Determination of the amide herbicides in milk using dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction prior to GC-MS
-
摘要:目的
实现牛奶中农药残留快速、准确的分析检测,更好地监督牛奶的食品安全问题.
方法采用分散液液微萃取技术(DLLME)作为前处理方法,气相色谱-质谱联用(GC-MS)作为色谱分析仪器,建立了牛奶中4种酰胺类除草剂(甲草胺、乙草胺、丙草胺和异丙甲草胺)的残留分析方法.
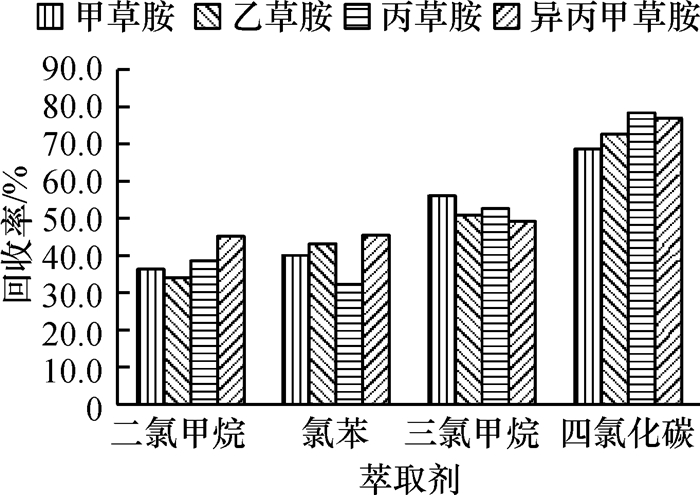
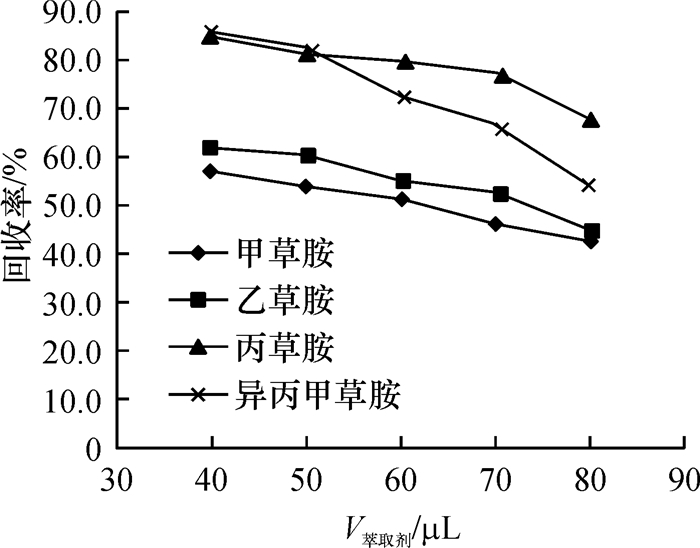
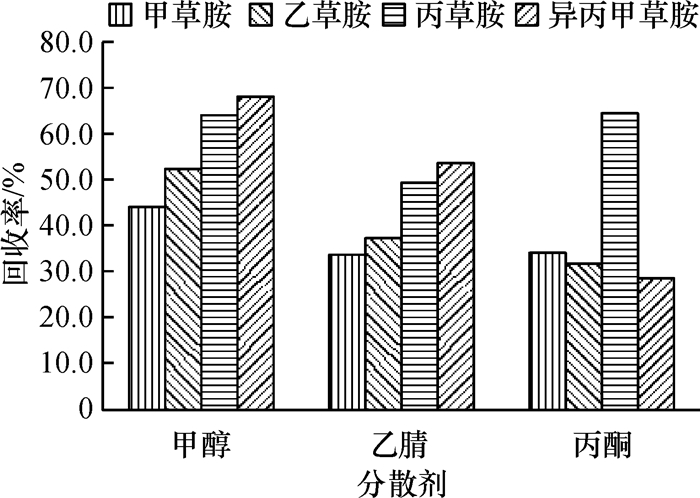
结果和结论对影响萃取效率的因素进行了分析和优化,最终选取40 μL四氯化碳作为萃取剂,1 000 μL甲醇作为分散剂,提取时间设置为1.0 min.在最优的试验条件下,4种酰胺类除草剂质量浓度在0.05~5.00 mg·L-1范围内均具有良好的线性相关,相关系数≥0.997 8.该方法灵敏度高,检出限在0.8~1.4 μg·L-1(S/N=3)范围内.该方法应用于实际牛奶样品的检测,4种目标物的平均添加回收率为67.0%~105.7%,相对标准偏差(RSD)为1.6%~8.3%.
Abstract:ObjectiveTo supervise the food safety problem in milk and achieve a rapid and accurate determination of pesticide residues in milk.
MethodIn this paper, a simple, sensitive and environment friendly dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction (DLLME) technique coupled with gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) was established for the extraction and determination of four amide herbicides (alachlor, acetochlor, pretilachlor, and metolachlor) in milk samples.
Result and conclusionThe factors that affected extraction efficiency were studied and optimized. Eventually, 40 μL carbon tetrachloride was used as the extractant, 1 000 μL methanol was chosen as the dispersant and the extraction time was set to 1.0 min. Under the optimum conditions, the good linearity was exhibited from 0.05 to 5.00 mg·L-1 herbicide, with the correlation coefficient being more than 0.997 8. The method had a high sensitivity, and the limits of detection (S/N=3) of the four amide herbicides ranged from 0.8 to 1.4 μg·L-1. The recoveries of the target analytes from milk samples were found between 67.0% and 105.7%, and the relative standard deviations (RSD) varied from 1.6% to 8.3%. The method can be successfully applied for the analysis of amide herbicides in real milk samples.
-
酸性土壤(pH ≤ 5)占全球耕地面积的30%[1-2]。铝(Al)毒害是酸性土壤中作物生长的主要限制因子[3],在酸性条件下,难溶性Al会加速溶解,而含量在微摩尔水平的Al3+就可以抑制根系生长及其对水分和养分的吸收[4]。随着Al3+在植物体内的转移,在植物的生长过程中光合色素的合成会明显受阻,造成光合产物含量下降。同时,植物细胞内大量分布的Al3+会诱导产生大量的活性氧离子(Reactive oxygen species,ROS),给植物带来氧化压力,造成植物细胞内脂质的过氧化,进而破坏植物细胞质膜等结构,给植物的生长带来更进一步的伤害,最终导致作物产量下降[5]。近年来,土壤酸化现象越来越严重,尤其是工业化活动产生酸雨和大量施用生理酸性肥料,导致土壤中碱性盐基离子减少,Al3+和H+增加,进一步对作物的生长造成负面影响[6]。
大豆Glycine max (Linn.) Merr.是对Al胁迫敏感的作物之一,特别是在我国质地黏重、肥力差、酸性强的砖红壤和赤红壤上种植的大豆,Al毒害严重阻碍它们的生长[7-9]。不同的大豆品种对Al耐受性有较大的差异,耐Al品种在Al胁迫下的反应更加迅速,有机酸(柠檬酸盐等)的分泌量和抗氧化酶(SOD、CAT和POD等)活性相比于Al敏感品种均显著上升[10-12]。目前已经在许多植物中鉴定出与耐Al相关的基因,包括与有机酸分泌相关的ALMT基因家族和与有毒物质排出相关的MATE基因家族等[13]。然而,培育耐Al性强且适宜大面积推广的大豆品种需要较长的周期,因此,仍需要更高效的方法缓解Al胁迫。
纳米技术作为一个新兴的领域,在提高农业投入有效性和作物产量、改善粮食安全等方面展示出良好的效果和广阔的前景[14]。纳米氧化锌(Zinc oxide nanoparticles,ZnO NPs)是目前应用较广泛的纳米粒子[15],其特殊的纳米结构和纳米特性,吸引了众多科学家的关注,也逐渐在农业生产当中表现出积极效应,例如促进种子萌发、幼苗生长,缓解非生物胁迫和提高植物抗性等[16-18]。然而,ZnO NPs带来的负面影响不可忽视,有研究表明,ZnO NPs存在剂量效应:高剂量的ZnO NPs不利于植物的生长,会抑制植物的发芽和叶绿素的生物合成,减少生物量的积累,在植物体内产生氧化应激信号等[19]。作为一种具有超微粒径的颗粒,ZnO NPs可以从生理、生化以及分子层面对植物产生显著的影响,其作用大小主要取决于植物品种、生长阶段、生长环境以及ZnO NPs的施用方法等[20]。
综上所述,一定浓度的ZnO NPs可以促进植物生长发育和缓解植物非生物胁迫,然而目前关于ZnO NPs能否缓解大豆Al胁迫从而促进大豆生长发育的研究还鲜有报道。基于此,本研究利用耐Al性不同的大豆品种,探索不同含量的ZnO NPs对不同基因型大豆生长生理指标的影响,综合评价其在缓解大豆Al胁迫中的作用。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 试验概况
试验于2021年3月在广东省广州市华南农业大学校内(23°9'N、113°21'E)开展,所用土壤采集自校内砂壤土,土壤基本农化性状为pH 4.58(水、土质量比为2.5∶1),有机碳56.37 g/kg,铵态氮37.69 mg/kg,硝态氮91.9 mg/kg,有效磷87.11 mg/kg和速效钾62.98 mg/kg。盆栽培养期间日平均温度为21 ℃。
1.2 试验材料
耐Al品种‘华春2号’和普通品种‘华春6号’[21]由华南农业大学农学院国家大豆改良中心广东分中心提供;w(ZnO NPs)> 99.6%;使用十八水合硫酸铝[(Al2(SO4)3·18H2O)]模拟Al胁迫。
1.3 试验方法
1.3.1 盆栽试验
普通盆栽试验用盆规格为高150 mm、顶部直径200 mm、底部直径150 mm,每盆装入供试土壤1 kg。Al胁迫处理Al含量为0.3 g/kg(Al3+/土壤,m/m)。ZnO NPs含量分别为 0、25、50、100和150 mg/kg(ZnO NPs/土壤,m/m)。大豆播种前,分少量多次,均匀拌入Al2(SO4)3·18H2O和ZnO NPs。选择饱满一致、无虫蛀、发芽率高的‘华春2号’和‘华春6号’种子播种,出苗6 d后定植,每盆4株,生长期间保持土壤含水量(ω)为70%左右。每个处理设3次重复。生长30 d后,测定幼苗期大豆的株高、鲜质量、根长。取叶片测叶绿素含量、总超氧化物歧化酶(Total superoxide dismutase,T-SOD)活性和丙二醛(Malondialdehyde,MDA)浓度。
1.3.2 大豆鲜质量与根长测定
采用直尺 (单位:mm) 测量幼苗株高 (植株根颈部到顶部心叶之间的距离) 和根长 (植株根颈部到主根根尖的距离)。将植株用去离子水洗净并吸干表面水分,使用电子天平测定鲜质量。
1.3.3 叶绿素含量测定
随机摘取新鲜的成熟叶片,取 0.5 g 叶片洗净剪碎放入研钵中,加入少许CaCO3、石英砂及 3 mL 无水丙酮,研成匀浆,再加入 10 mL 无水丙酮继续研磨充分,于黑暗条件下静置 2 h。随后用滤纸和漏斗将提取液转移至 50 mL容量瓶中,用无水丙酮冲洗研钵、研棒和残渣,最后定容至 50 mL 并且摇匀。取叶绿素提取液在紫外分光光度计上测定D663 nm 和D645 nm,随后根据朗博−比尔定律计算叶片中的叶绿素 a 和叶绿素 b 含量[22]。
$$ 叶绿素{\rm{a}}含量/({\rm{mg \cdot g^{-1}}}) = 12.7{{D}}_{663\ {\rm{nm}}}-2.69{{D}}_{645\ {\rm{nm}}},$$ $$ 叶绿素{\rm{b}}含量/({\rm{mg\cdot g^{-1}}}) = 22.9{{D}}_{645\ {\rm{nm}}}-4.68{{D}}_{663\ {\rm{nm}}}。$$ 1.3.4 T-SOD活性及MDA浓度测定
使用购买自南京建成生物研究所的T-SOD试剂盒(货号:A001-1)和MDA试剂盒(货号:A003-1)测定T-SOD活性和MDA浓度,测定方法分别为黄嘌呤氧化酶法[23]和硫代巴比妥酸法[24]。
SOD活性:准确称量新鲜的大豆根系0.1 g,加入5 mL磷酸盐缓冲溶液(pH = 7.4)在冰水浴下进行研磨,制成组织匀浆后,于3500 r/min离心10 min,上清液即为待测样品。准备2支试管,分别为测定管和对照管。在测定管中依次加入试剂一应用液1 mL、样品0.05 mL、试剂二0.1 mL、试剂三0.1 mL和试剂四应用液0.1 mL;在对照管内依次加入试剂一应用液1 mL、蒸馏水0.05 mL、试剂二0.1 mL、试剂三0.1 mL和试剂四应用液0.1 mL。用旋涡混匀器充分混匀,置37 ℃恒温水浴40 min。加入显色剂后室温放置10 min,用紫外分光光度计测量D550 nm,按下列公式进行换算。
$$ \begin{split} &{\rm{T-SOD}}活性= \dfrac{({{D}}_{550\; {\rm{nm}},\;对照}-{{D}}_{550\;{\rm{nm}},\;测定})}{{{D}}_{550\;{\rm{nm}},\;对照 }} \div\\ &\quad \quad 50{\text{%}}\times \dfrac{反应液总体积}{取样体积}\div 匀浆液质量浓度, \end{split} $$ $$ 匀浆液质量浓度= \dfrac{组织湿质量}{匀浆介质体积}。 $$ MDA浓度:准确称量新鲜的大豆根系0.1 g,加入5 mL磷酸盐缓冲溶液(pH = 7.4)在冰水浴下进行研磨,制成组织匀浆后,于3500 r/min离心10 min,上清液即为待测样品。准备4支试管,分别为空白管、标准管、测定管和对照管。在空白管内依次加入无水乙醇溶液0.2 mL、试剂一0.2 mL、试剂二应用液3 mL和试剂三应用液1 mL;在标准管内依次加入10 nmol/mL四乙氧基丙烷溶液0.2 mL、试剂一0.2 mL、试剂二应用液3 mL和试剂三应用液1 mL;在测定管内依次加入样品0.2 mL、试剂一0.2 mL、试剂二应用液3 mL和试剂三应用液1 mL;在对照管内依次加入样品0.2 mL、试剂一0.2 mL、试剂二应用液3 mL和50%(φ)冰醋酸溶液1 mL。加入所有试剂后,用旋涡混匀器混匀,95 ℃水浴40 min后用自来水冷却。以3 500 r/min离心10 min,取上清液,用紫外分光光度计测量D532 nm。按下列公式计算MDA浓度。
$$ \begin{split} {\rm{MDA}}浓度=& \dfrac{({{{{D}}}}_{532\;{\rm{nm}},\;测定}-{{D}}_{532\;{\rm{nm}},\;对照})}{({{D}}_{532\;{\rm{nm}},\;标准}-{{D}}_{532\;{\rm{nm}},\;空白})}\times\\ & 标准品浓度\times 样本稀释倍数。 \end{split} $$ 1.4 数据分析
试验数据采用SPSS 20.0数据处理系统和Excel 2019进行统计分析,试验结果经方差分析后进行Duncan’s多重比较和t检验比较各处理间的差异。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 ZnO NPs对Al胁迫条件下大豆植株鲜质量和根长的影响
在未添加ZnO NPs情况下,对不同品种施加0.3 g/kg的Al处理,Al显著抑制了‘华春6号’的鲜质量和根长,而对‘华春2号’的鲜质量和根长无显著影响(图1)。对Al胁迫下的2个品种施加不同含量的ZnO NPs,当ZnO NPs为150 mg/kg时,‘华春6号’和‘华春2号’的鲜质量达到最大值,同没有ZnO NPs处理相比,分别提高了100.6%和42.7%((图1A、1B))。根长方面,150 mg/kg ZnO NPs处理后,‘华春6号’的根长达到最大值(27.0 cm),‘华春2号’的根长也达到27.2 cm;当ZnO NPs含量为50和100 mg/kg时,‘华春2号’的根长显著低于无ZnO NPs处理的(图1C、1D)。由此说明在Al胁迫下,150 mg/kg的ZnO NPs有助于提高大豆植株的鲜质量和根长,从而改善大豆的生长。
![图 1 ZnO NPs对Al胁迫条件下大豆植株鲜质量和根长的影响]() 图 1 ZnO NPs对Al胁迫条件下大豆植株鲜质量和根长的影响柱子上不同小写字母表示在相同Al处理下ZnO NPs处理间差异显著(P < 0.05,Duncan’s法);“*”和“**”分别表示相同含量ZnO NPs处理下相同品种无Al胁迫和Al胁迫之间在0.05和0.01水平差异显著(t检验)Figure 1. Effect of ZnO NPs on fresh weigh and root length of soybean plantlets under Al stressDifferent lowercase letters above the bars indicate significant differences among ZnO NPs treatments under the same Al treatment(P < 0.05, Duncan’s method); “*” and “**” respectively indicate significant differences at 0.05 and 0.01 levels between no Al and Al stresses of the same variety under the same content of ZnO NPs(t test)
图 1 ZnO NPs对Al胁迫条件下大豆植株鲜质量和根长的影响柱子上不同小写字母表示在相同Al处理下ZnO NPs处理间差异显著(P < 0.05,Duncan’s法);“*”和“**”分别表示相同含量ZnO NPs处理下相同品种无Al胁迫和Al胁迫之间在0.05和0.01水平差异显著(t检验)Figure 1. Effect of ZnO NPs on fresh weigh and root length of soybean plantlets under Al stressDifferent lowercase letters above the bars indicate significant differences among ZnO NPs treatments under the same Al treatment(P < 0.05, Duncan’s method); “*” and “**” respectively indicate significant differences at 0.05 and 0.01 levels between no Al and Al stresses of the same variety under the same content of ZnO NPs(t test)2.2 ZnO NPs对Al胁迫条件下大豆植株叶绿素含量的影响
由图2 所示,随着ZnO NPs含量的增加,Al胁迫的存在对2个品种叶绿素a和叶绿素b含量的影响不同。在未添加ZnO NPs情况下,Al胁迫对‘华春6号’的叶绿素a和叶绿素b含量无明显影响,而显著增加了‘华春2号’的叶绿素a和叶绿素b含量,分别达到12.8 和7.7 mg/g。Al胁迫下,当ZnO NPs含量为25 mg/kg时,‘华春6号’和‘华春2号’的叶绿素a含量达到最高水平,相比于未添加ZnO NPs处理分别上升了20.3%和2.9%(图2A、2B)。不同含量的ZnO NPs处理对‘华春6号’的叶绿素b含量变化影响不明显;‘华春2号’中,ZnO NPs处理显著降低了叶绿素b含量,在ZnO NPs含量为100 mg/kg时达到最低(3.5 mg/g)(图2C、2D)。
![图 2 ZnO NPs对Al胁迫条件下大豆植株叶绿素a和叶绿素b含量的影响]() 图 2 ZnO NPs对Al胁迫条件下大豆植株叶绿素a和叶绿素b含量的影响柱子上不同小写字母表示在相同Al处理下ZnO NPs处理间差异显著(P < 0.05,Duncan’s法);“*”和“**”分别表示相同含量ZnO NPs处理下相s同品种无Al胁迫和Al胁迫之间在0.05和0.01水平差异显著(t检验)Figure 2. Effect of ZnO NPs on chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b contents of soybean plantlets under Al stressDifferent lowercase letters above the bars indicate significant differences among ZnO NPs treatments under the same Al treatment (P < 0.05, Duncan’s method) ; “*” and “**” respectively indicate significant differences at 0.05 and 0.01 levels between no Al and Al stresses of the same variety under the same content of ZnO NPs (t test)
图 2 ZnO NPs对Al胁迫条件下大豆植株叶绿素a和叶绿素b含量的影响柱子上不同小写字母表示在相同Al处理下ZnO NPs处理间差异显著(P < 0.05,Duncan’s法);“*”和“**”分别表示相同含量ZnO NPs处理下相s同品种无Al胁迫和Al胁迫之间在0.05和0.01水平差异显著(t检验)Figure 2. Effect of ZnO NPs on chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b contents of soybean plantlets under Al stressDifferent lowercase letters above the bars indicate significant differences among ZnO NPs treatments under the same Al treatment (P < 0.05, Duncan’s method) ; “*” and “**” respectively indicate significant differences at 0.05 and 0.01 levels between no Al and Al stresses of the same variety under the same content of ZnO NPs (t test)2.3 ZnO NPs对Al胁迫条件下大豆T-SOD活性和MDA浓度的影响
T-SOD是植物体内重要的抗氧化酶,其活性的高低直接反映植物细胞的抗氧化能力。当不添加ZnO NPs时,Al胁迫对‘华春6号’和‘华春2号’的T-SOD活性均无显著影响(图3A、3B)。当添加不同含量的ZnO NPs后,‘华春6号’的T-SOD活性随着ZnO NPs含量增加而升高,150 mg/kg处理时达到最大值,而‘华春2号’中T-SOD活性最大值出现在50 mg/kg处理中。无论哪个品种,在Al胁迫条件下添加ZnO NPs处理后,T-SOD的活性均高于未添加ZnO NPs处理,说明ZnO NPs处理有利于提高大豆根系中T-SOD的活性,增强大豆的抗氧化能力,从而应对外界造成的氧化伤害。
![图 3 ZnO NPs对Al胁迫下大豆T-SOD活性及MDA浓度的影响]() 图 3 ZnO NPs对Al胁迫下大豆T-SOD活性及MDA浓度的影响柱子上不同小写字母表示在相同Al处理不同ZnO NPs处理间差异显著(P < 0.05,Duncan’s法);“*”和“**”分别表示相同含量ZnO NPs相同品种无Al胁迫和Al胁迫之间在0.05和0.01水平差异显著(t检验)Figure 3. Effect of ZnO NPs on T-SOD activity and MDA concentration of soybean plantlets under Al stressDifferent lowercase letters above the bars indicate significant differences among ZnO NPs treatments under the same Al treatment (P < 0.05, Duncan’s method); “*” and “**” respectively indicate significant differences at 0.05 and 0.01 levels between no Al and Al stresses of the same variety under the same content of ZnO NPs (t test)
图 3 ZnO NPs对Al胁迫下大豆T-SOD活性及MDA浓度的影响柱子上不同小写字母表示在相同Al处理不同ZnO NPs处理间差异显著(P < 0.05,Duncan’s法);“*”和“**”分别表示相同含量ZnO NPs相同品种无Al胁迫和Al胁迫之间在0.05和0.01水平差异显著(t检验)Figure 3. Effect of ZnO NPs on T-SOD activity and MDA concentration of soybean plantlets under Al stressDifferent lowercase letters above the bars indicate significant differences among ZnO NPs treatments under the same Al treatment (P < 0.05, Duncan’s method); “*” and “**” respectively indicate significant differences at 0.05 and 0.01 levels between no Al and Al stresses of the same variety under the same content of ZnO NPs (t test)当ZnO NPs含量为0时,Al胁迫显著增加了‘华春6号’的MDA浓度,而对‘华春2号’的MDA浓度无显著影响(图3C、3D)。当添加不同含量的ZnO NPs后,‘华春6号’的MDA浓度随ZnO NPs含量增加而上升,可能是由于ZnO NPs与Al3+协同作用对大豆植株造成了损害。而‘华春2号’呈相反趋势,随着ZnO NPs含量上升,‘华春2号’中MDA浓度呈下降−升高−下降的变化,并在ZnO NPs含量为50 mg/kg时达到最低水平,与无ZnO NPs处理相比下降了20.9%,此时能有效抵抗Al3+对‘华春2号’的损伤。综上,Al胁迫使2种大豆的MDA水平升高,当施用的ZnO NPs含量小于100 mg/kg时,能有效控制2种大豆的MDA浓度,从而降低植物细胞内脂质过氧化水平,达到保护植物细胞的目的。
3. 讨论与结论
低浓度的ZnO NPs对植物的生长具有促进作用[25]。在其对植物的生长具有毒性的报道中,试验处理的纳米颗粒的质量浓度大多都达到了较高的水平(≥ 1 000 mg/L)[26-27]。金属纳米材料在使用过程中,离子会部分释放并被植物吸收,发挥营养元素的功能,当浓度过量时会不可避免地激活植物自身的防御机制,如增加木质素和胼胝质的生物合成,进而限制植物的生长[28-29]。本研究表明Al胁迫显著抑制耐Al性较弱的‘华春6号’的鲜质量和根长,这与前人观察到的结果[30]一致。而ZnO NPs对Al胁迫下‘华春6号’的根长具有显著促进作用,说明低含量的金属纳米颗粒具有改善处于Al胁迫条件下的大豆的生长发育的潜力。此外,Al胁迫增加了耐Al品种‘华春2号’的叶绿素含量,而敏感品种‘华春6号’的叶绿素含量受到Al胁迫的明显抑制。这与前人的研究结果存在一定差异,前期研究普遍认为随着Al3+在植物体内的积累,在植物生长后期,Al胁迫会抑制光合色素的生物合成,影响植物光合作用,最终导致叶片黄化和产量下降[31]。本研究主要集中在大豆苗期,Al胁迫对光合色素的影响较小或许和处理周期较短有关。ZnO NPs促进了‘华春2号’叶绿素a的生物合成,这进一步说明了低剂量条件下ZnO NPs可促进植物生长。也有研究尝试将ZnO NPs和有机改良剂一起作为叶面喷肥在小麦中使用,发现ZnO NPs可以和有机改良剂协同作用,促进小麦生长,如提高生物量和叶绿素含量等[32]。
Al3+诱导植物细胞产生的过量ROS会破坏正常的细胞结构。这一过程中植物SOD的活性会增强,消除过量的ROS,保护植物细胞。不同作物对Al胁迫的反应程度有所不同,受到的伤害也有区别[33]。本研究中,Al胁迫增加了大豆根系中MDA浓度,表明Al胁迫加剧了大豆根系中脂质的过氧化,但是Al处理后大豆根系中的T-SOD活性没有显著升高。当ZnO NPs加入土壤后,大豆根系中的T-SOD活性显著增强,MDA浓度基本随之下降。前期研究在镉污染的水稻中发现,ZnO NPs可以通过提高SOD活性以及降低MDA浓度从而保护水稻正常生长[34]。这说明ZnO NPs可以通过激活植物体内的SOD,提高植物抗氧化能力,降低植物细胞内脂质的过氧化水平,从而保护植物细胞,促进植物生长[34]。
综上,Al胁迫严重影响大豆的生长发育,施用ZnO NPs可在一定程度上缓解Al胁迫对植株产生的负面作用。低剂量的ZnO NPs(50 mg/kg)可以显著增加大豆SOD活性,降低MDA浓度,降低细胞脂质过氧化程度,提高植物抗氧化能力,增强大豆对含Al土壤的耐受性;而较高剂量的ZnO NPs或将对大豆的生长造成不利的影响。因此,合理施用ZnO NPs是缓解植物Al胁迫、改善植物生长的关键。
-
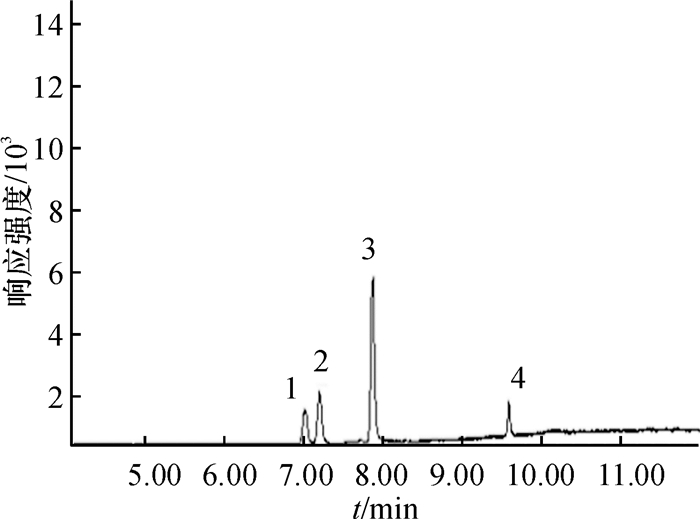
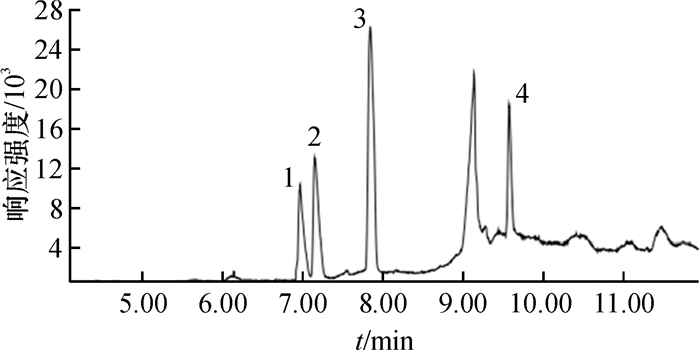
表 1 4种酰胺类除草剂的保留时间和特征离子
Table 1 The retention time and characteristic ions of four amide herbicides

表 2 方法的线性、相关系数、检出限
Table 2 Linearity, correlation coefficients, and limit of detection of the method

表 3 4种酰胺类除草剂在牛奶样品中的添加回收率和相对标准偏差
Table 3 Recoveries and relative standard deviations of four amide herbicides in milk samples

表 4 不同方法对酰胺类除草剂分析测定的比较
Table 4 Comparisons of DLLME-GC-MS with other methods for the extraction and determination of amide herbicides

-
[1] 盛姣, 柏连阳, 刘祥英.酰胺类除草剂及其安全剂研究进展[J].江西植保, 2005, 28(4): 163-165. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-3704.2005.04.007 [2] 张一宾.酰胺类除草剂的全球市场、品种及发展趋向[J].现代农药, 2011, 10(1): 41-43. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-5284.2011.01.012 [3] COLEMAN S, LINDERMAN R, HODGSON E, et al. Comparative metabolism of chloroacetamide herbicides and selected metabolites in human and rat liver microsomes[J]. Environ Health Perspect, 2000, 108(12): 1151-1157. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=b460f06ff7ad9681ebfef23eb056cbd9&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[4] 高晓昇, 张艳, 王松雪, 等.牛奶中拟除虫菊酯类农药残留检测:QuEChERS-气相色谱分析方法的研究与建立[J].中国奶牛, 2010 (8): 56-60. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4264.2010.08.020 [5] 陈虹, 韩勇, 钟明, 等.水样中几种酰胺类除草剂的SPE-GC/ECD法检测[J].化学试剂, 2010, 32(4): 325-327. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-3283.2010.04.012 [6] 李建中, 储晓刚, 蔡会霞, 等.高效液相色谱法同时测定大豆中12种酰胺类除草剂的残留量[J].色谱, 2006, 24(6): 585-588. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-8713.2006.06.011 [7] 周瑶敏, 熊艳, 袁林峰, 等.分散固相萃取法快速测定大米中的酰胺类除草剂[J].中国粮油学报, 2010, 25(8): 113-116. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zglyxb201008025 [8] 沈伟健, 徐锦忠, 杨雯筌, 等.两种离子源技术气相色谱-质谱法检测茶叶中酰胺类除草剂的残留量[J].色谱, 2007, 25(5): 753-757. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-8713.2007.05.028 [9] REZAEE M, ASSADI Y, MILANI HOSSEINI M R, et al. Determination of organic compounds in water using dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction[J]. J Chromatogr A, 2006, 1116(1/2): 1-9. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference/8395795
[10] ZHAO R S, DIAO C P, CHEN Q F, et al. Sensitive determination of amide herbicides in environmental water samples by a combination of solid-phase extraction and dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction prior to GC-MS[J]. J Sep Sci, 2009, 32(7): 1069-1074. doi: 10.1002/jssc.v32:7
[11] 白沙沙, 李芝, 臧晓欢, 等.磁性石墨烯固相萃取-分散液液微萃取-气相色谱法测定水和绿茶中酰胺类除草剂残留[J].分析化学, 2013, 41(8): 1177-1182. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/fxhx201308008 [12] 王鹤, 陈忠林, 沈吉敏, 等.液液微萃取/气相色谱法速检水中四种酰胺类除草剂[J].中国给水排水, 2011, 27(12): 90-93. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgjsps201112025 [13] CAMPILLO N, VIÑAS P, FÉREZ-MELGAREJO G, et al. Dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction for the determination of macrocyclic lactones in milk by liquid chromatography with diode array detection and atmospheric pressure chemical ionization ion-trap tandem mass spectrometry[J]. J Chromatogr A, 2013, 1282: 20-26. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2013.01.086
[14] FARAJZADEH M A, DJOZAN D, MOGADDAM M R, et al. Extraction and preconcentration technique for triazole pesticides from cow milk using dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction followed by GC-FID and GC-MS determinations[J]. J Sep Sci, 2011, 34(11): 1309-1316. doi: 10.1002/jssc.v34.11
[15] GAO S Q, YANG X, YU W, et al. Ultrasound-assisted Ionic liquid/Lonic liquid-dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction for the determination of sulfonamides in infant formula milk powder using high-performance liquid chromatography[J]. Talanta, 2012, 99: 875-882. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2012.07.050
[16] YIANTZI E, PSILLAKIS E, TYROVOLA K, et al. Vortex-assisted liquid-liquid microextraction of octylphenol, nonylphenol and bisphenol-A[J]. Talanta, 2010, 80(5): 2057-2062. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2009.11.005
[17] XU X Q, YANG H H, WANG L, et al. Analysis of chloroacetanilide herbicides in water samples by solid-phase microextraction coupled with gas chromatography-mass spectrometry[J]. Anal Chim Acta, 2007, 591(1): 87-96. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2007.03.044









 下载:
下载: