晚造香稻叶片POD活性的影响1)
Table 6 Effect of MnSO4 basal application on POD activity of aromatic rice leaf in early and late seasons

表 7 基施MnSO4对早、晚造叶片MDA含量的影响1)
Table 7 Effect of MnSO4 basal application on MDA content of aromatic rice leaf in early and late seasons

表 8 不同生育期香稻植株与糙米中全Mn含量(w)的相关性1)
Table 8 Correlation coefficients between Mn contents of aromatic rice plant and brown rice grain in different periods

-
[1] GREGORIO G B, SENADHIRA D, HTUT T. Improving iron and zinc value of rice for human nutrition[J]. Agr Develop, 1999, 23(9): 77-81. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=85d78aa8de1ea9428c0341228fe3bf54&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[2] 程式华, 胡培松.中国水稻科技发展战略[J].中国水稻科学, 2008, 22(3): 223- 226. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7216.2008.03.001 [3] 林光.香稻的发展现状与研究进展[J].中国农学通报, 2009, 25(8): 164-168. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gxnykx200706003 [4] WONGPORNCHAI S, DUMRI K, JONGKAEWWATTANA S, et al. Effects of drying methods and storage time on the aroma and milling quality of rice (Oryza sativa L.) cv. Khao Dawk Mali 105[J]. Food Chem, 2004, 87(3): 407-414. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2003.12.014
[5] CORDEIRO G M, CHRISTOPHER M J, HENRY R J, et al. Identification of microsatellite markers for fragrance in rice by analysis of the rice genome sequence[J]. Mol Breed, 2002, 9(4): 245-250. doi: 10.1023/A:1020350725667
[6] JEZUSSEK M, JULIANO B O, SCHIEBERLE P. Comparison of key aroma compounds in cooked brown rice varieties based on aroma extract dilution analysis[J]. J Agric Food Chem, 2002, 50(5): 1101-1105. doi: 10.1021/jf0108720
[7] 王国峰, 黄金龙, 刘兰芳, 等.优质白香稻新品种古榆香稻1号的选育与应用[J].现代农业, 2004(11): 14. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/xiandny200411011 [8] 游晴如, 黄庭旭.稻米香味的研究与育种利用[J].福建稻麦科技, 2003(3): 33. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/fjdmkj200203014 [9] 曹恭, 梁鸣早.锰:平衡栽培体系中植物必需的微量元素[J].土壤肥料, 2004(1): 2-3. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgysjsxb-e201705024 [10] 孙羲.植物营养原理[M].北京:中国农业出版社, 1997: 205-212. [11] BURNELL J N. The biochemistry of manganese in plants[M]//GRAHAM R D, HANNAM R J, UREN N C. Manganese in soils and plants. Dordrecht, Netherlands: Springer, 1988: 125-137.
[12] MUKHOPADHYAY M J, SHARMA A. Manganese in cell metabolism of higher plants[J]. Bot Rev, 1991, 57(2): 117-149. doi: 10.1007/BF02858767
[13] 匡廷云, 杨宗年, 崔澂.锰在光合作用中的作用[J].植物学报, 1966, 14(2): 139-143. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZWXB196602008.htm [14] CLAIRMONT K B, HAGAR W G, DAVIS E A. Manganese toxicity to chlorophyll synthesis in tobacco cells[J]. Plant Physiol, 1986, 80(1): 291-293. doi: 10.1104/pp.80.1.291
[15] 卢海博, 龚学臣, 乔永明, 等.杂谷干物质积累及光合特性的研究[J].作物杂志, 2014(1): 121-124. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7283.2014.01.028 [16] 李勇, 王红光, 李瑞奇, 等.表油菜素内酯对冬小麦开花后光合特性和物质生产的影响[J].河北农业大学学报, 2015, 1(2):1-7. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hbnydxxb2015010003 [17] 窦俊辉, 喻树迅, 范术丽, 等. SOD与植物胁迫抗性[J].分子植物育种, 2010, 8(2): 359-364. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/fzzwyz201002026 [18] 梁艳荣, 胡晓红, 张颖力, 等.植物过氧化物酶生理功能研究进展[J].内蒙古农业大学学报(自然科学版), 2003, 24(2): 110-113. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/nmgnydxxb200302026 [19] 冯绪猛, 罗时石, 胡建伟, 等.农药对水稻叶片丙二醛及叶绿素含量的影响[J].核农学报, 2003, 17(6): 481-484. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8551.2003.06.019 [20] 孙永健, 孙圆圆, 刘凯, 等.水氮互作对结实期水稻衰老和物质转运[J].植物营养与肥料学报, 2009, 15(6): 1339-1349. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1008-505X.2009.06.014 [21] 周焱, 徐素君, 钱肖余.一种一次性完全提取植株中微量元素的新方法: HCl+Vc浸提法[J].江西医药, 1994, 29 (增刊): 147-150. [22] 余冰宾.生物化学实验指导[M].北京:清华大学出版社, 2003: 131-140. [23] 汤章诚.现代植物生理学实验指导[M].北京:科学出版社, 1999: 305-306. [24] ABIN S, MNV P. Iron-and manganese-assisted cadmium tolerance in Oryza sativa L.: Lowering of rhizotoxicity next to functional photosynthesis[J]. Planta, 2015, 241(6):1519-1528. doi: 10.1007/s00425-015-2276-6
[25] 王丰, 张国平, 白朴.水稻源库关系评价体系研究进展与展望[J].中国水稻科学, 2005, 19(6): 556-560. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7216.2005.06.014



 下载:
下载:
