Agricultural high temperature disaster monitoring based on meteorological data mining in Guangdong Province
-
摘要:目的
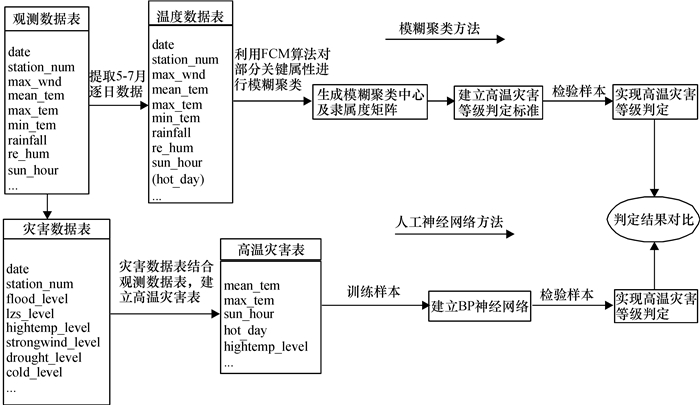
对广东省气象观测数据挖掘分析,以广东省农业气象灾害中的高温为例,预测可能存在的灾害及其等级.
方法在缺乏灾害判定规则和历史灾情等先验知识的条件下,应用模糊C均值聚类算法(FCM)挖掘得出关键属性的聚类中心和隶属度矩阵,建立灾害等级判定规则,进而通过气象观测数据预测可能即将发生的农业气象灾害及其等级.通过误差反向传播(BP)神经网络算法对气象观测历史数据及同期发布的灾害等级数据进行学习,训练后的网络模型可以准确地揭示内在的灾害发生规律,进而通过气象观测数据精确地预测可能即将发生的农业气象灾害及其等级.
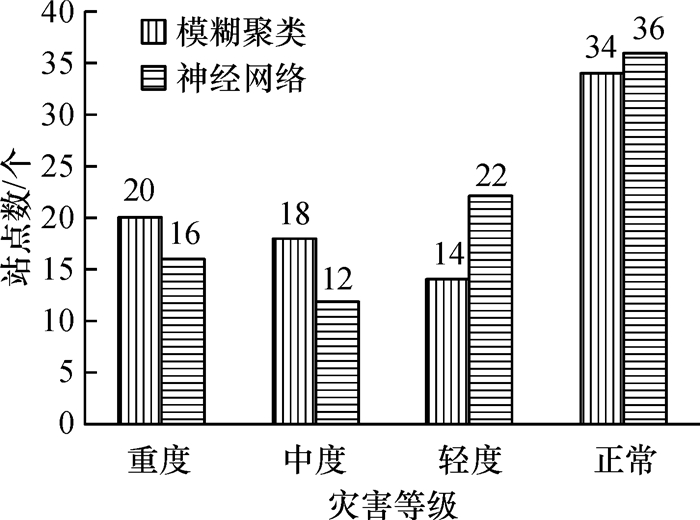
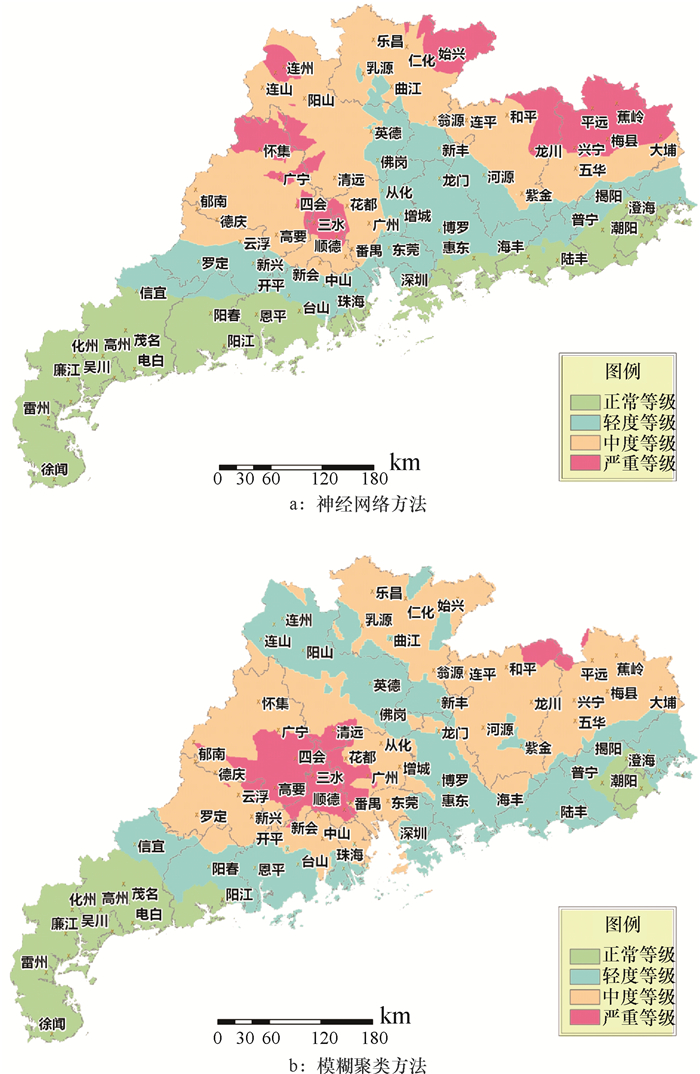
结果和结论BP和FCM 2种数据挖掘方法在缺乏先验知识的条件下,均可以通过气象观测数据准确预测农业气象灾害,结果对比表明前者预测气象站点灾害等级的精度略优于后者.
Abstract:ObjectiveTo forecast agrometeorological disasters and their levels as an example of high te-mperature disaster in Guangdong Province.
MethodDue to lack of disaster decision rule and historical disaster level data, high temperature disaster level rules were built using fuzzy clustering algorithm (FCM) based on the meteorological data in the long term. Those rules were concluded from the cluster centers of the key attribute and membership degree matrix according to the maximum membership degree principle. Based on these rules, possible disasters and their levels were predicted by dynamic meteorological data. The back propagation network algorithm (BP) in the absence of disa-ster decision rules was applied to study historical meteorological observation data and synchronous disaster level released by the meteorological bureau. The trained BP network models were accurate to discover the inner rules of disasters, so the BP network models were fit for predicting the possible disasters and their level through dynamic observation of data at many meteorological stations.
Result and conclusionComparing the results of the two methods of data mining, the neural network is found slightly better than the fuzzy clustering to predict the meteorological disaster level.
-
表 1 广东省气象遥测站多要素逐日观测数据结构
Table 1 Data structures of the meteorological observation in Guangdong Province

表 2 广东省农业气象灾害发布数据结构
Table 2 Data structures of public agricultural meteorological disasters in Guangdong Province

表 3 高温模糊等级与模糊聚类中心
Table 3 High temperature fuzzy levels and fuzzy cluster centers

表 4 各站点神经网络方法预测灾害等级与实际发布结果对比1)
Table 4 The comparison between public disaster level and predicted result based on neural network at every meteorological station

-
[1] 李祎君, 王春乙, 赵蓓, 等.气候变化对中国农业气象灾害与病虫害的影响[J].农业工程学报, 2010, 26(S1): 263-271. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/mykj201407223 [2] 娄伟平, 诸晓明, 周锁铨, 等.绍兴市农业生态和农业气象灾害监测预警系统[J].农业工程学报, 2007, 23(12): 182-186. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-6819.2007.12.035 [3] 阳园燕, 何永坤, 罗孳孳, 等.三峡库区水稻高温热害监测预警技术研究[J].西南农业学报, 2013, 26(3): 1249-1254. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4829.2013.03.080 [4] 夏于, 杜克明, 孙忠富, 等.基于物联网的小麦气象灾害监控诊断系统应用研究[J].中国农学通报, 2013, 29(23): 129-134. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgnxtb201323024 [5] 王长委, 胡月明, 谢健文, 等.基于WebGIS的广东省农作物生物灾害动态监测系统的研制[J].华南农业大学学报, 2008, 29(4): 104-107. http://xuebao.scau.edu.cn/zr/hnny_zr/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=200804131&journal_id=hnny_zr [6] 莫建飞, 钟仕全, 陈燕丽, 等.广西主要农业气象灾害监测预警系统的开发与应用[J].自然灾害学报, 2013, 22(2): 150-157. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QKC20132013060500055124 [7] SHI J, CUI L L. Characteristics of high impact weather and meteorological disaster in Shanghai, China[J]. Natural Hazards, 2012, 60(3): 951-969. doi: 10.1007/s11069-011-9877-6
[8] TAO F L, ZHANG S, ZHANG Z. Changes in rice disasters across China in recent decades and the meteorological and agronomic causes[J]. Regional Environ Change, 2013, 13(4): 743-759. doi: 10.1007/s10113-012-0357-7
[9] 刘亚彬, 刘黎明, 许迪, 等.基于信息扩散理论的中国粮食主产区水旱灾害风险评估[J].农业工程学报, 2010, 26(8): 1-7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6819.2010.08.001 [10] 李明阳, 刘方, 徐婷, 等.基于GIS的森林资源空间数据挖掘方法研究:以紫金山为例[J].西北林学院学报, 2012, 27(3): 180-186. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7461.2012.03.36 [11] WU J J, ZHOU L, LIU M, et al. Establishing and assessing the integrated surface drought index (ISDI) for agricultural drought monitoring in mid-eastern China[J]. Int J Appl Earth Observa and Geoinforma, 2013, 23: 397-410. doi: 10.1016/j.jag.2012.11.003
[12] BARTOK J, HABALA O, BEDNAR P, et al. Data mining and integration for predicting dignificant meteorological phenomena[J]. Proceedia Comput Sci, 2010, 1(1): 37-46. doi: 10.1016/j.procs.2010.04.006
[13] PETERS J F, SURAJ Z, SHAN S, et al. Classification of meteorological volumetric radar data using rough set methods[J]. Pattern Recognition Letters, 2003, 24(6): 911-920. doi: 10.1016/S0167-8655(02)00203-9
[14] 吴正龙, 熊范纶, 滕明贵.基于模糊聚类的模糊关联规则挖掘[J].小型微型计算机系统, 2004, 25(7): 1295-1297. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1220.2004.07.046 [15] 仝凌云, 潘佳, 刁鑫.一种用于机场气象预测的模糊神经网络模型[J].计算机工程, 2008, 34(15): 185-186. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/jsjgc200815067 [16] 董全, 黄小玉, 宗志平.人工神经网络法和线性回归法对降水相态的预报效果对比[J].气象, 2013, 39(3): 324-332. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6362.2013.03.012 [17] 余运河, 胡邦辉, 孔玉寿, 等. RLS-BP人工神经网络算法在降水预报中的应用[J].气象科学, 2004, 24(3): 333-341. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-0827.2004.03.012 [18] 曲培青, 施润和, 刘剋, 等.基于遥感和BP人工神经网络的城乡气象站点划分分析[J].地球信息科学学报, 2010, 12(5): 726-732. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqxxkx201005020 [19] 黄子洋, 李毅, 高太长.一种基于神经网络的气象要素插值方法与分析[J].解放军理工大学学报:自然科学版, 2008, 9(4): 404-408. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/jfjlgdxxb200804018 [20] 陆建江, 张亚非, 宋自林.模糊关联规则的研究与应用[M].北京:科学出版社, 2008:28-40. [21] 吕志军, 王照飞, 谢福鼎, 等.基于FCM聚类的时间序列模糊关联规则挖掘[J].大连理工大学学报, 2010, 50(5): 806-810. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dllgdxxb201005032 [22] 范春年, 傅德胜.用神经网络方法进行气象温度预测[J].计算机应用与软件, 2004(3): 108-110. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-386X.2004.03.044 [23] 陈安, 陈宁, 周龙骧, 等.数据挖掘技术及应用[M].北京:科学出版社, 2006:139-146. [24] 张迎春, 肖冬荣, 赵远东.基于时间序列神经网络的气象预测研究[J].武汉理工大学学报:交通科学与工程版, 2003, 27(2): 237-240. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/whjtkjdxxb200302028 [25] 高丹, 迟道才, 王铁良.基于MATLAB神经网络的水稻需水量的预报模型[J].沈阳农业大学学报, 2005, 36(5): 599-602. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1700.2005.05.020



 下载:
下载: