Spatial patterns and environmental factors of rapidly degraded mangroves at Dongzhaigang Harbor in Hainan
-
摘要:目的
对我国一些红树林湿地生态系统近期出现的急速退化现象作相关分析.
方法以海南东寨港整个港湾红树林区为研究典型区域,应用3S技术,分析近30年间东寨港红树林湿地景观格局的演变过程;同时采用高分辨率影像数据,聚焦分析了演丰东河沿岸、塔市及三江3个片区红树林群落退化特征及空间分布规律;结合大量野外样方调查数据,系统分析了近海岸红树林生态系统退化的主要影响因素.
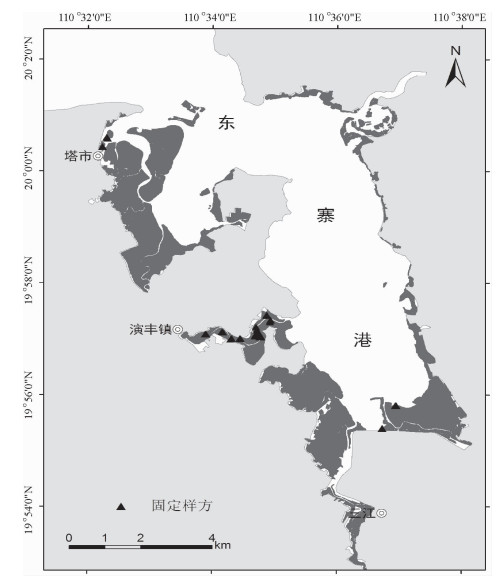
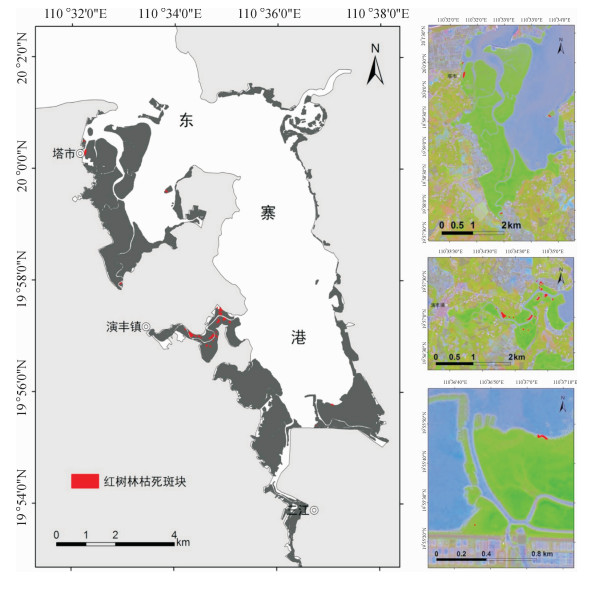
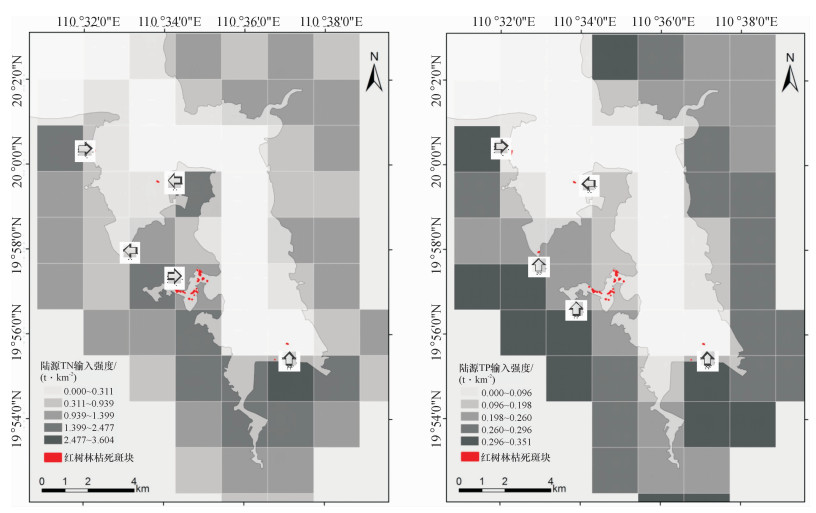
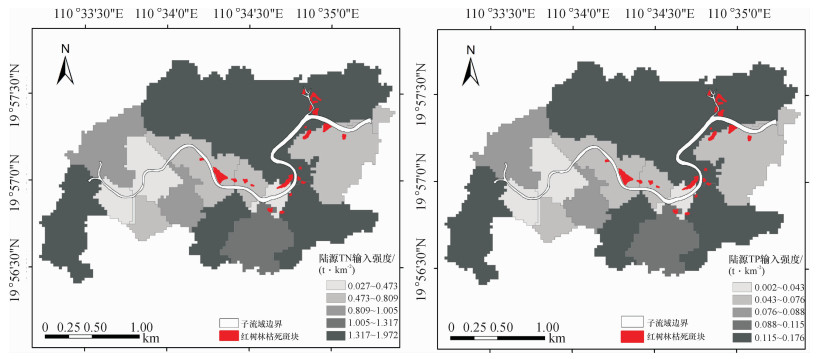
结果和结论从1999-2013年,东寨港红树林面积由1 709.4 hm2减少至1 679.5 hm2,年均减少2.1 hm2.而沿海岸线2 km缓冲区范围内,周边养殖塘面积则由1987年的59.1 hm2增至2013年的1 986.9 hm2.截止2013年,东寨港红树林枯死面积约为4 hm2.从空间分布上来看,红树林枯死群落主要分布于地形低洼积水处或污染物传输通道两侧.东寨港河流型红树林群落退化最为严重,集中分布于演丰东河中下游河段;同时,近海湾的前沿地段也有退化群落零星分布.处于地带性演替后期的红树林群落,退化程度较高.陆源污染物输入强度是影响红树林退化群落分布的重要因素.
Abstract:ObjectiveThe purpose of this study was to analyze mangrove degradation in some coastlandsof southern China.
MethodMangrove of Dongzhaigang Harbor in Hainan Province was investigated as acase study. Landscape pattern dynamics of mangrove wetland from 1987 to 2013 were analyzed at Dongzhaigang Harbor by interpreting five phase remote sensing images. The degradation characteristics of mangrove forest and its spatial patterns were also further studied using SPOT5 and aerial imagery. Furthermore, the influencing factors of mangrove degradation such as topographical factors and terrestrial contaminant loading were analyzed by surveying numerous sampling plots.
Result and conclusionIt was foundthat mangrove area decreased from 1 709.4 hm2 in 1999 to 1 679.5 hm2 in 2013, while the area of pondsin the 2 km coastal buffers increased from 59.1 hm2 in 1987 to 1 986.9 hm2 in 2013. The dead area ofmangrove patches had reached 4 hm2 by the end of 2013. Spatially, mangrove degradation mainly locatedin low-lying land and both sides of contaminant transport channels. The degradation degree of River-typemangrove communities was the most serious, whose major distribution was in the middle and lower reaches of Yanfengdong River. Meanwhile, the degraded mangrove communities also distributed sporadicallyin frontier areas of Dongzhaigang Harbor. The degradation degree was higher for mangrove communities inthe climax stage of succession. The distribution of degraded mangrove communities was mainly determined by terrestrial pollutant loading.
-
防风Saposhnikovia divaricata (Turcz.) Schischk.为伞形科多年生草本植物,主要分布在中国、韩国和日本[1],以未抽薹的干燥根入药[2]。防风药用历史悠久,在中医临床实践中已有
2000 多年的历史,是我国传统中药材的重要组成部分,具有解表祛风、胜湿、止痛解痉的功效[3]。现代研究表明防风中含有挥发油、色原酮、有机酸、香豆素以及多糖等多种类别的化学成分,其中,香豆素类是防风的主要药效成分之一,具有抗炎、抗病毒、抗菌、保护心脏、诱导癌细胞凋亡等药理作用[4]。香豆素类化合物通过苯丙烷途径产生,根据母核上的取代基及其位置的不同,可分为简单香豆素、呋喃香豆素和吡喃香豆素,具有多种生物活性;在香豆素合成通路中多数基因均是以基因家族的形式存在于植物中,对香豆酰辅酶A 2'−羟化酶(p-Coumaroyl CoA 2'-hydroxylase, C2'H)参与香豆素合成,属于2−氧代戊二酸依赖性双加氧酶(2-Oxoglutarate-dependent dioxygenase,2OGD)超家族[5]。邻羟基化反应是香豆素生物合成的关键步骤,C2'H通过催化对香豆酰辅酶A和阿魏酰辅酶A的邻位羟基化,生成伞形酮前体与东莨菪碱前体,最后通过自发或酶促环化形成香豆素核心骨架。目前,在拟南芥[6]、甘薯[7]、芸香[8]、白花前胡[9]等物种中发现C2'H对对香豆酰辅酶A和阿魏酰辅酶A这2种底物均具有高度特异性;然而,在防风中尚未克隆到C2'H基因。因此,本研究拟克隆防风SdC2'H基因,解析其对香豆素生物合成的调控作用。
毛状根是发根农杆菌Agrobacterium rhizogenes侵染植物受伤部位使植物表面产生的一种病理表现[10],具有遗传稳定、繁殖速度快、容易进行基因操作等优点。毛状根不仅是研究植物基因功能的良好遗传体系[11],还可以合成具植物特征的次生代谢产物,因此在药用植物研究方面,毛状根的培养技术受到诸多关注,在丹参[12]、人参[13]、长春花[14]等药用植物中取得显著进展。近年来,很多学者利用毛状根培养体系在不同植物中进行基因功能研究。例如,在丹参毛状根中过表达SmSCR1基因显著提高毛状根中丹参酮的含量[15];在黄芩毛状根中过表达肉桂酸4−羟化酶(Cinnamate 4-hydroxylase,C4H)和4−香豆酰辅酶A连接酶(4-Coumaroyl coenzyme A ligase,4CL)基因显著增加毛状根中黄酮的含量[16];在何首乌毛状根中过表达2种尿苷二磷酸依赖性糖基转移酶(Uridine-diphosphate-dependent glycosyltransferases,UGTs)基因使毛状根中2, 3, 5, 4'−四羟基二苯乙烯−2−O−β−D−葡萄糖苷(2, 3, 5, 4'- Tetrahydroxy stilbene-2-O-β-D-glucoside,THSG)含量显著提高[17]。而在防风毛状根中进行基因过表达功能验证的研究报道较少。本研究前期利用茉莉酸甲酯(Methyl jasmonate,MeJA)诱导的防风毛状根转录组测序数据[18]筛选出香豆素生物合成途径的关键基因C2'H,利用无缝克隆技术,构建含有SdC2'H基因的过表达载体,利用毛状根遗传转化体系开展SdC2'H基因功能研究,解析该基因在防风香豆素生物合成中的作用,为阐明香豆素生物合成的分子调控网络提供基础。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 试剂与仪器
植物RNA提取试剂盒(货号:ZP405)、cDNA合成试剂盒(货号:AT311)、快速高保真DNA聚合酶(货号:AS131)、同源重组无缝克隆试剂盒(货号:CU201)购于北京全式金生物科技有限公司;SanPrep柱式DNA胶回收试剂盒(货号:B518131)、限制性内切酶Bg1 II和BstE II、SanPrep柱式质粒DNA小量抽提试剂盒(货号:B518191)、植物DNA提取试剂盒(货号:B518262)以及大肠埃希菌DH5α感受态细胞购于上海生工生物工程股份有限公司;pMD-19T载体以及DNA marker(BM2000、BM15000)购于TaKaRa公司;K599发根农杆菌感受态细胞采购自华越洋生物科技(北京)有限公司。
仪器包含PCR仪ProFlex™(美国ThermoFish)、恒温振荡培养箱YAMATOIC412C(美国Yamato)、离心机(美国ThermoFish)、琼脂糖凝胶电泳仪DYY-8C(北京六一)、凝胶成像系统GIS-2010(上海Tanon)。
1.2 PCR引物及程序
由上海生工生物工程股份有限公司完成所有PCR引物合成及测序工作,试验所用引物信息及PCR反应程序参见表1、2。
表 1 引物信息Table 1. Primer information编号
Code项目
Item名称
Name正向序列(5′→3′)
Forward sequence反向序列(5′→3′)
Reverse sequenceS1 SdC2'H基因克隆 SdC2'H-1 ATGCATATTGTTAATCATGG TCATATCTTTGCAAACTCGA S2 SdC2'H基因过表达载体构建 SdC2'H-2 TGACCATGGTAGATCTATGCATA
TTGTTAATCATGGAGTCCCCAATTCGAGCTGGTCACCTCATATC
TTTGCAAACTCGAGAGTGTCCS3 植物双元表达载体构建 1304 GCAACAGGATTCAATCTTAAGA ATTGTGAAGATAGTGGAAAAGG S4 毛状根中rolB验证 rolB GCCAGCATTTTTGGTGAACT GGCACTGAACTTGCCGTTAT S5 转基因毛状根外源SdC2'H鉴定 hrHyg ATCATCGAAATTGCCGTCAA ATGGCGTGATTTCATATGCG S6 利用RT-qPCR检测EF1-α表达 EF1-α AGGCTCTTCAGGAGGCTCTTC CAATGTGACAGGTGTGGCAATC S7 利用RT-qPCR检测SdC2'H表达 q-C2'H ATGCATATTGTTAATCATGGAGTCC GCAACGCAAAGAATCTACGA 1.3 防风SdC2'H基因克隆及生物信息学分析
采用植物RNA提取试剂盒提取新鲜防风叶片总RNA,采用cDNA合成试剂盒逆转录获得cDNA。使用Vector N TI设计引物S1(表1)对SdC2'H基因进行PCR扩增,采用反应程序1(表2);反应体系(20 μL)为cDNA 1.0 μL、2× TransTag HiFi PCR SuperMixⅡ 10.0 μL、上游引物(10 μmol·L−1)1.0 μL、下游引物(10 μmol·L−1)1.0 μL、ddH2O 7.0 μL。利用琼脂糖凝胶电泳纯化PCR扩增产物,在16 ℃恒温条件下与pMD-19T载体过夜连接。将连接产物转入大肠埃希菌DH5α感受态细胞,在含50 mg·L−1 Amp的LB平板上筛选阳性克隆,随机选取若干阳性克隆进行PCR鉴定,对确认符合要求的阳性菌液样本进行测序。
表 2 PCR 程序Table 2. PCR programs编号
Code项目
Item程序
Program1 SdC2'H基因克隆 94 ℃ 5 min;94 ℃ 30 s, 45 ℃ 30 s,72 ℃ 1 min,35次循环;72 ℃ 10 min 2 SdC2'H基因过表达载体构建 94 ℃ 3 min;94 ℃ 30 s,68 ℃ 30 s,72 ℃ 1 min,35次循环;72 ℃ 10 min 3 植物双元表达载体构建 95 ℃ 5 min;95 ℃ 30 s,55 ℃ 30 s,72 ℃ 1.5 min,35次循环;72 ℃ 10 min 4 毛状根中rolB验证 94 ℃ 5 min;94 ℃ 30 s,55 ℃ 30 s, 72 ℃ 1 min,35次循环;72 ℃ 10 min 5 转基因毛状根外源SdC2'H鉴定 94 ℃ 5 min;94 ℃ 30 s,55 ℃ 55 s,72 ℃ 1 min,35次循环;72 ℃ 10 min 6 利用RT-qPCR检测EF1-α表达 95 ℃ 30 s;95 ℃ 5 s,58 ℃ 30 s,72 ℃ 10 s,40次循环 7 利用RT-qPCR检测SdC2'H表达 95 ℃ 30 s;95 ℃ 5 s,58 ℃ 30 s,72 ℃ 10 s,40次循环 基于Expasy-ProtParam在线平台解析SdC2'H蛋白的理化参数;通过SOPMA在线工具预测其二级结构组成;利用Swiss-Model进行三级结构建模;通过SiqnalP6.0 Server在线平台进行信号肽特征预测;借助NCBI的CD-search工具进行保守结构域鉴定;从GenBank选取16个跨物种同源序列,将其与本研究获得的防风SdC2'H序列共同导入MEGA 11软件进行多序列比对,基于近邻聚类算法构建系统进化树。
1.4 构建过表达SdC2'H基因的植物双元表达载体
选取pCAMBIA1304载体Bg1 II与BstE II酶切位点作为SdC2'H基因插入位点,按照同源重组无缝克隆试剂盒的要求设计同源臂引物S2(表1),并进行PCR扩增,采用反应程序2(表2);对质粒pCAMBIA1304进行Bg1 II和BstE II双酶切处理(37 ℃、1 h);按照Basic Assembly反应体系对琼脂糖凝胶电泳纯化扩增产物的目标基因及线性化载体(物质的量比2∶3)进行重组连接,在PCR仪中于50 ℃温育15 min;将重组连接产物转化至大肠埃希菌Trans1-T1感受态细胞,在含50 mg·L−1 Kan的LB固体培养基上随机挑选阳性单菌落;对扩大培养的阳性菌液进行PCR分子鉴定与测序验证,将确认无误的重组质粒命名为pCA-SdC2'H。
1.5 构建重组发根农杆菌K599
利用冻融法将重组pCA-SdC2'H质粒导入发根农杆菌K599感受态细胞,在含50 mg·L−1 Kan、50 mg·L−1 Str的YEB固体培养基上随机选取阳性克隆;选取引物S3(表1)配合PCR程序3(表2)对阳性克隆进行PCR检测与测序;将经测序确认的重组农杆菌接种至含有相应抗生素的YEB液体培养基中,于28 ℃摇床以180 r·min−1振荡培养至对数期,测定菌液D600 nm为0.6~1.0时离心,收集菌体,以等体积1/2MS液体培养基进行重悬[18]。
1.6 过表达SdC2'H基因防风毛状根的诱导、验证及培养
在超净工作台中将防风无菌苗的叶片剪出伤口,并放置在重悬于等体积1/2MS液体培养基的菌液中,于28 ℃摇床中震荡侵染;10 min后取出外植体在滤纸上擦干,接种于MS固体培养基,放置于25 ℃恒温培养箱共培养3 d;3 d后将外植体在无菌水中冲洗掉多余农杆菌,吸干水分并转接到含有50 mg·L−1 Cef的固体MS培养基中除菌培养[18]。以发根农杆菌K599诱导防风毛状根建立空白对照组(CK),同时分别利用携带pCAMBIA1304空载体的工程菌诱导防风毛状根构建阴性对照组(NC),以及携带SdC2'H过表达载体的工程菌诱导防风毛状根构建过表达组(SdC2'H+);每周继代培养并梯度降低Cef质量浓度,直至诱导获得防风毛状根;随后通过植物DNA提取试剂盒获取各处理组毛状根系基因组DNA,分别选取引物S4、S5(表1)配合程序4、5(表2)进行rolB基因及hrHyg外源基因的PCR鉴定。参照西芸霏[18]的方法对上述鉴定正确的防风毛状根进行液体扩大培养,操作如下:无菌条件下称取1.5 g长势一致的防风毛状根系样本,接种于含1/2MS液体培养基的锥形瓶中,置于25 ℃恒温摇床以130 r·min−1进行振荡培养,每7 d更换1次新鲜培养基;持续培养21 d后收获毛状根样本,经蒸馏水冲洗后用于后续SdC2'H基因表达量检测与香豆素含量测定。每个处理设3次生物学重复。
1.7 防风毛状根中SdC2'H基因表达水平检测
通过植物RNA提取试剂盒提取各处理组毛状根系总RNA,并选用cDNA合成试剂盒进行cDNA合成,反应体系为防风毛状根RNA 4 μL、Anchored Oligo (dT)18 1 μL、2× TS Reaction Mix 10 μL、TransScript RT/RI Enzyme Mix 1 μL、gDNA Remover 1 μL、RNase-free Water 1 μL,反应条件为42 ℃孵育15 min,85 ℃加热5 s失活TransScript RT/RI与gDNA Remover。以防风EF1-α基因作为内参基因,利用RT-qPCR检测防风毛状根样品中SdC2'H基因的表达水平;以引物S6(表1)对EF1-α进行扩增,采用PCR反应程序6(表2),以引物S7(表1)对SdC2'H进行扩增,采用PCR程序7(表2),反应体系均为基因1.0 μL、上游引物(10 μmol·L−1)1.0 μL、下游引物(10 μmol·L−1)1.0 μL、SYBR Green Master Mix 10.0 μL、ddH2O 7.0 μL;采用2−△△CT法计算SdC2'H基因的相对表达水平[19]。
1.8 防风毛状根中香豆素含量的测定
用蒸馏水将毛状根冲洗干净,并用滤纸吸干水分后置于60 ℃烘箱,干燥后的毛状根用研钵磨成细粉,过0.6 mm孔径筛,称取0.2 g样品,加入6 mL甲醇,于60 ℃超声提取1 h,冷却,滤纸过滤,过0.22 μm滤膜。采用HPLC测定香豆素含量[20]。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 SdC2'H基因克隆与生物信息学分析
如图1所示,PCR扩增产物呈现813 bp的特异性条带,经测序证实其实际长度与预期完全一致,包含完整的813 bp开放阅读框。
BLAST比对结果显示,该序列与Kitagawia praeruptora的C2'H cDNA序列相似性为93.33%,氨基酸序列相似性为94.44%,确证其为防风SdC2'H基因序列,并成功提交至GenBank数据库(登录号:PV169361)。生物信息学分析显示,防风SdC2'H蛋白分子式为C
1386 H2 191N357O401S9,理论相对分子质量为305603330 ,等电点为6.61,不稳定指数为37.50(<40),是一个不稳定蛋白;亲水性为−0.184(<0),为亲水性蛋白。SdC2'H蛋白质的二级结构以α−螺旋和卷曲结构为主,分别占比34.81%和47.41%,另外延伸链占据17.78%。由三级结构模型预测可知,该蛋白主要由α−螺旋和无规则卷曲组成。SdC2'H蛋白位于跨膜区和膜内部的概率很低,主要定位于膜外。信号肽预测值均为0,说明不含典型信号肽序列。保守结构域分析结果进一步显示,防风SdC2'H属于PLN03178超家族,聚类分析结果如图2所示。防风SdC2'H的氨基酸序列与伞形科植物紫花前胡Angelica decursiva和K. praeruptora的序列聚在一起,亲缘关系较近,说明防风SdC2'H和其他伞形科植物C2'H具有相似的功能。2.2 过表达SdC2'H基因防风毛状根的验证
基于图3所示方法构建防风pCA-SdC2'H双元表达载体,经PCR验证(图4)显示,特异性扩增条带长度为813 bp,与SdC2'H基因预期长度一致,测序比对证实其与GenBank注册序列(PV169361)相似性为100%,确证成功构建了防风pCA-SdC2'H双元表达载体。侵染7、30 d后的毛状根样本如图5所示,空白对照(CK)、空载体阴性对照(NC)及过表达SdC2'H(SdC2'H+)3个处理组均长势良好。
图6a为各处理防风毛状根系中rolB基因的PCR验证结果,扩增获得长度为703 bp的条带,经测序比对,与K599发根农杆菌中rolB基因序列完全匹配(相似性100%)。如图6b所示,SdC2'H+组特异性扩增出418 bp条带,经测序比对,与hrHyg基因序列完全匹配(相似性100%),确证SdC2'H基因成功外源整合至毛状根基因组,并排除内源性基因干扰。上述结果证实,本研究成功诱导了过表达SdC2'H基因的防风毛状根。
![图 6 基于rolB (a)和hrHyg (b)扩增的防风毛状根鉴定]() 图 6 基于rolB (a)和hrHyg (b)扩增的防风毛状根鉴定SdC2'H+:过表达SdC2'H,NC:空载体阴性对照,CK:空白对照,M:DNA marker。Figure 6. Identification of Saposhnikovia divaricata hairy roots based on rolB (a) and hyHyg (b) amplificationSdC2'H+: Overexpressing SdC2'H, NC: Negative control containing empty vector, CK: Blank control, M: DNA marker.
图 6 基于rolB (a)和hrHyg (b)扩增的防风毛状根鉴定SdC2'H+:过表达SdC2'H,NC:空载体阴性对照,CK:空白对照,M:DNA marker。Figure 6. Identification of Saposhnikovia divaricata hairy roots based on rolB (a) and hyHyg (b) amplificationSdC2'H+: Overexpressing SdC2'H, NC: Negative control containing empty vector, CK: Blank control, M: DNA marker.2.3 防风毛状根中SdC2'H基因的表达水平
通过RT-qPCR定量检测防风毛状根中SdC2'H基因表达水平,应用GraphPad Prism 9.5软件进行t检验。如图7所示,SdC2'H+处理组基因表达水平显著高于空白对照组(CK) (P<
0.0001 )。![图 7 SdC2'H在不同处理防风毛状根系中的相对表达水平]() 图 7 SdC2'H在不同处理防风毛状根系中的相对表达水平CK:空白对照,NC:空载体阴性对照,SdC2'H+:过表达SdC2'H;****表示在P<0.000 1水平差异显著(t检验)。Figure 7. Relative expression levels of SdC2'H in Saposhnikovia divaricata hairy roots of different treatmentsCK: Blank control, NC: Negative control containing empty vector, SdC2'H+: Overexpressing SdC2'H; **** indicates significant difference at P<0.000 1 level (t test).
图 7 SdC2'H在不同处理防风毛状根系中的相对表达水平CK:空白对照,NC:空载体阴性对照,SdC2'H+:过表达SdC2'H;****表示在P<0.000 1水平差异显著(t检验)。Figure 7. Relative expression levels of SdC2'H in Saposhnikovia divaricata hairy roots of different treatmentsCK: Blank control, NC: Negative control containing empty vector, SdC2'H+: Overexpressing SdC2'H; **** indicates significant difference at P<0.000 1 level (t test).2.4 防风毛状根中香豆素含量
如图8所示,经1/2MS液体培养基培养21 d后,各处理防风毛状根均长势良好。采用HPLC检测各处理组防风毛状根系中香豆素含量(图9),经采用GraphPad Prism 9.5软件进行t检验,SdC2'H+组香豆素含量均显著高于空白对照组(CK) (P<0.001)与空载体阴性对照组(NC) (P<0.01)。
![图 9 不同处理防风毛状根系中的香豆素含量]() 图 9 不同处理防风毛状根系中的香豆素含量CK:空白对照,NC:空载体阴性对照,SdC2'H+:过表达SdC2'H;**和***分别表示在P<0.01和P<0.001水平差异显著(t检验)。Figure 9. Coumarin contents in Saposhnikovia divaricata hairy roots of different treatmentsCK: Blank control, NC: Negative control containing empty vector, SdC2'H+: Overexpressing SdC2'H; ** and *** indicate significant differences at P<0.01 and P<0.001 levels respectively (t test).
图 9 不同处理防风毛状根系中的香豆素含量CK:空白对照,NC:空载体阴性对照,SdC2'H+:过表达SdC2'H;**和***分别表示在P<0.01和P<0.001水平差异显著(t检验)。Figure 9. Coumarin contents in Saposhnikovia divaricata hairy roots of different treatmentsCK: Blank control, NC: Negative control containing empty vector, SdC2'H+: Overexpressing SdC2'H; ** and *** indicate significant differences at P<0.01 and P<0.001 levels respectively (t test).3. 讨论与结论
香豆素作为苯骈−α−吡喃酮类的芳香族天然产物,在药用植物中广泛存在,具有抗肿瘤、抗凝血及抗氧化等重要的药理活性[21]。本研究从防风中成功克隆SdC2'H基因,其开放阅读框为813 bp,编码蛋白含270个氨基酸。SdC2'H蛋白一级结构分析显示其具有亲水性及结构不稳定特征,且缺乏典型信号肽序列。二级结构以α−螺旋和无规则卷曲为主,初步解析了该蛋白的折叠构象特征。由C2'H蛋白构建的系统进化树可见,防风SdC2'H蛋白与伞形科植物紫花前胡亲缘关系最近,推测防风SdC2'H可能与紫花前胡C2'H具有相似功能,为后续解析防风香豆素生物合成的分子机制提供了依据。
近年来,有关功能基因对药用成分生物合成调控的研究日益深入。Hwang等[22]利用根瘤菌注射法,在黄芪茎外植体中诱导过表达AmUGT15基因的毛状根,其黄芪甲苷总量是野生型对照组的4.2倍。侯嘉铭等[23]利用发根农杆菌转化法将CHI基因在甘草毛状根中过表达,其黄酮类有效成分的含量显著增加。本研究在防风中构建过表达载体pCA-SdC2'H,利用发根农杆菌诱导防风子叶外植体,获得过表达SdC2'H基因的防风毛状根系,其SdC2'H基因的表达水平显著高于空白对照,且香豆素含量显著高于空白对照和空载体阴性对照,证实该基因通过增强对对香豆酰辅酶A的催化效率正向调控香豆素合成通路。前人通过系统进化树分析发现,白花前胡PpC2'H与欧防风PsC2'H具有较高的序列相似性[24]。已有研究表明,C2'H及F6'H介导的邻位羟基化反应是香豆素生物合成的关键步骤,其中游离肉桂酸衍生物作为非活性底物参与催化过程[8, 25],例如,拟南芥AtF6'H1和甘薯IbF6'H1对阿魏酰辅酶A表现出严格的底物特异性。本研究中SdC2'H基因对香豆素合成具有正向调控作用,这一结果也与在拟南芥中过表达F6'H1促进东莨菪碱生成的研究结果[26]相似,说明防风中SdC2'H基因和AtF6'H1基因可能具有高度相似的功能。
本研究成功构建了过表达SdC2'H基因的防风毛状根培养体系,明确了SdC2'H基因在香豆素生物合成中的促进作用。今后,将继续以防风毛状根为研究对象,对影响香豆素生物合成的其他关键基因进行研究,进一步解析香豆素生物合成的分子调控机制。
-
表 1 研究区N、P输出系数1)
Table 1 Nitrogen and phosphorus export coefficients in the study area

表 2 1987-2013年东寨港红树林面积变化情况
Table 2 Changes of mangrove area in Dongzhaigang Harbor from 1987 to 2013

表 3 各样地的群落退化特征1)
Table 3 Community degradation characteristics of sample plots

表 4 各样地的群落特征与退化特征相关性分析1)
Table 4 The correlation analyses of community characteristics and degradation characteristics of sample plots

表 5 各样地的地形因子与退化特征相关性分析1)
Table 5 The correlation analyses of topographical factors and community degradation characteristics of sample plots

-
[1] ALONGI D. Present state and future of the World' s mangrove forests[J]. Envir Conserv, 2002, 29 (3):331-349. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=JJ029814689
[2] RAKOTOMAVO A, FROMARD F. Dynamics of mangrove forests in the Mangoky River delta, Madagascar, under the influence of natural and human factors[ J]. Forest Ecol Management, 2010, 259 (6):1161-1169. doi: 10.1016/j.foreco.2010.01.002
[3] 伍淑婕, 梁士楚.人类活动对红树林生态系统服务功能的影响[J].海洋环境科学, 2008, 27 (5):537-542. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-6336.2008.05.033 [4] 赵晓涛, 杨威, 周丹, 等.影响我国河口地区可持续发展的五大问题[J].海洋开发与管理, 2008, 25 (3):91- 93. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9857.2008.03.020 [5] REDDI E U B, RAMAN A V, SATYANARAYANA B, et al. Degradation of mangrove ecosystem due to hinterland farm practices: A case for Coringa, East Coast of India [J].南京林业大学学报:自然科学版, 2003, 27 (2):1- 6. http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-NJLY200302001.htm [6] 廖宝文, 李玫, 陈玉军, 等.海南东寨港红树林生态系统研究[M].青岛:中国海洋大学出版社, 2007:2-31. [7] 徐蒂, 廖宝文, 朱宁华, 等.海南东寨港红树林退化原因初探[J].生态科学, 2014, 33 (2):294-300. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=STKX201402017&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ [8] BROOK R A. Discovery of Sphaeroma terebrans, a woodboring isopod, in the red mangrove, Rhizophora mangle, habitat of Northern Florida Bay[J]. AMBIO:J Human Envir, 2004, 33 (3):171-173. doi: 10.1579/0044-7447-33.3.171
[9] 邱勇, 李俊, 黄勃, 等.影响东寨港红树林中光背团水虱分布的生态因子研究[ J].海洋科学, 2013, 37 (4): 21-25. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hykx201304004 [10] 王胤, 左平, 黄仲琪, 等.海南东寨港红树林湿地面积变化及其驱动力分析[ J].四川环境, 2006, 25 (3):44-49. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3644.2006.03.011 [11] LIU K, LI X, SHI X, et al. Monitoring mangrove forest changes using remote sensing and GIS data with decisiontree learning[J]. Wetlands, 2008, 28 (2):336-346. doi: 10.1672/06-91.1
[12] 吴哲, 陈歆, 刘贝贝, 等.基于InVEST模型的海南岛氮磷营养物质负荷的风险评估[ J].热带作物学报, 2013, 34 (9):1791-1797. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2561.2013.09.029 [13] 李廷友, 林振山.海水围塘混合养殖生态系统氮磷平衡的研究[ J].井冈山大学学报:自然科学版, 2010, 31 (2):32-35. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/jgsxyxb201002008 [14] 王兵, 郑秋红, 郭浩.基于Shannon - Wiener指数的中国森林物种多样性保育价值评估方法[ J].林业科学研究, 2008, 21(2):268-274. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-1498.2008.02.025 [15] 薛春汀.人类活动对密克罗尼西亚联邦库赛埃岛红树林海岸的影响[J].海洋湖沼通报, 2002, (2):17-23. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6482.2002.02.003 [16] 范航清, 刘文爱, 钟才荣, 等.中国红树林蛀木团水虱危害分析研究[J].广西科学, 2014, 21 (2):140-152. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gxkx201402012 [17] 廖宝文, 李玫, 陈玉军, 等.中国红树林恢复与重建技术[M].北京:科学出版社, 2010:120-122.



 下载:
下载: