Isolation and identification of bacteria degrading soy lecithin and dimethoate and comparision of enzyme activities
-
摘要:目的
明确2株有机磷降解菌Yj2和Yj3对大豆卵磷脂和乐果有机磷的降解特性及酶活性。
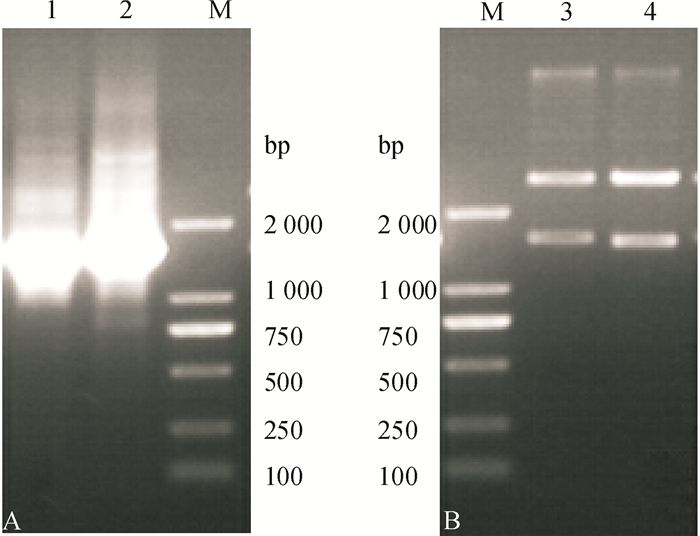
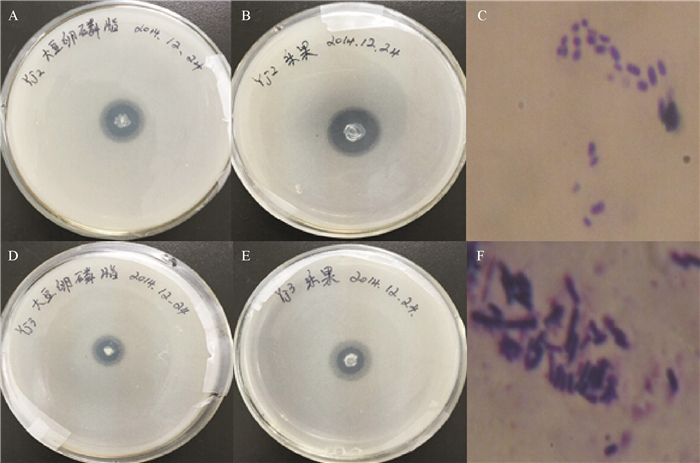
方法利用16S rDNA鉴定从大豆土壤中分离得到的Yj2和Yj3菌株,在菌株最佳生长条件下,测定了不同磷源时菌体的酶活性并分级纯化了有机磷降解酶。
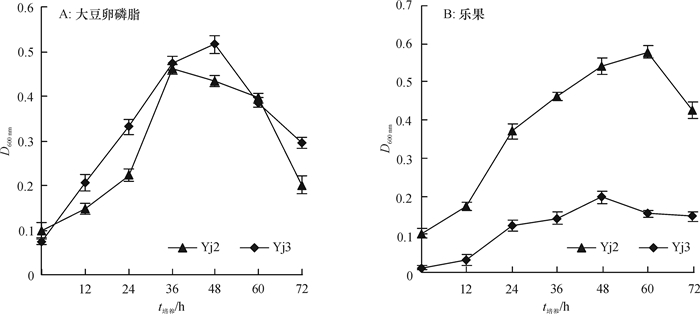
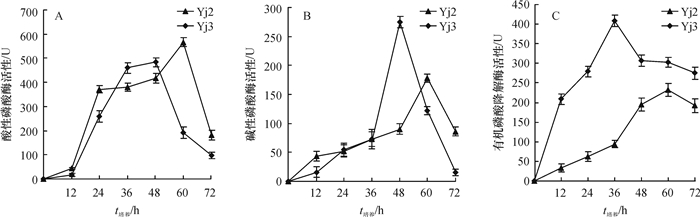
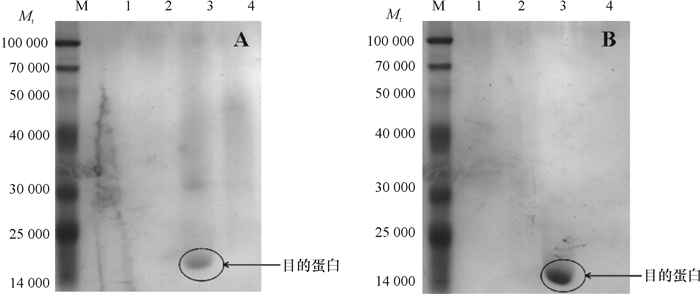
结果Yj2为醋酸钙不动杆菌Acinetobacter sp.,其最佳生长碳源为葡萄糖,氮源为硫酸铵,pH为8;Yj3为芽孢杆菌Bacillus sp.,其最佳生长碳源为葡萄糖,氮源为蛋白胨,pH为9。大豆卵磷脂为磷源时,Yj3的菌体生长情况稍优于Yj2。乐果为磷源时,Yj2的菌体生长情况稍优于Yj3;72 h内Yj2酸性和碱性磷酸酶活性整体高于Yj3,而有机磷降解酶活性低于Yj3。硫酸铵沉淀法+阳离子交换层析分别从Yj2和Yj3菌体中成功分离纯化了有机磷降解酶,SDS-PAGE结果显示纯化的蛋白均为单一条带。Yj2硫酸铵沉淀法+阳离子交换层析的提纯倍数是硫酸铵沉淀的7.77倍,硫酸铵沉淀为粗酶的1.35倍。Yj3硫酸铵沉淀法+阳离子交换层析的提纯倍数是硫酸铵沉淀的5.07倍,硫酸铵沉淀为粗酶的1.53倍。
结论菌株Acinetobacter sp. Yj2和Bacillus sp. Yj3都具有降解大豆卵磷脂及乐果有机磷的特性,对有机磷降解起主要作用的是酸性磷酸酶、碱性磷酸酶及有机磷降解酶,它们在2株菌株对大豆卵磷脂和乐果降解过程中所起的作用有明显差异。可从Yj2和Yj3菌体分离纯化获得提纯倍数较高的有机磷降解酶蛋白。
Abstract:ObjectiveIn order to clarify degradation characteristics and enzyme activities of two organic phosphorus degrading bacteria in soy lecithin and dimethoate.
MethodBacterium strains Yj2 and Yj3 were isolated from soy soil and identified by 16S rDNA identification method. The growth conditions of Yj2 and Yj3 were optimized by orthogonal test. The enzyme activities from two strains were determined under different phosphorus sources, and organophosphate degrading enzymes were classified and purified.
ResultYj2 was identified as Acinetobacter sp., and Yj3 was identified as Bacillus sp.. The result of growth condition optimization showed that the best carbon and nitrogen source and pH values for strain Yj2 and Yj3 were glucose, ammonium sulfate, pH 8 and glucose, peptone, pH 9, respectively. The growth of Yj3 was slightly better than that of Yj2 when the phosphorus source was soy lecithin. However, the growth trend was the opposite with dimethoate as the phosphorus source. Within 72 h of dimethoate being the phosphorus source, acid phosphatase activity and alkaline phosphatase activity of Yj2 were generally higher than that of Yj3, but organophosphate degradation enzyme activiy of Yj2 was lower than those of Yj3. The organophosphorus degradation enzymes were isolated and purified respectively from strains Yj2 and Yj3 by ammonium sulfate precipitation followed with cation exchange chromatography. SDS-PAGE results showed that the purified proteins were both a single band. The purification ratio of ammonium sulfate precipitation followed with cation exchange was 7.77 times higher than that of the ammonium sulphate precipitation for Yj2, and the latter was 1.35 times higher than crude enzyme for Yj2. The corresponding purification ratios for Yj3 were 5.07 and 1.53 times respectively.
ConclusionAcinetobacter sp. Yj2 and Bacillus sp. Yj3 both can degrade soy lecithin and dimethoate. The activities of acid phosphatase, alkaline phosphatase and organophosphate degradation enzymes, which play the main roles on degrading organic phosphate, have obvious differences between two strains in soy lecithin and dimethoate degrading process. The organophosphate degradation enzymes with relatively high purity can be isolated and purified from YJ2 and Yj3, respectively.
-
-
表 1 有机磷降解酶分级纯化的酶活力分析
Table 1 Classification and purification of organophosphate degradation enzyme activity analysis

-
[1] WANG Y, YE X S, DING G D, et al. Overexpression of phyA and appA genes improves soil organic phosphorus utilisation and seed phytase activity in Brassica napus[J]. Plos one, 2013, 8(4):1- 9. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/OAPaper/oai_pubmedcentral.nih.gov_3616117
[2] 杜育梅, 刘国道.植物利用磷素的有效性研究进展[J].华南热带农业大学学报, 2007, 1(2):41-47. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7054.2007.02.010 [3] SHARMA S B, SAYYED R Z, TRIVEDI M H, et al. Phosphate solubilizing microbes: Sustainable approach for managing phosphorus deficiency in agricultural soils[J/OL]. Springer Plus, 2013, 2: 587-601. http://www.springerplus.com/content/2/1/587.
[4] YI Y M, HUANG W Y, GE Y. Exopolysaccharide: A novel important factor in the microbial dissolution of tricalcium phosphorus[J]. World J Microbiol Biotech, 2008, 24(7): 1059-1065. doi: 10.1007/s11274-007-9575-4
[5] 刘渊, 李喜焕, 孙星, 等.磷胁迫下大豆酸性磷酸酶活性变化及磷效率基因型差异分析[J].植物遗传资源学报, 2012, 13(4):521-528. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-1810.2012.04.003 [6] 问县芳, 袁永泽, 习海玲, 等.一种新型有机磷降解酶的二异丙基氟磷酸酯水解特性研究[J].华中师范大学学报, 2013, 47(1):53-56. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1190.2013.01.013 [7] SALMAN A, FARD A T, NASIR A, et al. Comparative analysis of organophosphate degrading enzymes from diverse species[J]. Bioinformation, 2010, 5(2):67. doi: 10.6026/bioinformation
[8] 黄雅, 李政一, 赵博生.有机磷农药乐果降解的研究现状与进展[J].环境科学与管理, 2009, 43(4):20-24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1212.2009.04.007 [9] 萨姆克鲁斯J拉塞尔. 分子克隆实验指南[M]. 3版. 北京: 科学出版社, 2002: 8. [10] BAKERMANS C, MADSEN E. Diversity of 16S rDNA and naphthalene dioxygenase genes from coal-tar-waste-contaminated aquifer waters[J]. Microb Ecol, 2002, 44(2):95-106. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=JJ022007414
[11] 伊鋆. 高效解磷细菌的筛选及解磷机理的研究[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2011: 30 [12] 金彬明, 刘佳明.海洋微生物有机磷降解酶的纯化与性质研究[J].中国微生态学杂志, 2007, 19(1):37-39. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-376X.2007.01.015 [13] 伍宁丰, 梁果义, 邓敏捷, 等.有机磷农药降解酶及其基因工程研究进展[J].生物技术通报, 2003(5):9-12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-5464.2003.05.003 [14] 段雪梅, 冯胜, 王小冬, 等.一株分离自太湖有机聚集体上的有机磷降解细菌的鉴定及其降解特性研究[J].农业环境科学学报, 2008, 27(2):741-747. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1672-2043.2008.02.062 [15] 肖佳沐, 袁海平, 楼紫阳, 等.一株乐果降解菌的筛选、鉴定及其降解特性研究[J].环境污染与防治, 2010, 32(12):67-71. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3865.2010.12.015 [16] BHADBHADE B J, SARNAIK S S, KANEKAR P P. Biomineralization of an organophosphorus pesticide, monocrotophos, by soil bacteria[J]. J Appl Microbiol, 2002, 93(2):224-234. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=JJ026440155
[17] 史延华. CP1菌株的分离、筛选及其对毒死蜱的降解[J].微生物学通报, 2011, 38(9):1331-1338. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/wswxtb201109002 [18] 王莉. Hyphomicrobium sp.MAP-1菌株修复甲胺磷乙酰甲胺磷和水胺硫磷污染土壤的实验研究[J].农业环境科学学报, 2013, 32(1):81-87. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK201300020382 [19] 许育新, 冯昭中, 陆鹏, 等.甲基对硫磷降解菌PF32的分离鉴定及其降解特性研究[J].农药学学报, 2009, 11(3):329-334. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-7303.2009.03.008 [20] 赵小蓉, 林启美, 李保国.C、N源及C/N比对微生物溶磷的影响[J].植物营养与肥料学报, 2002, 8(2): 197-204. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1008-505X.2002.02.013 [21] 陈燕飞.pH对微生物的影响[J].太原师范学院学报(自然科学版), 2009, 8(3): 121-124. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2027.2009.03.032 [22] 钟传青, 黄为一.不同种类解磷微生物的溶磷效果及其磷酸酶活性的变化[J].土壤学报, 2005, 42(2):286-293. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0564-3929.2005.02.017 [23] 丁洪, 李生秀, 郭庆元, 等.酸性磷酸酶活性与大豆耐低磷能力的相关研究[J].植物营养与肥料学报, 1997, 3(2):123-128. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1008-505X.1997.02.005 [24] 闫建国, 汝少国, 王蔚.久效磷对黄鳝乙酰胆碱酯酶、羧酸酯酶和磷酸酶活性的影响[J].安全与环境学报, 2006, 6(3):61-63. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6094.2006.03.019 [25] MUNNECKE D M. Enzymatic detoxification of waste organophosphorus pesticides[J].J Agric Food Chem, 1980, 28(1): 105-111. doi: 10.1021/jf60227a025
[26] 伍宁丰, 邓敏捷, 史秀云, 等.一种新的有机磷降解酶的分离纯化及酶学性质研究[J].科学通报, 2003, 48(23): 2446-2450. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2003.23.008 [27] 刘玉焕, 钟英长.华丽曲霉Z58有机磷农药降解酶的纯化和性质[J].微生物学报, 2000, 40(4):430-434. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-6209.2000.04.016



 下载:
下载: