Synthesis and identification of artificial antigen for dibutyl phthalate
-
摘要:目的
制备并鉴定1种新型邻苯二甲酸二丁酯人工抗原。
方法以4-硝基邻苯二甲酸为原料,经过酯化、还原生成4-氨基邻苯二甲酸二丁酯(DBAP),DBAP再与戊二酸酐反应,衍生生成4-戊二酸单酰邻苯二甲酸二丁酯(DBCP)。将合成的半抗原衍生物DBCP通过活性酯法与牛血清蛋白(BSA)或卵清蛋白(OVA)偶联,得到人工抗原。通过免疫新西兰大白兔获得抗血清,经间接竞争酶联免疫法(icELISA)检测抗体特异性。
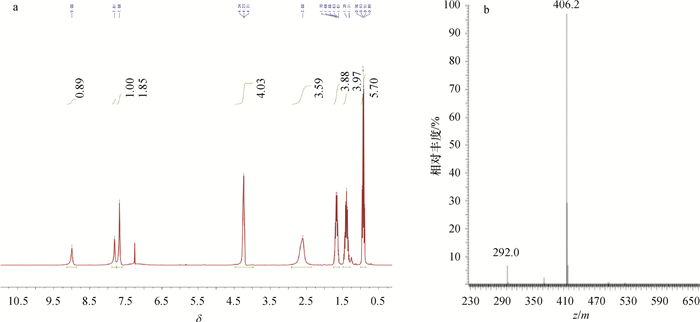
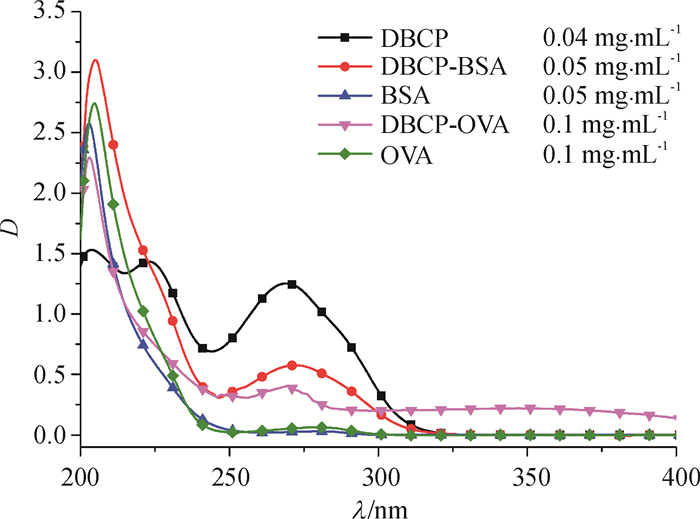
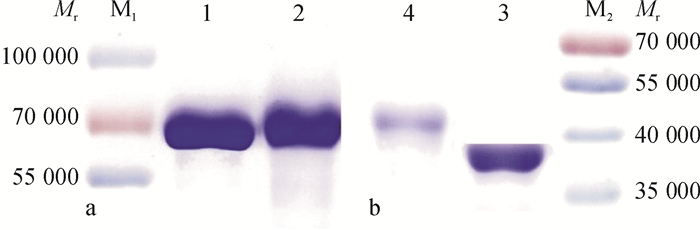
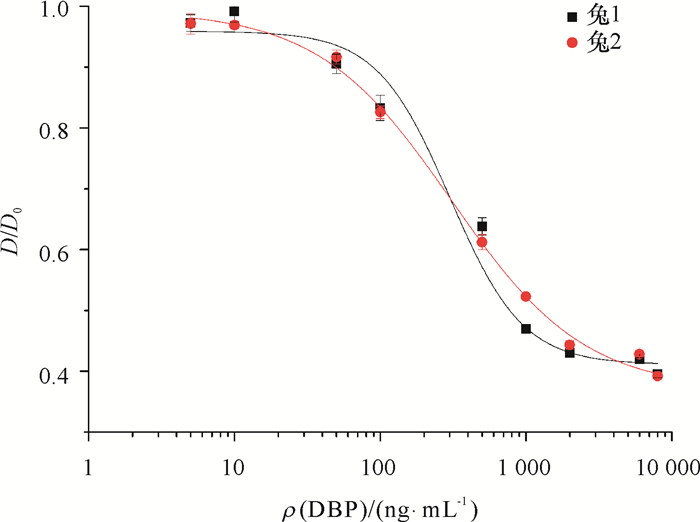
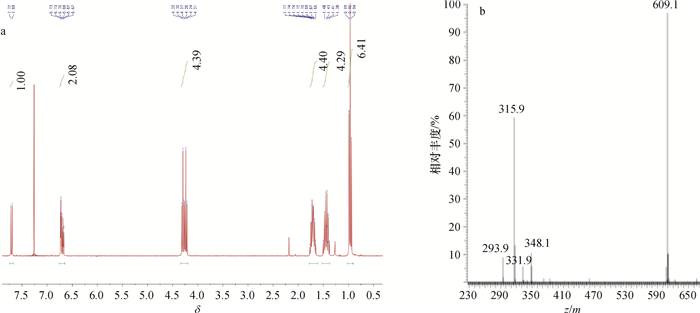
结果经质谱、氢核磁共振谱图鉴定,半抗原衍生物合成成功,经紫外光谱、SDS-聚丙烯酰胺凝胶电泳和免疫试验证实偶联成功,并计算得出DBCP与载体蛋白BSA和OVA的结合比分别为11:1和17:1。经icELISA法检测,兔1和兔2的血清效价均达到1:128 000,IC50分别为301和308 ng·mL-1,反应特异性较好。
结论半抗原衍生物的合成是方便、安全的。邻苯二甲酸人工抗原的成功制备使获得DBP多克隆抗体以及建立DBP免疫分析方法成为可能。
Abstract:ObjectiveThis study was aimed to prepare and identify a new kind of artificial antigen for dibutyl phthalate.
MethodDibutyl 4-aminophthalate (DBAP) was obtained via esterification and reduction of 4-nitrophthalic acid. The hapten derivative monoglutaryl 4-amino-dibutyl phthalate (DBCP) was prepared through DBAP reacting with glutaric anhydride. DBCP was conjugated to bovine serum albumin (BSA) or ovalbumin (OVA) to make artificial immunogen via activated ester method. Then the antiserum of two female New Zealand white rabbits was obtained after injecting with artificial immunogens which were successfully coupled. Indirect competitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (icELISA) was used to analyze the sensitivity and specificity of the antiserum.
ResultThe successful synthesis of hapten derivative was identified by mass spectrometry (MS) and 1H nuclear magnetic resonance (1H NMR). The successful coupling was proved by ultraviolet spectroscopy (UV) and SDS polyacrylamide gels electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE). Furthermore, the numbers of DBCP molecules per BSA/OVA molecules for two conjugates were 11:1 and 17:1 respectively, estimated by ultraviolet spectrophotometry. The icELISA method indicated high specificity for the antiserum with the highest titer being 1:128 000 for samples from both rabbits, and the IC50 being 301 and 308 ng·mL-1 respectively.
ConclusionThe hapten derivative can be synthesized in a convenient and secure way. The successful synthesis of the artificial antigen for dibutyl phthalate makes it possible to get polyclonal antibodies and establish immunoassay for DBP.
-
Keywords:
- dibutyl phthalate /
- artificial antigen /
- spectrum /
- immunity identification
-
-
表 1 抗血清效价测定结果
Table 1 Detection result of serum titer

表 2 多克隆抗体与DBCP结构类似物的交叉反应
Table 2 Cross-reactivity of the polyclonal antibody against DBCP related compounds

-
[1] XU F, WANG W, JIANG H, et al. Indirect competitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the detection of dibutyl phthalate in white wine, compared with GC-MS[J]. Food Analytical Methods, 2014, 7(8): 1619-1626. doi: 10.1007/s12161-014-9797-7
[2] WEI C X, DING S M, YOU H H, et al. An immunoassay for dibutyl phthalate based on direct hapten linkage to the polystyrene surface of microtiter plates[J]. PLOS One, 2011, 6(12): e29196. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0029196
[3] KUANG H, LIU L, XU L, et al. Development of an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for dibutyl phthalate in Liquor[J]. Sensors, 2013, 13(7): 8331-8339. doi: 10.3390/s130708331
[4] 王民生.邻苯二甲酸酯(塑化剂)的毒性及对人体健康的危害[J].江苏预防医学, 2011, 22(4): 68-70. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/jsyfyx201104035 [5] 刘慧杰, 舒为群.邻苯二甲酸酯类化合物的毒理学效应及对人群健康的危害[J].第三军医大学学报, 2004, 26(19): 1778-1781. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-5404.2004.19.026 [6] 谭君, 林竹光. GC-EI-MS内标法分析鱼肉中邻苯二甲酸酯[J].化学学报, 2007, 65(24): 2875-2882. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0567-7351.2007.24.013 [7] 杨涛.台湾塑化剂风暴对饮料及饮料包装行业的影响[J].塑料包装, 2011, 21(4): 35-39. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9828.2011.04.009 [8] 王少杰, 孟雨吟, 李秋顺, 等.高效液相色谱法测定蔬菜中邻苯二甲酸二丁酯残留[J].山东农业科学, 2012, 44(1): 112-114. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4942.2012.01.033 [9] 方丽, 林泽鹏, 林晨, 等.气质联用法测定食品包装材料中22种邻苯二甲酸酯残留方法的探讨[J].食品工业, 2015, 36(1): 291-296. [10] FENG X, LU S, LIU D, et al. Direct competitive immunosorbent assay for detection of MEHP in human urine[J]. Chemosphere, 2013, 92(1): 150-155. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.02.062
[11] ZHANG M, LIU S, ZHUANG H, et al. Determination of dimethyl phthalate in environment water samples by a highly sensitive indirect competitive ELISA[J]. Appl Biochem Biotechnol, 2012, 166(2): 436-445. doi: 10.1007/s12010-011-9439-0
[12] 王建华, 张冲.小分子抗原人工合成进展[J].应用化学, 2011, 28(4): 367-375. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/yyhx201104001 [13] ZHANG M, WANG Q, ZHUANG H. A novel competitive fluorescence immunoassay for the determination of dibutyl phthalate[J]. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2006, 386(5): 1401-1406. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=JJ023471637
[14] 庄惠生, 李玉科, 张明翠.环境荷尔蒙邻苯二甲酸二甲酯的人工全抗原合成与表征[J].化学试剂, 2005, 27(9): 559-560. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-3283.2005.09.014 [15] ZHOU J, ZHAO S, ZHANG J, et al. An indirect competitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for bisphenol-A based on the synthesis of a poly-l-lysine-hapten conjugate as a coating antigen[J]. Anal Methods, 2013, 5(6): 1570. doi: 10.1039/c3ay26220k
[16] 郑劼, 张焜, 赵肃清.双酚A人工抗原的光谱表征及免疫鉴定研究[J].光谱学与光谱分析, 2008, 28(7): 1583-1586. doi: 10.3964/j.issn.1000-0593.2008.07.032 [17] 万宇平, 陶光灿, 李勇, 等.邻苯二甲酸二丁酯(塑化剂)ELISA检测方法的研究[J].食品工业, 2013, 34(9): 194-196. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Thesis/y2419255 [18] 赵肃清, 蔡燕飞, 雷红涛, 等.农药甲胺磷人工抗原的光谱鉴定研究[J].光谱学与光谱分析, 2004, 24(2): 207-209. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0593.2004.02.024 [19] 宋娟, 王榕妹, 王悦秋, 等.半抗原的设计、修饰及人工抗原的制备[J].分析化学, 2010, 38(8): 1211-1218. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/fxhx201008026



 下载:
下载: