Seedling growth, morphology and physiological characteristics of Triadica rotundifolia and Croton lachnocarpus under drought stress
-
摘要:目的
为华南石灰岩地区植被恢复的树种选择及人工造林提供理论依据.
方法应用温室盆栽生长法,通过不同浇水频度控制干旱条件,并用常规方法测定各项指标.
结果和结论在干旱胁迫条件下,圆叶乌桕Triadica rotundifolia和毛果巴豆Croton lachnocarpus的苗高净生长量分别比对照减少2%~5%和8%~10%,基径净生长量增加17%~35%和10%~30%;随着干旱胁迫的加剧,2种植物幼苗的地上部和地下部生物量、根冠比均呈现下降趋势.生理检测结果表明,圆叶乌桕苗木的可溶性蛋白含量、过氧化物酶(POD)活性、超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)活性和丙二醛(MDA)含量均低于毛果巴豆;2种植物苗木的可溶性蛋白含量和POD活性对干旱胁迫的响应比较敏感,但SOD活性和MDA含量对干旱胁迫的响应变化不明显.茎部解剖结构比较结果表明,2种植物在茎部皮层、韧皮部、木质部和髓部比例存在较大的差异,干旱胁迫会导致其木质部与髓部厚度比值增加,反映了2个树种可通过增加木质部与髓部结构来适应干旱胁迫.模糊隶属函数值分析结果表明,无论是轻度干旱,还是中度和重度干旱,圆叶乌桕的耐旱能力均强于毛果巴豆,其生理指标和茎部结构对干旱胁迫响应的不同反映了其耐干旱胁迫机制存在差异.
Abstract:ObjectiveSeedling growth, morphology and physiological characteristics of Triadica rotundifolia and Croton lachnocarpus were investigated under drought stress to provide scientific basis for species selection and artificial reforestation in the limestone region of South China.
MethodPot culture experiment was applied in this study to simulate drought stress by watering frequency.The physiological indicators were measured with comventional methods.
Result and conclusionThe results showed that height growth of T.rotundifolia and C. lachnocarpus declined by 2%-5% and 8%-10% respectivly, while basal diameter growth increased by 17%-35% and 10%-30% respectivly under drought stress. Seedling aboveground biomass, underground biomass, total biomass, and root-shoot ratio could be enhanced by light drought stress, but they declined with the increase of drought stress. Results of physiological examination showed that the soluble protein content, peroxidase (POD) activity, activity of superoxide dismutase (SOD), and malondialdehyde (MDA) content varied with species and drought stress. Soluble protein content and POD activity were more sensitive than the activity of SOD and MDA content. Comparison of the stem anatomical structure showed that there were differences in the structure of cortex, phloem, xylem and marrow. Drought would result in increasing ratio of xylem and marrow, which indicated that they could adapt to drought stress by adjusting xylem and marrow structure. Analyses of subordinate functions showed that the drought tolerance of T.rotundifolia were higher than that of C. lachnocarpus under various drought stresses. They may possess different resistance mechanisms to drought stress based on their difference in physiological responses and stem anatomical structures.
-
石灰岩山地土层浅薄,储水能力差,是限制植物生长的重要因素[1].然而,在石灰岩特殊生境中却拥有丰富的特有植物类群[2-5],那些石灰岩特有种是如何适应石灰岩干旱瘠薄环境的?认识石灰岩特有种耐旱生态学特性可为石灰岩退化山地植被恢复的树种选择提供科学依据.近年有关石灰岩植物生理生态特性的研究已受到关注[6-10].莫凌等[7]比较研究了西南喀斯特地区红背山麻杆Alchornea trewioides和圆叶乌桕Triadica rotundifolia等4种植物的水分特征,发现圆叶乌桕的各项测定指标均居于中间.张中峰等[8]比较研究了红背山麻秆和圆叶乌桕物等4种植物对光与水分的适应能力,揭示了圆叶乌桕拥有较高的光饱和点,对光的利用能力较强,但其水分利用效率较低.
圆叶乌桕和毛果巴豆Croton lachnocarpus均为自然分布于粤北石灰岩山区特有的大戟科(Euphorbiaceae)植物.其中,圆叶乌桕自然分布于我国广东、广西、贵州、湖南、云南以及越南北部的石灰岩地区[11],毛果巴豆为我国特有种,生长于华南地区海拔30~800 m山地疏林下林缘或灌丛中[12].本研究应用盆栽生长试验法,比较研究了不同干旱条件对圆叶乌桕和毛果巴豆生长、茎部形态及生理生化特性的影响,拟为华南石灰岩地区植被恢复的树种选择及人工造林提供理论科学依据.
1. 材料与方法
1.1 试验地概况
试验地位于广州市天河区华南农业大学树木园(113°18′26″E、23°06′26″N).广州市地处南亚热带季风区,年平均气温21.8 ℃,年平均降雨量1 623.6~1 899.8 mm.
1.2 材料及试验设计
供试种子采自广东省清远市清新区白湾石灰岩次生林.随采随播育苗,2013年6月移栽入盆中,育苗容器为营养袋,规格为18 cm×16 cm(直径×高),以V(黄心土):V(河砂):V(有机质)=2:1:1作为基质,每盆1株,并保持一致的日常生长管理.试验前测量苗高和基径,作为基础生长量(表 1).每隔30 d记录成活率,测量苗高和基径;90 d时完成试验,统计成活率,并进行生物量、生理指标及茎部解剖研究.
表 1 2种供试植物的苗木基本情况Table 1. Seedling sizes of two species for experiments
供试土壤的平均田间持水量为(25.78±6.25)%,平均容重为(1.26±0.12)g·cm-3.采用盆栽控水法设置了4个梯度的干旱试验.每个试验组设3个重复,每个重复5株幼苗.试验前先浇透所有参试植株,然后对照组(CK)和轻度干旱(T1)、中度干旱(T2)、重度干旱(T3)处理组分别按间隔1、3、6、9 d的浇水频度进行循环控水,使其土壤含水量及占田间持水量的比例达到并保持在表 2所示的范围之内.试验时间为90 d.
表 2 2种植物不同干旱处理组苗木的土壤含水量Table 2. Soil moisture of two species under different drought treatments
1.3 测定指标及方法
1.3.1 土壤含水量
用土壤水分探测仪(型号FOM,厂家Easttest)测定土壤的体积含水量.土壤含水量=体积含水量/土壤容重×100%.
1.3.2 幼苗存活率
按下式统计幼苗的存活率:存活率=(处理后存活苗数/处理前存活苗数)×100%.
1.3.3 幼苗生物量检测
幼苗经105 ℃烘箱中烘15 min杀青后,置于70 ℃烘干24 h,测定地上部、地下部生物量和总生物量,并计算根冠比(植株地下部生物量/地上部生物量).
1.3.4 可溶性蛋白质量分数的测定
利用考马斯亮蓝G-250法[13]测定可溶性蛋白质量分数(单位:mg·g-1).
1.3.5 保护性酶活性测定
过氧化物酶(POD)活性(单位:U·g-1·min-1)采用愈创木酚法测定[13];超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)活性(单位:U·g-1):采用氮蓝四唑(NBT)光化还原法测定[13].
1.3.6 丙二醛(MDA)含量测定
采用硫代巴比妥酸(TBA)比色法测定MDA的质量摩尔浓度(单位:μmol·g-1)[13].
1.3.7 茎部解剖试验
选取经90 d处理后苗木基茎处一段,用FAA固定液(用体积分数为70%的乙醇溶液配制)固定,滑走切片法制片,切片厚度为30 μm,番红固绿染色,中性树胶封片.采用Motic Images Plus 3.0图像分析软件测量,每个测量指标重复20次,求平均值.
1.4 数据分析
采用模糊隶属函数法对圆叶乌桕和毛果巴豆抗旱能力进行综合评定[14].

式中:X(u)为某一植物在某一处理下的隶属函数值;X为该植物在该处理下的平均测定值;Xmax和Xmin分别为所有参试植物在该处理下平均测定值中的最大值和最小值.
采用Microsoft excel 2003和SPSS19.0(Statistical product and service solutions)分析软件进行数据处理与统计分析.
2. 结果与分析
2.1 干旱胁迫对幼苗成活率的影响
供试苗木在不同干旱条件下生长90 d后,圆叶乌桕所有处理组苗木成活率均为100%;毛果巴豆CK组和T1处理组苗木成活率为100%,而T2和T3处理组个别植株出现老叶枯萎、凋落和生长缓慢,甚至出现死亡,成活率分别为73.3%和80.0%.
2.2 干旱胁迫对幼苗生长量的影响
生长检测结果表明,在干旱胁迫处理90 d时,干旱胁迫组苗木的平均苗高净生长量小于CK组;随着干旱胁迫强度的增加,苗高净生长量呈下降趋势,但胁迫组苗木基径平均净生长量大于CK组(表 3).方差分析结果表明,圆叶乌桕干旱胁迫组与CK组的苗高净生长量差异不明显,而T1处理组的基径净生长量与CK组的差异达到显著水平;毛果巴豆各干旱胁迫组与CK组苗高净生长量的差异达到显著水平,T2处理组与CK组苗木基径净生长量的差异达到显著水平.
表 3 2种植物不同干旱处理组苗木的净生长量比较1)Table 3. Seedling growth of two species under different drought treatments
2.3 干旱胁迫对幼苗生物量的影响
生物量测定结果表明,T1处理组有利于2种植物幼苗的地上部和地下部生物量增长,但T3处理组对其地上部和地下部生物量增长有抑制作用.随着干旱胁迫的加强,2种植物幼苗的总生物量和根冠比均呈下降趋势.方差分析结果显示,圆叶乌桕T1处理组与其他组幼苗总生物量的差异达到显著水平,但不同试验组间幼苗根冠比的差异未达到显著水平(表 4);而毛果巴豆不同组间苗木总生物量的差异均不显著,但CK组苗木的根冠比明显小于干旱胁迫组(表 4).
表 4 2种植物不同干旱处理组苗木的生物量和根冠比1)Table 4. Biomass and root shoot ratio of two species under different drought treatments
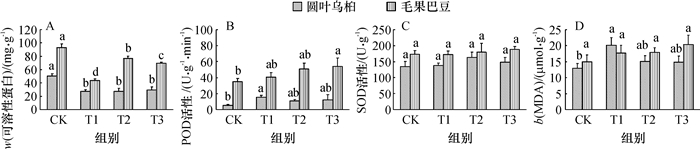
2.4 干旱胁迫对幼苗可溶性蛋白含量的影响
由图 1A可知,圆叶乌桕的可溶性蛋白含量明显低于毛果巴豆.干旱胁迫导致2种苗木可溶性蛋白含量下降.随着胁迫程度的加剧,圆叶乌桕不同干旱胁迫组间的可溶性蛋白含量未出现明显变化;但毛果巴豆不同干旱胁迫组间的变化显著,T1处理组胁迫时显著下降,T2处理组胁迫时达到最大,T3处理组胁迫时又下降,各试验组间差异达到统计学的显著性水平.
2.5 干旱胁迫对幼苗POD和SOD活性的影响
圆叶乌桕整体的POD活性低于毛果巴豆(图 1B).干旱胁迫导致2种苗木POD活性的增加.圆叶乌桕体内POD活性以T1处理组最高,随着胁迫的加剧呈现轻微下降;而毛果巴豆POD活性则随着干旱胁迫程度的增加呈逐渐上升趋势,以T3处理组的POD活性最高,且与CK组的差异达到统计学显著性水平.
在干旱胁迫下,圆叶乌桕幼苗体内SOD活性呈现先升后降的趋势,在T2处理时达到峰值,但各胁迫组与CK组的差异不明显(图 1C);随干旱胁迫强度的增加,毛果巴豆的SOD活性则呈现逐渐上升的趋势,在T3处理时达到最大,但各胁迫组与CK组的差异也未达到统计学显著性水平(图 1C).
2.6 干旱胁迫对幼苗MDA含量的影响
从图 1D可以看出,在干旱胁迫下,2种植物的MDA含量均有上升.随着胁迫的加剧,圆叶乌桕的MDA含量呈现先升后降的趋势,在T1处理时MDA含量显著高于CK组;而毛果巴豆叶片MDA含量随干旱胁迫强度的增加呈现逐渐上升的趋势,T3处理时MDA含量达到最大,但与CK组的差异不明显.
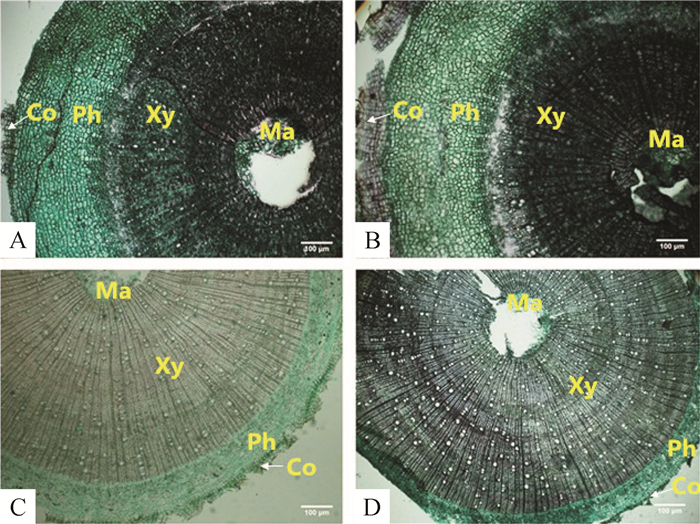
2.7 2种幼苗茎部结构的比较及对干旱胁迫的响应
比较研究了2种幼苗茎部的解剖结构.结果表明,2个树种的幼苗茎部均由表皮、皮层、维管柱和髓部构成,但圆叶乌桕茎部的韧皮部厚度比例较高,而毛果巴豆则以木质部厚度比例较高(图 2).由表 5可知,与CK组比较,在干旱胁迫下,圆叶乌桕和毛果巴豆苗木的皮层厚度比例均有增加,毛果巴豆随着干旱胁迫程度的增加而显著下降;圆叶乌桕幼苗CK组韧皮部厚度比例为32.9%,毛果巴豆幼苗CK组韧皮部厚度比例仅为17.3%,明显小于前者.在干旱条件下,圆叶乌桕的韧皮部比例增加,但毛果巴豆的韧皮部比例下降;圆叶乌桕CK组幼苗的木质部厚度比例为46.5%,而毛果巴豆CK组幼苗的木质部厚度比例为69.0%,在干旱条件下,前者木质部厚度比例的变化不大,后者呈增加趋势,T2和T3处理组与CK组的差异达到显著水平.与CK组比较,2种植物干旱胁迫组的髓部比例均有下降,但只有圆叶乌桕T1和T2组与CK组差异达到显著水平,毛果巴豆干旱胁迫组与CK组的差异未达到显著水平.值得关注的是2种植物幼苗茎部的木质部/髓部比值干旱胁迫组均显著大于CK组,在T1处理组条件下,木质部/髓部比值显著升高,但随着胁迫的加强,该值又呈现下降趋势.
表 5 2种植物不同干旱处理组苗木茎横切面各部分半径厚度比较1)Table 5. Comparisons of stem anatomical structure of two species under different drought treatments
2.8 2种幼苗耐旱综合能力评价
植物耐旱性是受多种因素影响的复杂综合性状,应用尽可能多的指标进行综合评价,可避免和弥补单个指标评定结果的片面性,使评定结果与实际结果更为接近.基于可溶性蛋白含量、POD酶、SOD酶和MDA含量4项生理指标及茎组织结构参数所进行的模糊隶属函数值综合评价结果(表 6)表明:无论是轻度干旱(T1处理组),还是中度干旱(T2处理组)或重度干旱(T3处理组),圆叶乌桕的综合耐旱能力均略强于毛果巴豆.
表 6 基于模糊隶属函数值对2种植物耐旱性的综合评价Table 6. Comprehensive assessments of drought tolerance of two species based on subordinate function values
3. 讨论
3.1 圆叶乌桕及毛果巴豆苗木对干旱胁迫的生长响应
干旱胁迫是石灰岩山地植物生长的主要限制因素.本研究结果揭示了干旱胁迫均不利于2种石灰岩乡土树种的苗高生长,但其基径增粗.这与其他耐旱植物对干旱胁迫的生长响应趋势[15]相似.茎部解剖结果表明,2种苗木茎部皮层、韧皮部、木质部和髓部比例存在一定的差异,干旱胁迫条件下,2种植物木质部与髓部厚度比值均显著增加,反映2个树种均可通过增加与水分输导相关的木质部与髓部比值来适应干旱胁迫.
此外,干旱胁迫条件下,2种植物的根冠比增大,反映了它们能通过提高根冠比来适应土壤干旱环境,具有较强的自我调节能力,这与香椿Toona sinensis[16]和柏木Cupressus funebris[17]等其他石灰岩适生植物对逆境的适应策略相似.
3.2 干旱胁迫对圆叶乌桕及毛果巴豆苗木生理生化特性的影响
本研究检测了2种苗木在干旱胁迫下的可溶性蛋白含量、POD活性、SOD活性和MDA含量的变化情况.综合来看,2种植物体内的可溶性蛋白含量和POD活性对干旱胁迫的响应比较敏感,但SOD活性和MDA含量对干旱胁迫的响应变化不明显.可溶性蛋白是植物体内渗透调节物质之一,具有亲水胶体性质,可增强细胞的保水能力,因此其含量大小可作为评价植物耐干旱胁迫的生理指标[18].干旱胁迫可导致2种植物可溶性蛋白含量的明显下降,但随着胁迫的强度增加,2种植物幼苗可溶性蛋白含量变化的趋势不完全一致,反映了干旱胁迫会抑制圆叶乌桕和毛果巴豆的细胞代谢和蛋白质合成,但2种植物对干旱条件的生理响应和生理适应策略有差异.
SOD和POD活性是评价植物耐旱性的常用指标[19-20].在干旱胁迫下,2种植物的POD活性均出现上升的变化,但圆叶乌桕以轻度干旱组最高,而毛果巴豆的POD活性随着干旱胁迫程度的增加而上升,以重度干旱组的POD活性最高,反映了2种植物在干旱胁迫下,均能通过提高体内POD酶活性,降低体内超氧自由基水平,减缓膜脂氧化速度和细胞的受害程度.
MDA含量的变化是反映植物体膜脂过氧化作用的重要指标[18].在干旱胁迫下,植物MDA含量增幅越小,说明抗旱性较强;相反,MDA含量增幅越大,抗旱性越弱[21].圆叶乌桕和毛果巴豆MDA含量对干旱胁迫响应的变化趋势与POD活性相近,圆叶乌桕在轻度干旱时其MDA含量显著高于对照组,而毛果巴豆所有干旱胁迫组与对照组MDA含量的差异均未达到显著水平.干旱胁迫可导致2种植物体内MDA含量增加,反映了其幼苗在干旱条件下体内的细胞膜产生了不同程度的过氧化损伤,但受损的程度不高.圆叶乌桕体内MDA含量对干旱胁迫程度的响应与石漠化造林银荆Acacia dealbata、滇揪Catalpa fargesii和任豆Zenia insignis树种幼苗相近[22],而毛果巴豆叶片MDA含量对干旱胁迫强度的响应与黄檗Phellodendron amurense幼苗[23]相近.
综上所述,在干旱胁迫下,圆叶乌桕和毛果巴豆幼苗可通过地上部与地下部生物量的分配和体内可溶性蛋白含量、保护酶活性和MDA含量的自我调节方式来维持植物体的正常生理代谢功能,减轻干旱伤害,达到适应干旱环境的目的,均表现较强的耐旱性能.模糊隶属函数值分析结果表明,无论是轻度干旱,还是中度和重度干旱,圆叶乌桕的耐旱能力略强于毛果巴豆.
-
表 1 2种供试植物的苗木基本情况
Table 1 Seedling sizes of two species for experiments

表 2 2种植物不同干旱处理组苗木的土壤含水量
Table 2 Soil moisture of two species under different drought treatments

表 3 2种植物不同干旱处理组苗木的净生长量比较1)
Table 3 Seedling growth of two species under different drought treatments

表 4 2种植物不同干旱处理组苗木的生物量和根冠比1)
Table 4 Biomass and root shoot ratio of two species under different drought treatments

表 5 2种植物不同干旱处理组苗木茎横切面各部分半径厚度比较1)
Table 5 Comparisons of stem anatomical structure of two species under different drought treatments

表 6 基于模糊隶属函数值对2种植物耐旱性的综合评价
Table 6 Comprehensive assessments of drought tolerance of two species based on subordinate function values

-
[1] 容丽, 王世杰, 俞国松, 等.荔波喀斯特森林4种木本植物水分来源的稳定同位素分析[J].林业科学, 2012, 48(7):14-22. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/lykx201207003 [2] 王发国, 秦新生, 陈红锋, 等.海南岛石灰岩特有植物的初步研究[J].热带亚热带植物学报, 2006, 14(1):45-54. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-3395.2006.01.008 [3] 吴静, 秦飞, 王维, 等.我国石灰岩地区特有植物研究进展[J].江苏林业科技, 2010, 37(2):50-54. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7380.2010.02.015 [4] CLEMENTS R, SODDHI N S, SCHILTHUIZEN M, et al. Limestone karsts of Southeast Asia: Imperiled arks of biodiversity[J].Bio Sci, 2006, 56(9):733-742. https://academic.oup.com/bioscience/article/56/9/733/262911
[5] ZHU H, WANG H, LI B, et al. Biogeography and floristic affinities of the limestone flora in Southern Yunnan, China[J]. Ann Missouri Bot Gard, 2003, 90(3):444-465. doi: 10.2307/3298536
[6] 韩玉杰, 徐志防, 叶万辉, 等.不同类型喀斯特植物的荧光特征及抗旱性比较[J].广西植物, 2007, 27(6):918-922. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3142.2007.06.022 [7] 莫凌, 黄玉清, 覃家科, 等.西南喀斯特地区四种植物水分生理的初步研究[J].广西植物, 2008, 28(3):402-406. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3142.2008.03.028 [8] 张中峰, 黄玉清, 莫凌, 等.岩溶区4种石山植物光合作用的光响应[J].西北林学院学报, 2009, 24(1):44-48. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/xblxyxb200901012 [9] QUEREJETA J I, ESTRADA-MEDINA H, ALLEN M F, et al. Utilization of bedrock water by Brosimum alicastrum trees growing on shallow soil atop limestone in a dry tropical climate[J]. Plant Soil, 2006, 287(1/2):187-197.
[10] QUEREJETA J I, ESTRADA-MEDINA H, ALLEN M F, et al. Water source partitioning among trees growing on shallow karst soils in a seasonally dry tropical climate[J]. Oecologia, 2007, 152(1):26-36. doi: 10.1007/s00442-006-0629-3
[11] WU Z Y, RAVEN P H. Flora of China:Vol.11[M]. Beijing:Science Press, 1999:284. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/OAPaper/oai_doaj-articles_705352a9b0cc17379072a697a986f5e7
[12] 张宏达, 丘华兴.值得注意的中国植物:续二[J].广西植物, 2003, 23(2):97-101. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3142.2003.02.001 [13] 李合生.植物生理生化实验原理和技术[M].北京:高等教育出版社, 2001. [14] 庄丽, 陈亚宁, 陈明, 等.模糊隶属法在塔里木河荒漠植物抗旱性评价中的应用[J].干旱区地理, 2005, 28(3):367-372. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6060.2005.03.019 [15] 贺少轩, 梁宗锁, 蔚丽珍, 等.土壤干旱对2个种源野生酸枣幼苗生长和生理特性的影响[J].西北植物学报, 2009, 29(7):1387-1393. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4025.2009.07.015 [16] 杨玉珍, 贾遂民, 彭方仁.干旱胁迫对不同种源香椿苗木生长的影响[J].林业科技开发, 2009, 23(6):52-55. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8101.2009.06.013 [17] 刘锦春, 钟章成.水分胁迫和复水对石灰岩地区柏木幼苗根系生长的影响[J].生态学报, 2009, 29(12):6439-6445. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2009.12.016 [18] 邹琦, 李德全, 郑国生, 等.作物抗旱生理生态研究[M].济南:山东科学技术出版社, 1994:24-29. [19] 时忠杰, 杜阿朋, 胡哲森, 等.水分胁迫对板栗幼苗叶片活性氧代谢的影响[J].林业科学研究, 2007, 20(5):683-687. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-1498.2007.05.016 [20] 谢志玉, 张文辉, 刘新成.干旱胁迫对文冠果幼苗生长和生理生化特征的影响[J].西北植物学报, 2010, 30(5):948-954. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/xbzwxb201005015 [21] 何开跃, 李晓储, 黄利斌, 等.干旱胁迫对木兰科5树种生理生化指标的影响[J].植物资源与环境学报, 2004, 13(4):20- 23. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7895.2004.04.005 [22] 徐利霞. 石漠化山区造林树种幼苗的抗旱性研究[D]. 重庆: 西南大学, 2007. [23] 李霞, 阎秀峰, 于涛.水分胁迫对黄檗幼苗保护酶活性及脂质过氧化作用的影响[J].应用生态学报, 2005, 16(12):2353-2356. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-9332.2005.12.025



 下载:
下载: